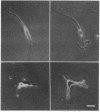
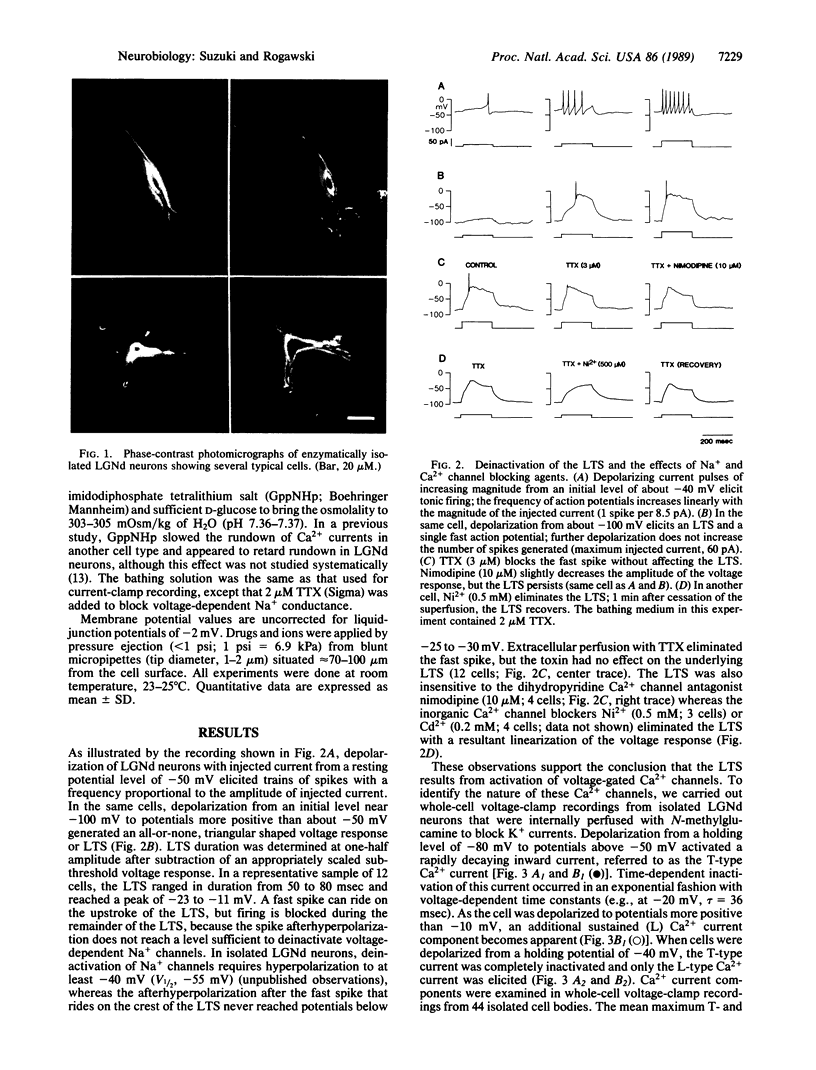
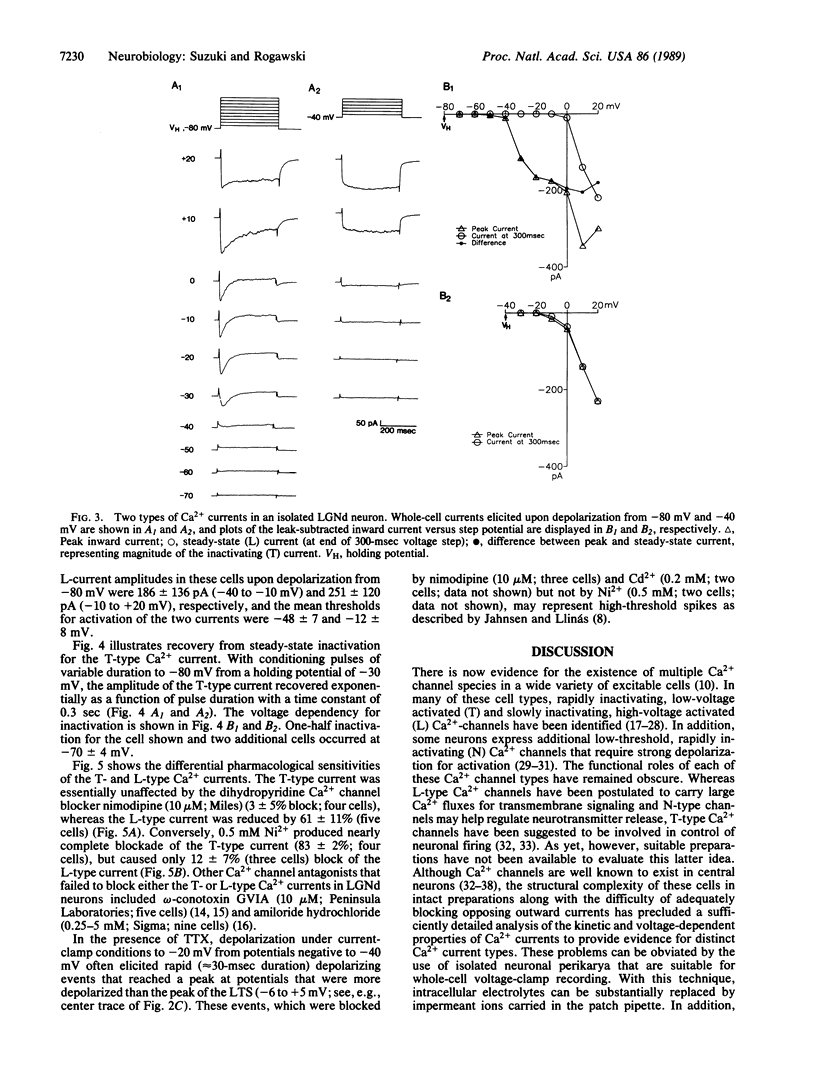
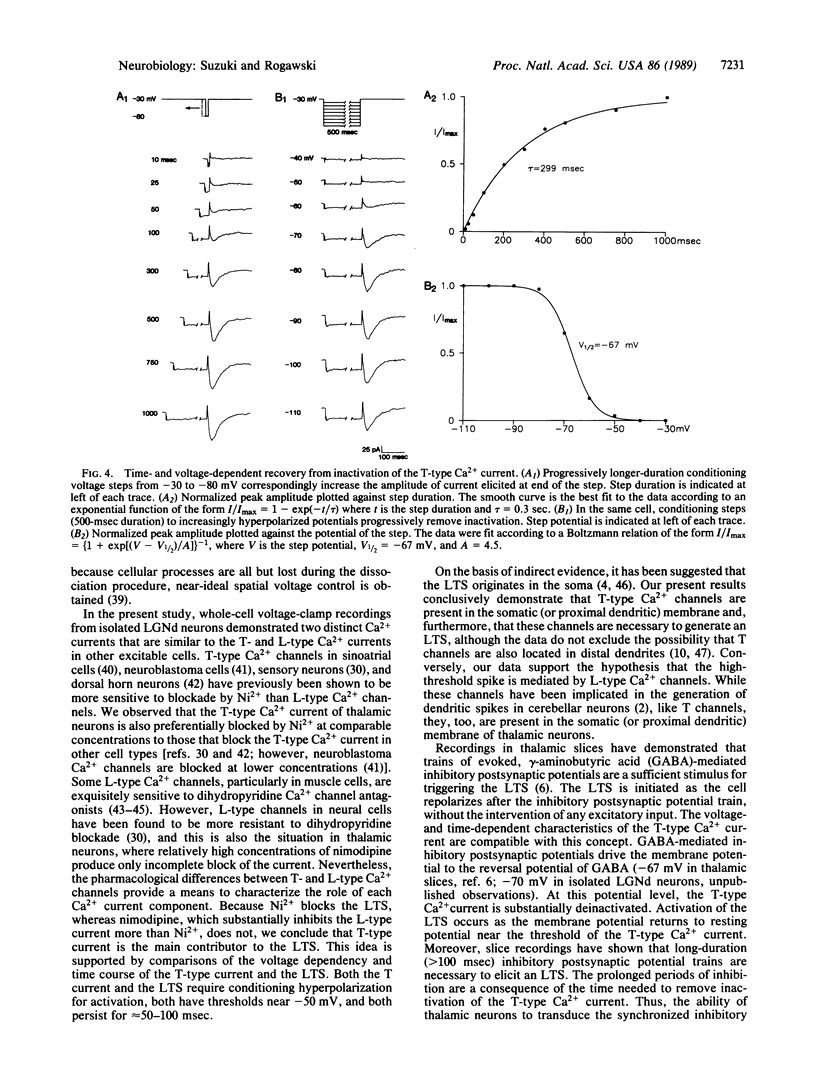
Abstract
Thalamic neurons undergo a shift from tonic to phasic (burst) firing upon hyperpolarization. This state transition results from deinactivation of a regenerative depolarizing event referred to as the low-threshold spike. Isolated adult guinea pig thalamic (dorsal lateral geniculate) neurons exhibited low-threshold spikes that could be blocked by low concentrations of nickel but were unaffected by the dihydropyridine nimodipine. Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from these cells demonstrated a low-threshold, rapidly inactivating (T) Ca2+ current that manifested similar voltage dependency and time course as the low-threshold spike. Like low-threshold spikes, the T-type Ca2+ current was eliminated by nickel but was unaffected by nimodipine. In thalamic neurons, T-type Ca2+ channels underlie the low-threshold spike and, therefore, play a critical role in regulating the firing pattern of these cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P., Sturek M., Puga A., Hermsmeyer K. Calcium channels in muscle cells isolated from rat mesenteric arteries: modulation by dihydropyridine drugs. Circ Res. 1986 Aug;59(2):229–235. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. Differences in kinetics, selectivity, and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Feltz A., Thomann J. M. Depolarization elicits two distinct calcium currents in vertebrate sensory neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):360–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00589247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Griffith W. H. Persistent slow inward calcium current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:303–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Kinetics and selectivity of a low-voltage-activated calcium current in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:547–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Single low-voltage-activated calcium channels in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:571–601. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Galvan M., Franz P., Sim J. A. Calcium-dependent inward currents in voltage-clamped guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Jul;404(3):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00581248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. A., Huguenard J. R., Prince D. A. Calcium currents in rat thalamocortical relay neurones: kinetic properties of the transient, low-threshold current. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:587–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschênes M., Paradis M., Roy J. P., Steriade M. Electrophysiology of neurons of lateral thalamic nuclei in cat: resting properties and burst discharges. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1196–1219. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Single-channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:173–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz P., Galvan M., Constanti A. Calcium-dependent action potentials and associated inward currents in guinea-pig neocortical neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 26;366(1-2):262–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Gutnick M. J. Low-threshold calcium electrogenesis in neocortical neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 16;81(1-2):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Pape H. C. Identification of two calcium currents in acutely dissociated neurons from the rat lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jun;61(6):1270–1283. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.6.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y. Calcium channels in isolated rat dorsal horn neurones, including labelled spinothalamic and trigeminothalamic cells. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:161–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G., Weight F. F. Na+ and Ca2+ currents of acutely isolated adult rat nodose ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):527–539. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Ionic basis for the electro-responsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:227–247. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Hablitz J. J., Wilson W. A. Voltage clamp discloses slow inward current in hippocampal burst-firing neurones. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):391–393. doi: 10.1038/286391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Calcium current activation kinetics in isolated pyramidal neurones of the Ca1 region of the mature guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:603–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Isolation of neurons suitable for patch-clamping from adult mammalian central nervous systems. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 May;16(3):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. M., Yoshikami D. A venom peptide with a novel presynaptic blocking action. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):282–284. doi: 10.1038/308282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel R. M. Neurons of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the albino rat. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Jan 1;159(1):45–67. doi: 10.1002/cne.901590105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R. The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: insights into central nervous system function. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1654–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.3059497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Yarom Y. Properties and distribution of ionic conductances generating electroresponsiveness of mammalian inferior olivary neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:569–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Properties of two types of calcium channels in clonal pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):161–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D. H., Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M., Tsien R. W., Yoshikami D. Omega-conotoxin: direct and persistent blockade of specific types of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R., Morad M. Two types of calcium channels in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5340–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Tsunoo A., Yoshii M. Characterization of two types of calcium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:231–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Tsunoo A., Yoshii M. Characterization of two types of calcium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:231–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):443–446. doi: 10.1038/316443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Porzig H., Kokubun S., Prod'hom B. Calcium channels in the heart. Properties and modulation by dihydropyridine enantiomers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;522:16–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb33338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski M. A., Inoue K., Suzuki S., Barker J. L. A slow calcium-dependent chloride conductance in clonal anterior pituitary cells. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Jun;59(6):1854–1870. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.6.1854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Kass R. S. Voltage-dependent block of calcium channel current in the calf cardiac Purkinje fiber by dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists. Circ Res. 1984 Sep;55(3):336–348. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent D., Benevides J. M., Yu M. H., King J., Thomas G. J., Jr Secondary structure and thermostability of the phage P22 tailspike. XX. Analysis by Raman spectroscopy of the wild-type protein and a temperature-sensitive folding mutant. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 5;199(3):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90620-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. M., Koch C. The control of retinogeniculate transmission in the mammalian lateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1986;63(1):1–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00235642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Deschenes M. The thalamus as a neuronal oscillator. Brain Res. 1984 Nov;320(1):1–63. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Llinás R. R. The functional states of the thalamus and the associated neuronal interplay. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jul;68(3):649–742. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.3.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Presser F., Morad M. Amiloride selectively blocks the low threshold (T) calcium channel. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2451291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M. Biphasic responses of thalamic neurons to GABA in isolated rat brain slices--II. Neuroscience. 1988 May;25(2):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Fox A. P., Hess P., McCleskey E. W., Nilius B., Nowycky M. C., Rosenberg R. L. Multiple types of calcium channel in excitable cells. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1987;41:167–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaari Y., Hamon B., Lux H. D. Development of two types of calcium channels in cultured mammalian hippocampal neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):680–682. doi: 10.1126/science.2433765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]