Abstract
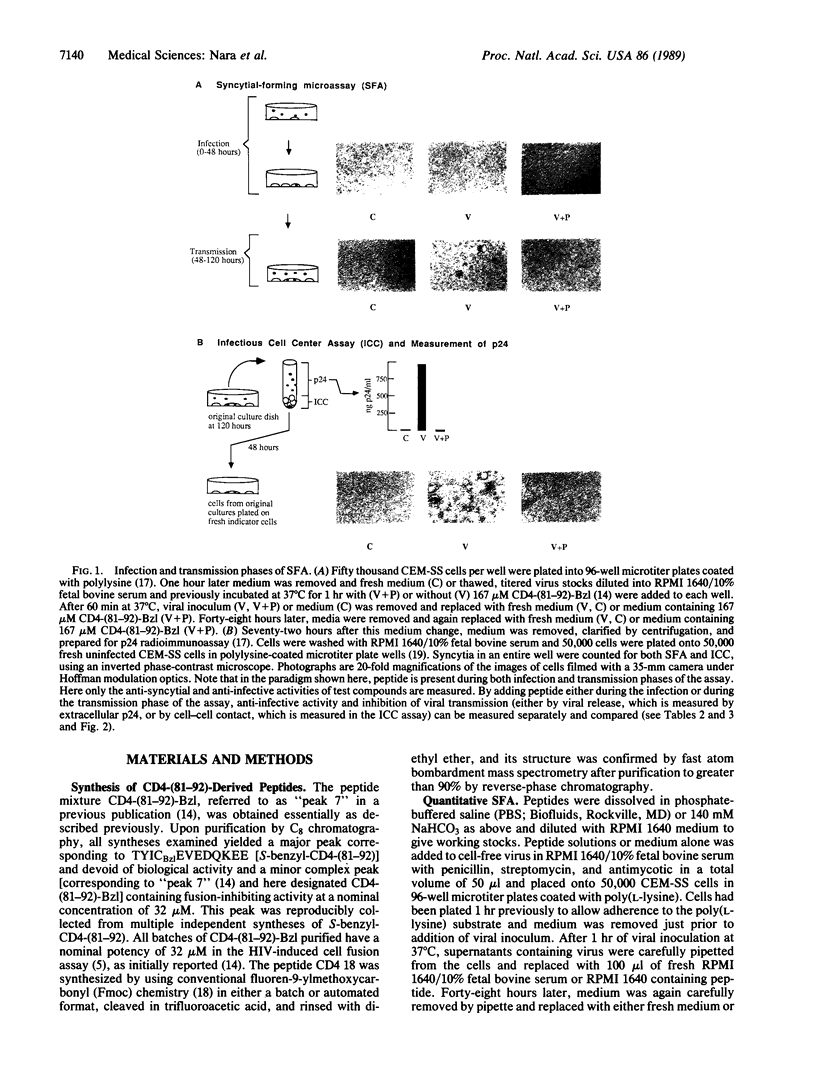
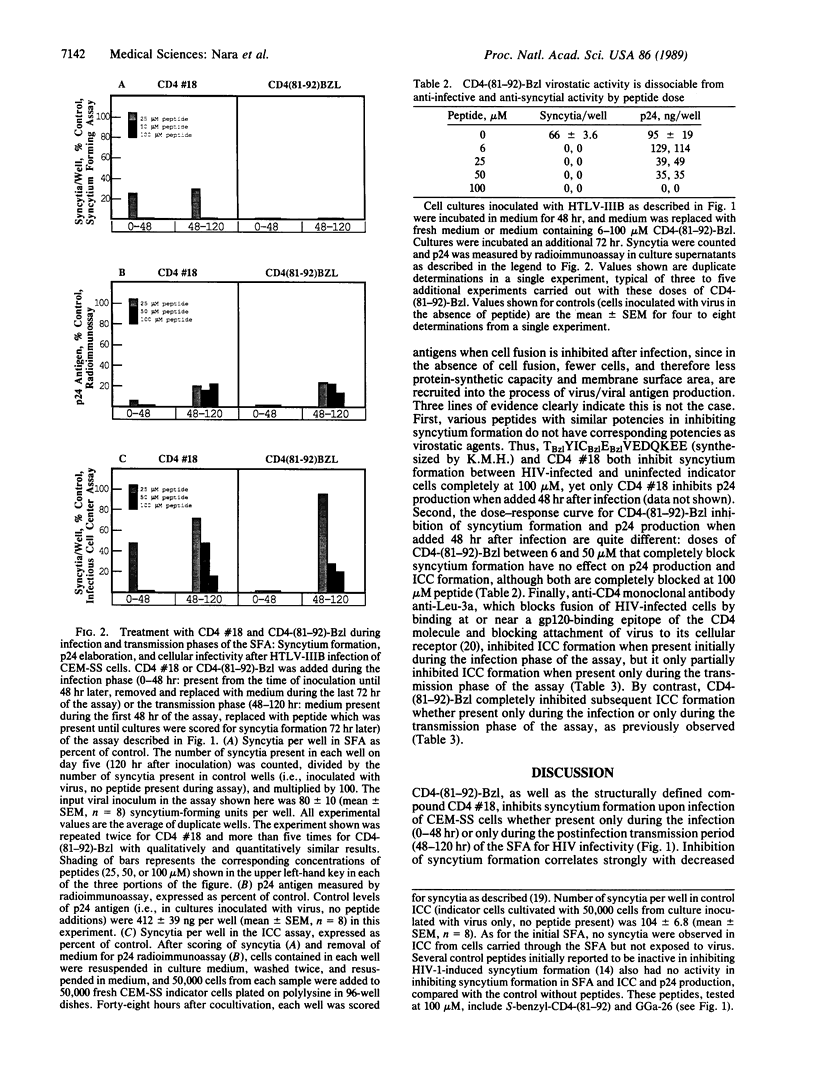
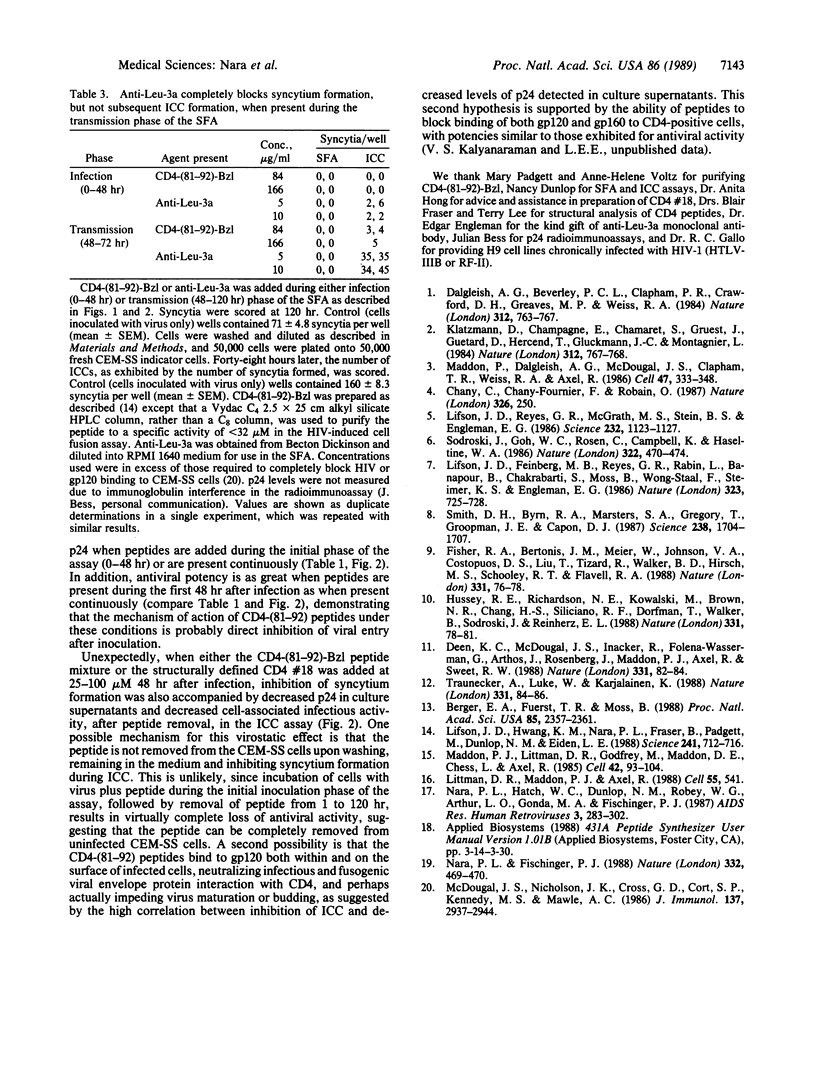
Benzylated derivatives of peptides corresponding to residues 81 through 92 of the CD4 molecule [CD4-(81-92)] inhibit human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1)-induced cell fusion and infection in vitro. If such peptides are to be considered as candidates in the therapy of HIV infection, it is crucial to know if the anti-HIV efficacy of CD4-based peptides is limited to blockade of infection and virus-induced cell fusion or if other stages of the viral life cycle are affected by these compounds. Accordingly, an in vitro quantitative microassay for acute HIV infection was divided into two kinetic phases corresponding to the two general stages of the viral life cycle: (i) viral infection and (ii) transmission of virus and viral protein products through cell contact or release of free virions. CEM-SS cell cultures were treated with peptide during either the infection or the transmission phase of the assay. When peptides were present during the infection phase, inhibition of syncytium formation correlated with decreased expression of viral core protein p24 and lack of infectious cell centers when cells exposed to virus were washed and replated onto fresh uninfected indicator cells. These data are consistent with complete inhibition of viral infection when peptide is present only during initial exposure to virus. Unexpectedly, parallel inhibition of syncytium formation, decreased p24 levels, and inhibition of infectious cell center formation were also seen even when peptides were added as late as 48 hr after inoculation, during the transmission period of the assay. Since viral binding and penetration are completed well before 48 hr in this assay system, CD4-(81-92) peptide derivatives appear to exert a virostatic effect on cultures already infected with HIV-1, decreasing p24 production, cytopathicity, and cell-mediated infectivity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. A soluble recombinant polypeptide comprising the amino-terminal half of the extracellular region of the CD4 molecule contains an active binding site for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2357–2361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Chany-Fournier F., Robain O. Cell fusion in viral diseases. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):250–250. doi: 10.1038/326250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen K. C., McDougal J. S., Inacker R., Folena-Wasserman G., Arthos J., Rosenberg J., Maddon P. J., Axel R., Sweet R. W. A soluble form of CD4 (T4) protein inhibits AIDS virus infection. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):82–84. doi: 10.1038/331082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Bertonis J. M., Meier W., Johnson V. A., Costopoulos D. S., Liu T., Tizard R., Walker B. D., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. HIV infection is blocked in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):76–78. doi: 10.1038/331076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Richardson N. E., Kowalski M., Brown N. R., Chang H. C., Siliciano R. F., Dorfman T., Walker B., Sodroski J., Reinherz E. L. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):78–81. doi: 10.1038/331078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Hwang K. M., Nara P. L., Fraser B., Padgett M., Dunlop N. M., Eiden L. E. Synthetic CD4 peptide derivatives that inhibit HIV infection and cytopathicity. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):712–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2969619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Reyes G. R., McGrath M. S., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3010463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Maddon P. J., Axel R. Corrected CD4 sequence. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):541–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Cort S. P., Kennedy M. S., Mawle A. C. Binding of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV/ARV/HIV to the CD4 (T4) molecule: conformation dependence, epitope mapping, antibody inhibition, and potential for idiotypic mimicry. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2937–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Fischinger P. J. Quantitative infectivity assay for HIV-1 and-2. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):469–470. doi: 10.1038/332469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Hatch W. C., Dunlop N. M., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Fischinger P. J. Simple, rapid, quantitative, syncytium-forming microassay for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):283–302. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Byrn R. A., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Groopman J. E., Capon D. J. Blocking of HIV-1 infectivity by a soluble, secreted form of the CD4 antigen. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1704–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.3500514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Lüke W., Karjalainen K. Soluble CD4 molecules neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):84–86. doi: 10.1038/331084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]