Abstract
In the title compound, C17H24NO2 +·Br−·H2O, the pentyl group chain in the cation extends nearly perpendicular [N—C—C—C = −64.4 (3)°] to the mean plane of the indole ring with the carboxyl end group twisted such that the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the indole and carboxy groups measures 43.2 (4)°. Both ions in the salt form intermolecular hydrogen bonds (O—H⋯Br and O—H⋯O) with the water molecule. As a result of the Br⋯H—O—H⋯Br interactions, a zigzag chain is formed in the c-axis direction. The crystal packing is influenced by the collective action of the O—H⋯O and O—H⋯Br intermolecular interactions as well as π–π stacking intermolecular interactions between adjacent benzyl rings of the indole group [centroid–centroid distance = 3.721 (13) Å] and intermolecular C—H⋯π interactions between a methyl hydrogen and the benzyl ring of the indole group. The O—H⋯Br interactions form a distorted tetrahedral array about the central Br atom. A MOPAC AM1 calculation provides support to these observations.
Related literature
For chemical and biological background, see: Zhu et al. (1994 ▶); Schwartz & Ulfelder (1992 ▶); Bengtsson et al. (2003 ▶); Hirons et al. (1994 ▶); Kurihara et al. (1977 ▶); Armitage & O’Brien (1992 ▶); Reers et al. (1991 ▶); Jung & Kim (2006 ▶); Menger & Pertusati (2008 ▶). A geometry optimized MOPAC AM1 computational calculation was performed using WebMO Pro (Schmidt & Polik, 2007 ▶).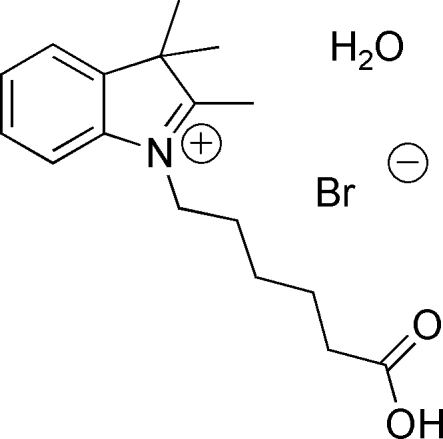
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H24NO2 +·Br−·H2O
M r = 372.30
Monoclinic,
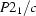
a = 14.4528 (3) Å
b = 15.3367 (2) Å
c = 8.0810 (2) Å
β = 99.437 (2)°
V = 1766.98 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 3.27 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.55 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini R diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.296, T max = 0.676
13155 measured reflections
3504 independent reflections
3049 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.098
S = 1.06
3504 reflections
209 parameters
3 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.52 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.43 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis Pro (Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis Pro; data reduction: CrysAlis Pro; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809049204/fl2265sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809049204/fl2265Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2O⋯O1W | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.637 (4) | 166 |
| O1W—H1W1⋯Br | 0.812 (19) | 2.431 (19) | 3.240 (2) | 175 (5) |
| O1W—H1W2⋯Bri | 0.817 (19) | 2.47 (2) | 3.262 (3) | 165 (5) |
| C4—H4B⋯Cg2i2 | 0.99 | 2.88 | 3.828 (3) | 162 |
Symmetry code: (i) 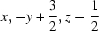 ; (ii)
; (ii) 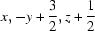 . Cg2 is the centroid of the C6–C11 ring.
. Cg2 is the centroid of the C6–C11 ring.
Acknowledgments
AW and YH acknowledges support from by DOE-CETBR grant No. DE-FG02-03ER63580 and NSF–RISE Award No. HRD-0627276. RJB acknowledges the NSF MRI program (grant No. CHE-0619278) for funds to purchase an X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound,C17H24NO2+, Br-, H2O, (I), a salt with a crystallized water molecule, was synthesized under microwave conditions (Scheme 1). It has been used as a precursor for cyanine dyes which have widespread application as fluorescent probes. They have been used in DNA sequencing, immunoassays, agarose gel and capillary electrophoresis staining (Zhu et al., (1994)), DNA analysis in polymerization chain reactions (Schwartz et al., (1992); Bengtsson et al., (2003)), in flow cytometry (Hirons et al., (1994)), or as fluorescent probes for membrane fluidity (Kurihara et al., 1977); Armitage et al., 1992)) as well as in membrane potential studies (Reers et al., (1991)). This precursor is of particular importance due to the presence of the carboxylic acid group, which when converted to the NHS ester, allows the attachment of these dyes to proteins.
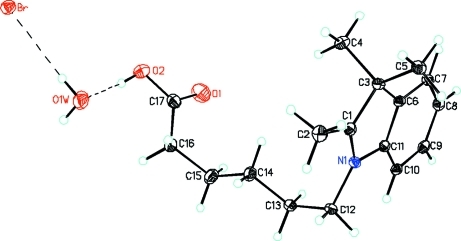
In the cation, the mean plane of indole ring bisects the angle between the two attached 3,3 dimethyl groups (angles C1–C3–C4 = 109.1 (2)°; C1–C3–C5 = 111.86 (19)°; C5–C3–C4 = 110.3 (2)°) whereas the third methyl group is nearly in the plane of the indole ring (torsion angle C2–C1–C3–C6 = 178.4 (2)°), Fig. 1. The pentyl group chain extends nearly perpendicular to the mean plane of the indole ring (torsion angle N1–C12–C13–C14 = -64.4 (3)°) with the carboxyl end group twisted such that the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the indole and carboxy groups measures 43.2 (4)° (torsion angle C14–C15–C16–C17 = 94.4 (4)°).
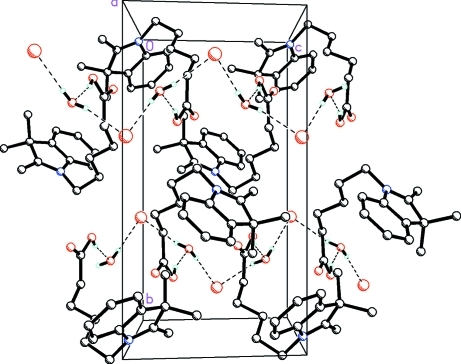
Both ions from the salt form intermolecular hydrogen bonds (O–H···Br & O–H···O) with the water molecule. As a result of the Br···H–O–H···Br interactions a zigzag one-dimensional chain is formed in the c direction.(Fig. 2). Crystal packing is influenced by the collective action of intermolecular O—H···O and O—H···Br hydrogen bond interactions as well as π-π stacking intermolecular interactions between the center of gravity of nearby benzyl rings of the indole group (Cg2···Cg2: 3.721 (13) Å; slippage = 1.514 Å; 2 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z) and π-ring C4–H4B···Cg2 intermolecular interactions between a methyl hydrogen and the benzene ring of the indole group [H···Cg = 2.88 Å; X—H···Cg = 162°; X···CgX-H = 3.828 (3) Å; Cg2 = C6–C11; x, 3/2 - y, 1/2 + z] in the unit cell (Fig. 3). In addition there are weak C—H···Br interactions between the phenyl H atoms of two adjoining cations which, together with the O–H···Br interactions, form a distorted tetrahedral array about the central Br.
A geometry optimized MOPAC AM1 computational calculation was performed on the cation in the absence of the bromide ion and water molecule using WebMO Pro (Schmidt & Polik, 2007). The Hartree-Fock closed-shell (restricted) wavefunction along with [AM1 (Austin Model 1)] was used and minimizations were terminated at an r.m.s. gradient of less than 0.01 kJ mol-1 Å-1]. As a result of this calculation the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the indole and carboxy groups changes from 43.2 (4)° to 34.5 (2) Å. From this it is apparent that the collective influence of O–H···O and O–H···Br hydrogen bonds, weaker C–H···Br intermolecular interactions, π-π stacking intermolecular interactions, and π-ring C–H···Cg2 intermolecular interactions significantly influence crystal packing for this molecule.
Experimental
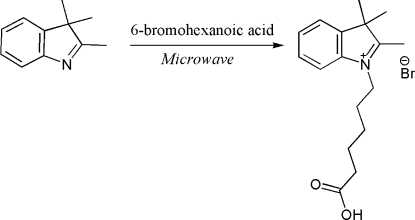
The title compound (I) has been previously synthesized by refluxing reagents with the solvent o-dichloro-benzene for 12–24 h followed by filtration (Jung et al., (2006); Menger et al. (2008)). For our study the title compound, (I), was synthesized as follows: 6-bromohexanoic acid (0.67 g, 0.0034 moles) and 2,3,3-trimethylindolenine (0.54 ml, 0.0034 moles) were added to a reaction vial via syringe and heated at 433 K for 1200 s and a ramp of 150 s in a Biotage Initiator microwave system (Scheme 2). The crystals were washed with acetone and dried under vacuum to yield (0.51 g, 42%). The sample was recrystallized by dissolving in dichloromethane then allowed to evaporate slowly at room temperature. 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ (p.p.m.): 7.87–8.01 (m, 1H), 7.78–7.87 (m, 1H), 7.26–7.64 (m, 2H) 4.45 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.87 (s, 3H), 2.24 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.85–1.81 (m, 2H), 1.6–1.5 (m, 8H), 1.44 (m, 3H); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 100 MHz): δ (p.p.m.): 196.5 (C), 174.2 (C), 141.8 (C), 141.0 (C), 129.3 (CH), 128.9 (CH), 123.5 (CH), 115.4 (CH), 54.1 (C), 47.4 (CH2), 33.3 (CH2), 26.9 (CH2), 25.4 (CH2), 24.0 (CH2), 22.0 (CH3), 14.0 (CH3).
Refinement
H1W1, H1W2 were obtained from a difference fourier map and refined with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). The rest of the H atoms were placed in their calculated positions and then refined using a riding model with C(O)—H distances ranging from 0.84 to 0.99 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2eq(C,O) [1.5Ueq for CH3].
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing the atom numbering scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. Dashed lines show the O2–H2O···O1W and O1W–H1W1···Br hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 2.
The molecular packing for (I) viewed down the a axis of the unit cell. Dashed lines indicate intermolecular O2–H2O···O1W, and O1W–H1W1···Br interactions. The O–H···Br···H–O interactions form a zigzag chain in the c direction.
Fig. 3.
The formation of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C17H24NO2+·Br−·H2O | F(000) = 776 |
| Mr = 372.30 | Dx = 1.399 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 8515 reflections |
| a = 14.4528 (3) Å | θ = 5.6–73.5° |
| b = 15.3367 (2) Å | µ = 3.27 mm−1 |
| c = 8.0810 (2) Å | T = 200 K |
| β = 99.437 (2)° | Needle, colorless |
| V = 1766.98 (6) Å3 | 0.55 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R diffractometer | 3504 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3049 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.033 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5081 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 73.7°, θmin = 5.8° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −17→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007) | k = −18→19 |
| Tmin = 0.296, Tmax = 0.676 | l = −10→8 |
| 13155 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0518P)2 + 1.5238P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3504 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 209 parameters | Δρmax = 0.52 e Å−3 |
| 3 restraints | Δρmin = −0.43 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br | 0.168343 (18) | 0.871933 (16) | 0.50535 (3) | 0.03689 (11) | |
| O1 | 0.5587 (2) | 0.7918 (2) | 0.1347 (5) | 0.0893 (10) | |
| O2 | 0.42824 (18) | 0.81569 (14) | 0.2331 (4) | 0.0661 (7) | |
| H2O | 0.3800 | 0.7873 | 0.2448 | 0.079* | |
| O1W | 0.28626 (17) | 0.7310 (2) | 0.3254 (3) | 0.0707 (8) | |
| H1W1 | 0.254 (3) | 0.764 (3) | 0.372 (5) | 0.106* | |
| H1W2 | 0.251 (3) | 0.714 (3) | 0.242 (4) | 0.106* | |
| N1 | 0.79026 (13) | 0.52889 (12) | 0.5047 (2) | 0.0254 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.76946 (16) | 0.56100 (15) | 0.6432 (3) | 0.0279 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.68861 (18) | 0.53476 (18) | 0.7221 (3) | 0.0379 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.6566 | 0.4853 | 0.6607 | 0.057* | |
| H2B | 0.6449 | 0.5838 | 0.7192 | 0.057* | |
| H2C | 0.7106 | 0.5178 | 0.8389 | 0.057* | |
| C3 | 0.84000 (16) | 0.63015 (14) | 0.7139 (3) | 0.0268 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.78975 (19) | 0.71914 (16) | 0.7114 (3) | 0.0367 (6) | |
| H4A | 0.7579 | 0.7317 | 0.5972 | 0.055* | |
| H4B | 0.8359 | 0.7649 | 0.7478 | 0.055* | |
| H4C | 0.7435 | 0.7173 | 0.7875 | 0.055* | |
| C5 | 0.88798 (19) | 0.60805 (17) | 0.8929 (3) | 0.0348 (5) | |
| H5A | 0.9155 | 0.5496 | 0.8944 | 0.052* | |
| H5B | 0.8416 | 0.6097 | 0.9687 | 0.052* | |
| H5C | 0.9375 | 0.6508 | 0.9297 | 0.052* | |
| C6 | 0.90648 (16) | 0.62789 (13) | 0.5885 (3) | 0.0252 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.98805 (16) | 0.67357 (15) | 0.5803 (3) | 0.0301 (5) | |
| H7A | 1.0118 | 0.7148 | 0.6643 | 0.036* | |
| C8 | 1.03446 (17) | 0.65748 (16) | 0.4452 (3) | 0.0327 (5) | |
| H8A | 1.0904 | 0.6886 | 0.4369 | 0.039* | |
| C9 | 1.00061 (17) | 0.59686 (16) | 0.3225 (3) | 0.0318 (5) | |
| H9A | 1.0338 | 0.5873 | 0.2319 | 0.038* | |
| C10 | 0.91882 (16) | 0.54979 (15) | 0.3296 (3) | 0.0281 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.8952 | 0.5078 | 0.2470 | 0.034* | |
| C11 | 0.87436 (15) | 0.56811 (14) | 0.4644 (3) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.73635 (17) | 0.46508 (15) | 0.3907 (3) | 0.0320 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.6940 | 0.4319 | 0.4522 | 0.038* | |
| H12B | 0.7800 | 0.4232 | 0.3508 | 0.038* | |
| C13 | 0.67861 (17) | 0.51091 (16) | 0.2403 (3) | 0.0339 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.7215 | 0.5454 | 0.1823 | 0.041* | |
| H13B | 0.6488 | 0.4661 | 0.1607 | 0.041* | |
| C14 | 0.60247 (18) | 0.57112 (19) | 0.2847 (3) | 0.0391 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.5631 | 0.5384 | 0.3527 | 0.047* | |
| H14B | 0.6323 | 0.6199 | 0.3540 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 0.5405 (2) | 0.6079 (2) | 0.1308 (4) | 0.0553 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.5107 | 0.5590 | 0.0617 | 0.066* | |
| H15B | 0.5800 | 0.6403 | 0.0628 | 0.066* | |
| C16 | 0.46391 (19) | 0.66849 (18) | 0.1732 (4) | 0.0430 (6) | |
| H16A | 0.4067 | 0.6601 | 0.0888 | 0.052* | |
| H16B | 0.4486 | 0.6516 | 0.2838 | 0.052* | |
| C17 | 0.4896 (2) | 0.7628 (2) | 0.1783 (4) | 0.0492 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br | 0.04080 (17) | 0.03133 (16) | 0.03975 (18) | −0.00006 (10) | 0.01018 (12) | 0.00063 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0628 (16) | 0.0726 (18) | 0.136 (3) | −0.0271 (14) | 0.0274 (17) | −0.0028 (18) |
| O2 | 0.0607 (14) | 0.0372 (11) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0081 (10) | 0.0028 (13) | −0.0153 (12) |
| O1W | 0.0458 (12) | 0.102 (2) | 0.0635 (16) | 0.0124 (13) | 0.0056 (11) | −0.0374 (15) |
| N1 | 0.0266 (9) | 0.0221 (8) | 0.0263 (10) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0300 (11) | 0.0264 (11) | 0.0259 (11) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0005 (9) | 0.0053 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0355 (13) | 0.0415 (14) | 0.0380 (14) | −0.0016 (10) | 0.0105 (11) | 0.0069 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0238 (11) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0033 (9) | −0.0004 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0450 (14) | 0.0296 (12) | 0.0366 (14) | 0.0056 (10) | 0.0100 (11) | −0.0002 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0439 (14) | 0.0343 (12) | 0.0244 (12) | −0.0008 (10) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0014 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0317 (11) | 0.0205 (10) | 0.0225 (11) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0015 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0334 (11) | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0319 (13) | −0.0025 (9) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0005 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0302 (11) | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0394 (14) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0082 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0348 (12) | 0.0313 (12) | 0.0306 (13) | 0.0075 (9) | 0.0089 (10) | 0.0065 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0347 (12) | 0.0244 (11) | 0.0239 (11) | 0.0050 (9) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0275 (10) | 0.0210 (10) | 0.0243 (11) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0045 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0327 (11) | 0.0234 (11) | 0.0374 (13) | −0.0030 (9) | −0.0020 (10) | −0.0040 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0330 (12) | 0.0330 (12) | 0.0332 (13) | 0.0007 (9) | −0.0018 (10) | −0.0069 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0352 (13) | 0.0426 (14) | 0.0381 (14) | 0.0067 (11) | 0.0023 (11) | −0.0017 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0538 (18) | 0.0570 (18) | 0.0493 (18) | 0.0244 (15) | −0.0087 (14) | −0.0133 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0363 (13) | 0.0373 (14) | 0.0526 (17) | 0.0073 (11) | −0.0014 (12) | −0.0026 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0405 (15) | 0.0418 (15) | 0.062 (2) | −0.0031 (12) | −0.0019 (13) | −0.0028 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C17 | 1.198 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.394 (4) |
| O2—C17 | 1.330 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9500 |
| O2—H2O | 0.8400 | C8—C9 | 1.389 (4) |
| O1W—H1W1 | 0.812 (19) | C8—H8A | 0.9500 |
| O1W—H1W2 | 0.817 (19) | C9—C10 | 1.394 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.302 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9500 |
| N1—C11 | 1.440 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.381 (3) |
| N1—C12 | 1.476 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.476 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.528 (3) |
| C1—C3 | 1.516 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9800 | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9800 | C13—C14 | 1.524 (3) |
| C2—H2C | 0.9800 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C6 | 1.507 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C5 | 1.536 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.518 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.545 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9800 | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9800 | C15—C16 | 1.526 (4) |
| C4—H4C | 0.9800 | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9800 | C16—C17 | 1.493 (4) |
| C5—H5C | 0.9800 | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C6—C11 | 1.382 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.382 (3) | ||
| C17—O2—H2O | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9A | 119.4 |
| H1W1—O1W—H1W2 | 104 (3) | C10—C9—H9A | 119.4 |
| C1—N1—C11 | 111.00 (19) | C11—C10—C9 | 115.8 (2) |
| C1—N1—C12 | 127.9 (2) | C11—C10—H10A | 122.1 |
| C11—N1—C12 | 120.96 (19) | C9—C10—H10A | 122.1 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 125.4 (2) | C10—C11—C6 | 124.3 (2) |
| N1—C1—C3 | 110.6 (2) | C10—C11—N1 | 127.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C3 | 124.0 (2) | C6—C11—N1 | 108.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | N1—C12—C13 | 110.80 (19) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | N1—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | N1—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.1 |
| C6—C3—C1 | 101.18 (18) | C14—C13—C12 | 114.4 (2) |
| C6—C3—C5 | 112.9 (2) | C14—C13—H13A | 108.7 |
| C1—C3—C5 | 111.86 (19) | C12—C13—H13A | 108.7 |
| C6—C3—C4 | 111.20 (19) | C14—C13—H13B | 108.7 |
| C1—C3—C4 | 109.1 (2) | C12—C13—H13B | 108.7 |
| C5—C3—C4 | 110.3 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.6 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C15—C14—C13 | 112.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14A | 109.1 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.1 |
| C3—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14B | 109.1 |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.1 |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.8 |
| C3—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C14—C15—C16 | 113.2 (3) |
| C3—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| C3—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15B | 108.9 |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15B | 108.9 |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.7 |
| C11—C6—C7 | 119.3 (2) | C17—C16—C15 | 114.2 (3) |
| C11—C6—C3 | 109.15 (19) | C17—C16—H16A | 108.7 |
| C7—C6—C3 | 131.6 (2) | C15—C16—H16A | 108.7 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 118.1 (2) | C17—C16—H16B | 108.7 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 120.9 | C15—C16—H16B | 108.7 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 120.9 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.6 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.3 (2) | O1—C17—O2 | 120.4 (3) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 119.4 | O1—C17—C16 | 124.5 (3) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 119.4 | O2—C17—C16 | 115.1 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 121.3 (2) | ||
| C11—N1—C1—C2 | −179.2 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.5 (3) |
| C12—N1—C1—C2 | 4.5 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | −0.7 (3) |
| C11—N1—C1—C3 | 1.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N1 | −179.0 (2) |
| C12—N1—C1—C3 | −175.3 (2) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | 0.2 (3) |
| N1—C1—C3—C6 | −1.7 (2) | C3—C6—C11—C10 | −180.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—C3—C6 | 178.4 (2) | C7—C6—C11—N1 | 178.82 (19) |
| N1—C1—C3—C5 | −122.2 (2) | C3—C6—C11—N1 | −1.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C3—C5 | 58.0 (3) | C1—N1—C11—C10 | 178.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—C3—C4 | 115.6 (2) | C12—N1—C11—C10 | −4.6 (3) |
| C2—C1—C3—C4 | −64.3 (3) | C1—N1—C11—C6 | 0.3 (2) |
| C1—C3—C6—C11 | 1.9 (2) | C12—N1—C11—C6 | 176.90 (19) |
| C5—C3—C6—C11 | 121.6 (2) | C1—N1—C12—C13 | 99.2 (3) |
| C4—C3—C6—C11 | −113.9 (2) | C11—N1—C12—C13 | −76.8 (3) |
| C1—C3—C6—C7 | −178.4 (2) | N1—C12—C13—C14 | −64.4 (3) |
| C5—C3—C6—C7 | −58.7 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −174.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—C6—C7 | 65.8 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −179.9 (3) |
| C11—C6—C7—C8 | 0.4 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 94.4 (4) |
| C3—C6—C7—C8 | −179.3 (2) | C15—C16—C17—O1 | 8.5 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.5 (4) | C15—C16—C17—O2 | −172.8 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.0 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2O···O1W | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.637 (4) | 166 |
| O1W—H1W1···Br | 0.81 (2) | 2.43 (2) | 3.240 (2) | 175 (5) |
| O1W—H1W2···Bri | 0.82 (2) | 2.47 (2) | 3.262 (3) | 165 (5) |
| C4—H4B···Cg2ii | 0.99 | 2.88 | 3.828 (3) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FL2265).
References
- Armitage, B. & O’Brien, D. F. (1992). J. Am. Chem. Soc.114, 7396–7403.
- Bengtsson, M., Karlsson, H. J., Westman, G. & Kubista, M. (2003). Nucleic Acids Res.31, e45/1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hirons, G. T., Fawcett, J. J. & Crissman, H. A. (1994). Cytometry, 15, 129–140. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jung, M. E. & Kim, W. (2006). Bio. Med. Chem.14, 92–97.
- Kurihara, K., Toyoshima, Y. & Sukigara, M. (1977). J. Phys. Chem.81, 1833–1837.
- Menger, F. M. & Pertusati, P. (2008). J. Org. Chem.73, 2939–2942. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2007). CrysAlis Pro and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Reers, M., Smith, T. W. & Chen, L. B. (1991). Biochemistry, 30, 4480–4486. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J. R. & Polik, W. F. (2007). WebMO Pro, Version 8.0.010e; WebMO, LLC: Holland, MI, USA, available from http://www.webmo.net.
- Schwartz, H. E. & Ulfelder, K. J. (1992). Anal. Chem.64, 1737–1740.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H., Clark, S. M., Benson, S. C., Rye, H. S., Glazer, A. N. & Mathies, R. A. (1994). Anal. Chem.66, 1941–1948. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809049204/fl2265sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809049204/fl2265Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report