Abstract
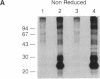
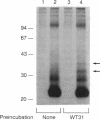
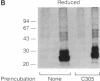
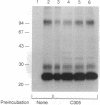
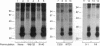
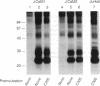
We have identified two cell surface glycoproteins of 34 and 38 kDa (gp34 and gp38) that associate with the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR). The coimmunoprecipitation of these proteins with the TCR is increased by treatment with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against the TCR prior to cell solubilization and immunoprecipitation. Treatment of T cells with mAbs directed against other cell surface molecules, CD2 or HLA, does not induce the association of these proteins with the TCR. The coimmunoprecipitation of gp34 and gp38 with the TCR requires solubilization in the presence of an alkylating agent, suggesting that subunit alkylation stabilizes the interaction. J.CaM1 and J.CaM2 are signal-transduction mutant cell lines derived from Jurkat. These cell lines fail to activate the inositol phospholipid second messenger pathway in response to anti-TCR mAbs. Treatment with mAb C305 (anti-TCR) induces the association of gp34 and gp38 with the TCR in J.CaM2 cells but not in J.CaM1. J.CaM1 modulates the TCR normally in response to anti-TCR antibody treatment. This observation suggests that gp34 and gp38 are involved in the signal-transduction pathway of the TCR complex rather than receptor internalization. Furthermore, since these proteins do associate with the TCR of J.CaM2, the induced association with the TCR is not a consequence of signal transduction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P., Lanier L. L. Structure, function, and serology of the T-cell antigen receptor complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:503–540. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockenstedt L. K., Goldsmith M. A., Dustin M., Olive D., Springer T. A., Weiss A. The CD2 ligand LFA-3 activates T cells but depends on the expression and function of the antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1904–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonyhadi M., Weiss A., Tucker P. W., Tigelaar R. E., Allison J. P. Delta is the Cx-gene product in the gamma/delta antigen receptor of dendritic epidermal cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):574–576. doi: 10.1038/330574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., Prendiville M. A., Terhorst C. The T3 complex on human thymus-derived lymphocytes contains two different subunits of 20 kDa. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jul;13(7):576–580. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitmeyer J. B., Daley J. F., Levine H. B., Schlossman S. F. The T11 (CD2) molecule is functionally linked to the T3/Ti T cell receptor in the majority of T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2899–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. A., Dazin P. F., Weiss A. At least two non-antigen-binding molecules are required for signal transduction by the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8613–8617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. A., Weiss A. Generation and analysis of a T-lymphocyte somatic mutant for studying molecular aspects of signal transduction by the antigen receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;546:91–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb21623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. A., Weiss A. Isolation and characterization of a T-lymphocyte somatic mutant with altered signal transduction by the antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6879–6883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter K. C., Germain R. N., Kroczek R. A., Saito T., Yokoyama W. M., Chan C., Weiss A., Shevach E. M. Thy-1-mediated T-cell activation requires co-expression of CD3/Ti complex. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):505–507. doi: 10.1038/326505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. Effects of magnesium and N-ethylmaleimide on the binding of 3H-hydroxybenzylisoproterenol to beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):804–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hombach J., Leclercq L., Radbruch A., Rajewsky K., Reth M. A novel 34-kd protein co-isolated with the IgM molecule in surface IgM-expressing cells. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3451–3456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03219.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Stobo J. D. Transmembrane signalling by the T cell antigen receptor. Perturbation of the T3-antigen receptor complex generates inositol phosphates and releases calcium ions from intracellular stores. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):446–456. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Brown M. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of a human T lymphocyte surface protein associated with the E-rosette receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):207–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner M., Gilon C., Schramm M. Locking of hormone in the beta-adrenergic receptor by attack on a sulfhydryl in an associated component. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3389–3396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Ruitenberg J. J., Allison J. P., Weiss A. Distinct epitopes on the T cell antigen receptor of HPB-ALL tumor cells identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2286–2292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R. The structure of the CD4 and CD8 genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:561–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Ortega G., Chan C., Kroczek R. A., Shevach E. M. Role of Ly-6 in lymphocyte activation. II. Induction of T cell activation by monoclonal anti-Ly-6 antibodies. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):709–722. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merćep M., Bonifacino J. S., Garcia-Morales P., Samelson L. E., Klausner R. D., Ashwell J. D. T cell CD3-zeta eta heterodimer expression and coupling to phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):571–574. doi: 10.1126/science.2845582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Patel M. D., Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Antigen activation of murine T cells induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a polypeptide associated with the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., Willems H. W., Reekers P. P., Capel P. J., Koene R. A. Polymorphism in mitogenic effect of IgG1 monoclonal antibodies against T3 antigen on human T cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):445–447. doi: 10.1038/304445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauquelin G., Bottari S., Andre C., Jacobsson B., Strosberg A. D. Interaction between beta-adrenergic receptors and guanine nucleotide sites in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3801–3805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J. B. Cell surface molecules and early events involved in human T lymphocyte activation. Adv Immunol. 1987;41:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Newton M., Crommie D. Expression of T3 in association with a molecule distinct from the T-cell antigen receptor heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6998–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Stobo J. D. Requirement for the coexpression of T3 and the T cell antigen receptor on a malignant human T cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1284–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Y., Chouaib S., Dupont B. A common pathway for T lymphocyte activation involving both the CD3-Ti complex and CD2 sheep erythrocyte receptor determinants. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1097–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]