Abstract
In the title compound, C18H19NO, the dihedral angle between 4-methylphenyl and 4-(dimethylamino)phenyl rings is 45.5 (3)°. The C—C=C—C torsion angle of 173.8 (3)° indicates that the molecule adopts an E configuration. The dimethylamino group is nearly coplanar with the attached benzene ring, making a dihedral angle of 2.7 (3)°. Weak intermolecular C—H⋯π interactions are observed in the crystal structure.
Related literature
The title compound is a chalcone derivative; for the biological activiy of chalcones, see: Modzelewska et al. (2006 ▶); Opletalova & Sedivy (1999 ▶); Lin et al. (2002 ▶); Hsieh et al. (1998 ▶); Lunardi et al. (2003 ▶); Tang et al. (2008 ▶). For the organic non-linear optical properties of chalcones, see: Indira et al. (2002 ▶); Ravindra et al. (2009 ▶). For related structures, see: Wang et al. (2004 ▶); Yang et al. (2006 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H19NO
M r = 265.34
Orthorhombic,
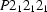
a = 7.276 (2) Å
b = 11.567 (3) Å
c = 17.642 (5) Å
V = 1484.8 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.07 mm−1
T = 193 K
0.59 × 0.35 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Mercury diffractometer
16704 measured reflections
1958 independent reflections
1846 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.055
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.061
wR(F 2) = 0.136
S = 1.31
1958 reflections
185 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 1999 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalStructure (Rigaku, 2000 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809052398/xu2690sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809052398/xu2690Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C7–C11 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11⋯Cg1i | 0.95 | 2.94 | 3.697 (3) | 138 |
| C9—H9⋯Cg2ii | 0.95 | 2.93 | 3.712 (3) | 141 |
| C16—H16B⋯Cg2iii | 0.98 | 2.70 | 3.643 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 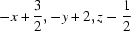 ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii) 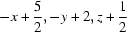 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Binzhou Medical University for financial support (grant No. BY2007KJ57).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chalcones are open chain flavonoids which consist of two substituted benzene rings bridged by a prop-2-en-1-one group. They are renowned for their broad biological activities (Opletalova & Sedivy, 1999), such as anticancer (Modzelewska et al., 2006), antitubercular (Lin et al., 2002), anti-inflammatory (Hsieh et al., 1998), trypanocidal (Lunardi et al., 2003) and antibacterial properties (Tang et al. 2008). In addition, chalcones are also finding applications as organic non-linear optical (NLO) materials for their excellent blue light transmittance and good crystal stabitily (Indira et al., 2002; Ravindra et al., 2009). As a part of our searches for NLO materials based on chalcones (Wang, et al., 2004; Yang, et al., 2006), the title compound (I) was synthesized and its crystal structure is reported. The crystal should exhibit second-order NLO properties, because it crystallizes in a non-centrosymmetric space group.
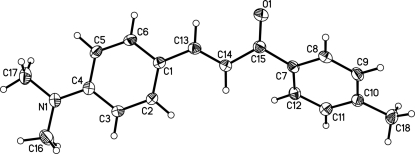
In the title compound(I) (Fig.1), the molecule adopts an E configuration with respect to C13═C14 double bond [1.340 (4) Å]: the torsion angle C1—C13—C14—C15=173.8 (3)°. The dihedral angle between the C1—C6 ring (Plane A) and the C7—C12 ring (Plane B) is 45.5 (3)°, showing the two phenyl rings are rotated oppositely with respect to the enone segment. The mean plane of C1—C13=C14—C15 (Plane C) makes dihedral angles of 8.7 (3)° and 36.7 (4)° with plane A and plane B, respectively. The phenone O1 atom deviates from plane C by 0.240 (3) Å, suggesting C=O is not coplanar with Plane C. The dimethylamino group (Plane D) is nearly coplanar with the phenyl ring to which it is bound. The dehedral angel beween plane A and plane D is 2.7 (3)°. While no classical hydrogen bonds are present, weak intermolecular C—H···π interactions are observed, which contribute to the stability of crystal packing (Table 1).
Experimental
The synthesis of the title compound was carried out by adding an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (10%, 10 ml) to a solution of 4-methylacetophenone (0.02 mol) and 4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde (0.02 mol). The reaction mixture was stirred for 5 h at room temperature and then neutralized with HCl solution (10%). The product was recrystallized three times from ethanol (95%). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were grown by slow evaporation of the acetone solution at room temperature.
Refinement
All of the H Atoms were placed in their calculated positions and then refined using the riding model with C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å, and with Uiso (H)=1.2 or 1.5Ueq(C). In the absence of significant anomalous scattering, Friedel pairs were merged.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with 30% probability displacement ellipsoids and atom labels for non-H atoms.
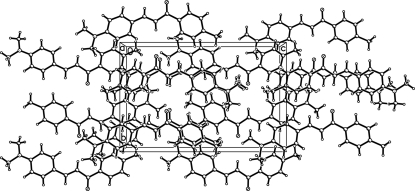
Fig. 2.
The packing of (I), viewed down the a axis.
Crystal data
| C18H19NO | F(000) = 568 |
| Mr = 265.34 | Dx = 1.187 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71070 Å |
| Hall symbol: p 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 5334 reflections |
| a = 7.276 (2) Å | θ = 3.0–27.5° |
| b = 11.567 (3) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| c = 17.642 (5) Å | T = 193 K |
| V = 1484.8 (7) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.59 × 0.35 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku Mercury diffractometer | 1846 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.055 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | h = −9→9 |
| ω scans | k = −14→14 |
| 16704 measured reflections | l = −19→22 |
| 1958 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.061 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.136 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.31 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0495P)2 + 0.3222P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1958 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 185 parameters | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.9451 (4) | 0.62914 (17) | 0.28002 (11) | 0.0570 (7) | |
| N1 | 1.0052 (4) | 0.9449 (2) | −0.14961 (12) | 0.0474 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.9388 (4) | 0.8121 (2) | 0.07087 (15) | 0.0340 (6) | |
| C2 | 1.0071 (4) | 0.9237 (2) | 0.05857 (14) | 0.0342 (6) | |
| H2 | 1.0393 | 0.9701 | 0.1010 | 0.041* | |
| C3 | 1.0288 (4) | 0.9681 (2) | −0.01345 (15) | 0.0355 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.0754 | 1.0442 | −0.0195 | 0.043* | |
| C4 | 0.9833 (4) | 0.9029 (2) | −0.07801 (15) | 0.0361 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.9100 (4) | 0.7916 (2) | −0.06585 (15) | 0.0389 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.8734 | 0.7458 | −0.1079 | 0.047* | |
| C6 | 0.8909 (4) | 0.7489 (3) | 0.00638 (17) | 0.0377 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.8431 | 0.6732 | 0.0127 | 0.045* | |
| C7 | 0.9790 (4) | 0.7943 (2) | 0.35669 (14) | 0.0339 (6) | |
| C8 | 1.0590 (4) | 0.7345 (2) | 0.41698 (16) | 0.0395 (6) | |
| H8 | 1.1025 | 0.6580 | 0.4094 | 0.047* | |
| C9 | 1.0757 (4) | 0.7849 (2) | 0.48706 (16) | 0.0424 (7) | |
| H9 | 1.1343 | 0.7435 | 0.5268 | 0.051* | |
| C10 | 1.0082 (4) | 0.8956 (3) | 0.50109 (15) | 0.0399 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.9305 (4) | 0.9556 (3) | 0.44122 (15) | 0.0410 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.8854 | 1.0317 | 0.4493 | 0.049* | |
| C12 | 0.9174 (4) | 0.9066 (2) | 0.36960 (15) | 0.0371 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.8659 | 0.9499 | 0.3291 | 0.045* | |
| C13 | 0.9252 (4) | 0.7595 (2) | 0.14493 (15) | 0.0370 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.8853 | 0.6813 | 0.1455 | 0.044* | |
| C14 | 0.9611 (4) | 0.8060 (2) | 0.21291 (14) | 0.0377 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.9896 | 0.8860 | 0.2163 | 0.045* | |
| C15 | 0.9573 (4) | 0.7358 (2) | 0.28210 (15) | 0.0382 (6) | |
| C16 | 1.0849 (5) | 1.0576 (3) | −0.16376 (19) | 0.0606 (9) | |
| H16A | 1.2040 | 1.0631 | −0.1381 | 0.091* | |
| H16B | 1.0025 | 1.1177 | −0.1444 | 0.091* | |
| H16C | 1.1022 | 1.0681 | −0.2184 | 0.091* | |
| C17 | 0.9558 (6) | 0.8769 (3) | −0.21540 (16) | 0.0685 (11) | |
| H17A | 0.8250 | 0.8568 | −0.2129 | 0.103* | |
| H17B | 1.0294 | 0.8059 | −0.2164 | 0.103* | |
| H17C | 0.9794 | 0.9218 | −0.2615 | 0.103* | |
| C18 | 1.0179 (5) | 0.9481 (3) | 0.57936 (17) | 0.0571 (9) | |
| H18A | 0.9012 | 0.9352 | 0.6058 | 0.086* | |
| H18B | 1.0408 | 1.0314 | 0.5751 | 0.086* | |
| H18C | 1.1179 | 0.9119 | 0.6080 | 0.086* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0875 (18) | 0.0342 (10) | 0.0492 (12) | −0.0048 (12) | 0.0013 (13) | 0.0026 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0567 (17) | 0.0519 (14) | 0.0335 (12) | −0.0061 (14) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0008 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0297 (12) | 0.0345 (12) | 0.0378 (13) | −0.0005 (12) | 0.0019 (11) | −0.0026 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0345 (13) | 0.0343 (13) | 0.0339 (13) | 0.0001 (12) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0039 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0334 (13) | 0.0394 (14) | −0.0019 (11) | −0.0012 (12) | −0.0015 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0335 (13) | 0.0400 (13) | 0.0348 (13) | 0.0043 (12) | −0.0008 (12) | −0.0008 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0375 (14) | 0.0431 (14) | 0.0360 (14) | −0.0043 (13) | −0.0030 (12) | −0.0099 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0354 (14) | 0.0350 (12) | 0.0426 (14) | −0.0062 (12) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0056 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0297 (13) | 0.0369 (13) | 0.0351 (13) | −0.0004 (12) | 0.0021 (11) | 0.0058 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0390 (15) | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0458 (15) | −0.0025 (13) | 0.0022 (13) | 0.0076 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0421 (15) | 0.0443 (15) | 0.0409 (14) | −0.0033 (14) | −0.0048 (13) | 0.0132 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0346 (14) | 0.0496 (15) | 0.0353 (13) | −0.0105 (13) | 0.0030 (12) | 0.0029 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0370 (14) | 0.0441 (15) | 0.0418 (15) | 0.0014 (13) | 0.0039 (13) | −0.0037 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0351 (14) | 0.0385 (13) | 0.0377 (14) | 0.0056 (13) | −0.0015 (12) | 0.0033 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0341 (14) | 0.0352 (13) | 0.0416 (14) | −0.0020 (12) | 0.0035 (12) | 0.0000 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0420 (15) | 0.0344 (13) | 0.0367 (14) | −0.0035 (13) | 0.0011 (12) | 0.0015 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0388 (14) | 0.0365 (14) | 0.0393 (14) | −0.0007 (12) | 0.0034 (13) | −0.0003 (12) |
| C16 | 0.060 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0499 (18) | −0.016 (2) | 0.0025 (17) | 0.0142 (16) |
| C17 | 0.086 (3) | 0.085 (3) | 0.0346 (16) | −0.017 (2) | 0.0006 (19) | −0.0049 (16) |
| C18 | 0.063 (2) | 0.074 (2) | 0.0347 (14) | −0.017 (2) | 0.0046 (16) | −0.0016 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C15 | 1.238 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.393 (4) |
| N1—C4 | 1.363 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C17 | 1.448 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.385 (4) |
| N1—C16 | 1.448 (4) | C10—C18 | 1.510 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.388 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.400 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C13 | 1.445 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.380 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.340 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.405 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.466 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.410 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.374 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C7—C12 | 1.393 (4) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.396 (4) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C7—C15 | 1.488 (4) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.372 (4) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C4—N1—C17 | 121.4 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.1 (3) |
| C4—N1—C16 | 121.8 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| C17—N1—C16 | 116.8 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 116.4 (2) | C11—C12—C7 | 120.5 (3) |
| C6—C1—C13 | 120.0 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—C13 | 123.6 (2) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.8 (2) | C14—C13—C1 | 128.8 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.1 | C14—C13—H13 | 115.6 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.1 | C1—C13—H13 | 115.6 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.3 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 121.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.4 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.4 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 122.2 (2) | O1—C15—C14 | 121.9 (2) |
| N1—C4—C5 | 120.7 (2) | O1—C15—C7 | 119.1 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.1 (2) | C14—C15—C7 | 118.9 (2) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.5 (2) | N1—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.8 | N1—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.8 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.9 (3) | N1—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 118.6 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 118.6 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 118.1 (2) | N1—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C12—C7—C15 | 122.3 (2) | N1—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C15 | 119.5 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.9 (2) | N1—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.6 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.6 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 121.3 (3) | C10—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.4 | C10—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.4 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 118.0 (3) | C10—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C18 | 121.0 (3) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C18 | 121.1 (3) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.1 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −2.7 (4) |
| C13—C1—C2—C3 | 175.8 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C18 | 176.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.0 (4) |
| C17—N1—C4—C3 | −179.3 (3) | C18—C10—C11—C12 | −178.4 (3) |
| C16—N1—C4—C3 | 3.0 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 1.4 (4) |
| C17—N1—C4—C5 | −0.5 (4) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −2.0 (4) |
| C16—N1—C4—C5 | −178.3 (3) | C15—C7—C12—C11 | 176.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | −179.5 (3) | C6—C1—C13—C14 | −178.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.7 (4) | C2—C1—C13—C14 | 4.6 (5) |
| N1—C4—C5—C6 | 179.0 (3) | C1—C13—C14—C15 | −173.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.2 (4) | C13—C14—C15—O1 | 9.7 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.1 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C7 | −173.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (4) | C12—C7—C15—O1 | −151.9 (3) |
| C13—C1—C6—C5 | −176.4 (3) | C8—C7—C15—O1 | 26.3 (4) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.3 (4) | C12—C7—C15—C14 | 31.4 (4) |
| C15—C7—C8—C9 | −178.0 (3) | C8—C7—C15—C14 | −150.4 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 2.1 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C7–C11 rings, respectively. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11···Cg1i | 0.95 | 2.94 | 3.697 (3) | 138 |
| C9—H9···Cg2ii | 0.95 | 2.93 | 3.712 (3) | 141 |
| C16—H16B···Cg2iii | 0.98 | 2.70 | 3.643 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, −y+2, z−1/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+5/2, −y+2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU2690).
References
- Hsieh, H. K., Lee, T. H., Wang, J. P., Wang, J. J. & Lin, C. N. (1998). Pharm. Res.15, 39–46. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Indira, J., Prakash Karat, P. & Sarojini, B. K. (2002). J. Cryst. Growth, 242, 209–214.
- Lin, Y. M., Zhou, Y., Flavin, M. T., Zhou, L. M., Nie, W. & Chen, F. C. (2002). Bioorg. Med. Chem.10, 2795–2802. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, F., Guzela, M., Rodrigues, A. T., Correa, R., Eger-Mangrich, I., Steindel, M., Grisard, E. C., Assreuy, J., Calixto, J. B. & Santos, A. R. S. (2003). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.47, 1449–1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Modzelewska, A., Pettit, C., Achanta, G., Davidson, N. E., Huang, P. & Khan, S. R. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem.14, 3491–3495. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Opletalova, V. & Sedivy, D. (1999). Ceska Slov. Farm.48, 252–255. [PubMed]
- Ravindra, H. J., Harrison, W. T., Suresh Kumar, M. R. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2009). J. Cryst. Growth, 311, 310–315.
- Rigaku (1999). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2000). CrystalStructure Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-P., Kuang, D.-Z., Feng, Y.-L., Li, W. & Chen, Z.-M. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Lu, C.-R. & Zhang, D.-C. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o696–o698. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yang, W., Wang, L. & Zhang, D.-C. (2006). J. Chem. Crystallogr.36, 195–198.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809052398/xu2690sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809052398/xu2690Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report