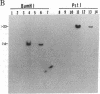
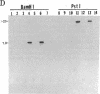
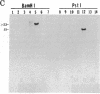
Abstract
Recently it was shown that a clinical strain of Escherichia coli contains a reverse transcriptase that is essential for the synthesis of a branched-RNA-linked multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA). We now have examined 113 independent clinical isolates of E. coli for the existence of msDNA and found that 7 strains contained msDNA. Four of them were further analyzed by hybridization analysis, which indicated that three of the msDNAs were different, having little sequence homology. When the reverse transcriptase gene associated with one of these msDNAs was used as a probe, it did not hybridize with chromosomal DNA from the other strains containing msDNA. These results indicate that some clinical E. coli strains carry their own unique msDNA-synthesizing systems; msDNAs produced by these systems have little, if any, sequence homology in their RNA and DNA molecules and the reverse transcriptases required for the production of msDNA also have little sequence similarity. Such extensive diversity of the msDNA-synthesizing systems supports the notion that they were acquired by the E. coli genome late during the evolution of E. coli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnn J., March P. E., Takiff H. E., Inouye M. A GTP-binding protein of Escherichia coli has homology to yeast RAS proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8849–8853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Functional expression of cloned yeast DNA in Escherichia coli: specific complementation of argininosuccinate lyase (argH) mutations. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 25;120(4):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90351-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhundale A. R., Furuichi T., Inouye S., Inouye M. Distribution of multicopy single-stranded DNA among myxobacteria and related species. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):914–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.914-917.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhundale A., Inouye M., Inouye S. A new species of multicopy single-stranded DNA from Myxococcus xanthus with conserved structural features. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9055–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhundale A., Lampson B., Furuichi T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Structure of msDNA from Myxococcus xanthus: evidence for a long, self-annealing RNA precursor for the covalently linked, branched RNA. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90596-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Dhundale A., Inouye M., Inouye S. Branched RNA covalently linked to the 5' end of a single-stranded DNA in Stigmatella aurantiaca: structure of msDNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Inouye S., Inouye M. Biosynthesis and structure of stable branched RNA covalently linked to the 5' end of multicopy single-stranded DNA of Stigmatella aurantiaca. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Hsu M. Y., Eagle S., Inouye M. Reverse transcriptase associated with the biosynthesis of the branched RNA-linked msDNA in Myxococcus xanthus. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90593-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson B. C., Inouye M., Inouye S. Reverse transcriptase with concomitant ribonuclease H activity in the cell-free synthesis of branched RNA-linked msDNA of Myxococcus xanthus. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90592-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson B. C., Sun J., Hsu M. Y., Vallejo-Ramirez J., Inouye S., Inouye M. Reverse transcriptase in a clinical strain of Escherichia coli: production of branched RNA-linked msDNA. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1033–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2466332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim D., Maas W. K. Reverse transcriptase-dependent synthesis of a covalently linked, branched DNA-RNA compound in E. coli B. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):891–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90693-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Ahnn J., Inouye M. The DNA sequence of the gene (rnc) encoding ribonuclease III of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4677–4685. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee T., Furuichi T., Inouye S., Inouye M. Multicopy single-stranded DNA isolated from a gram-negative bacterium, Myxococcus xanthus. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90541-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]