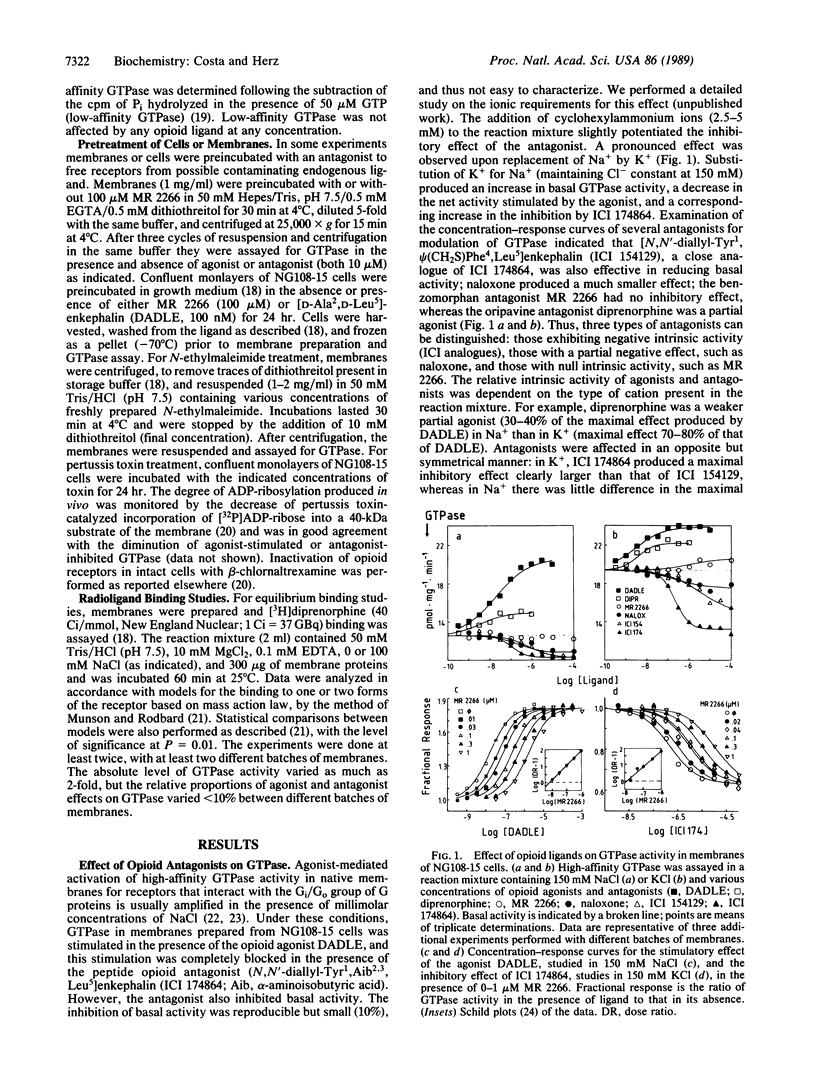
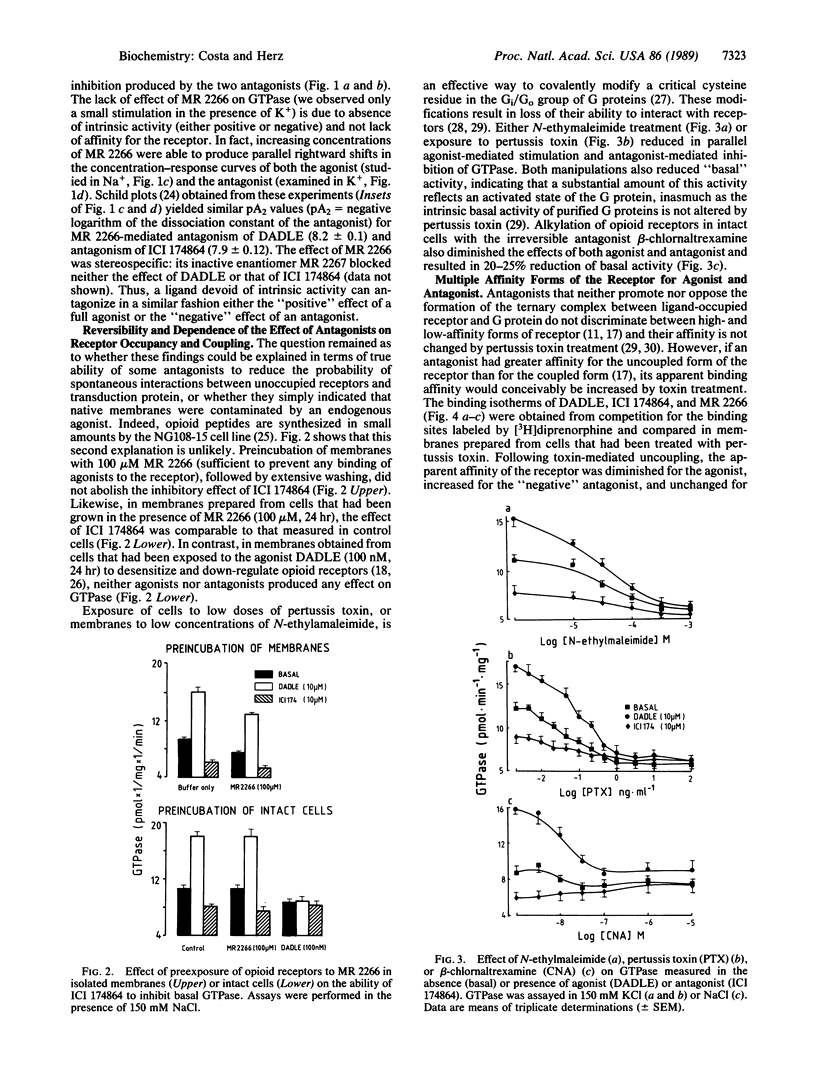
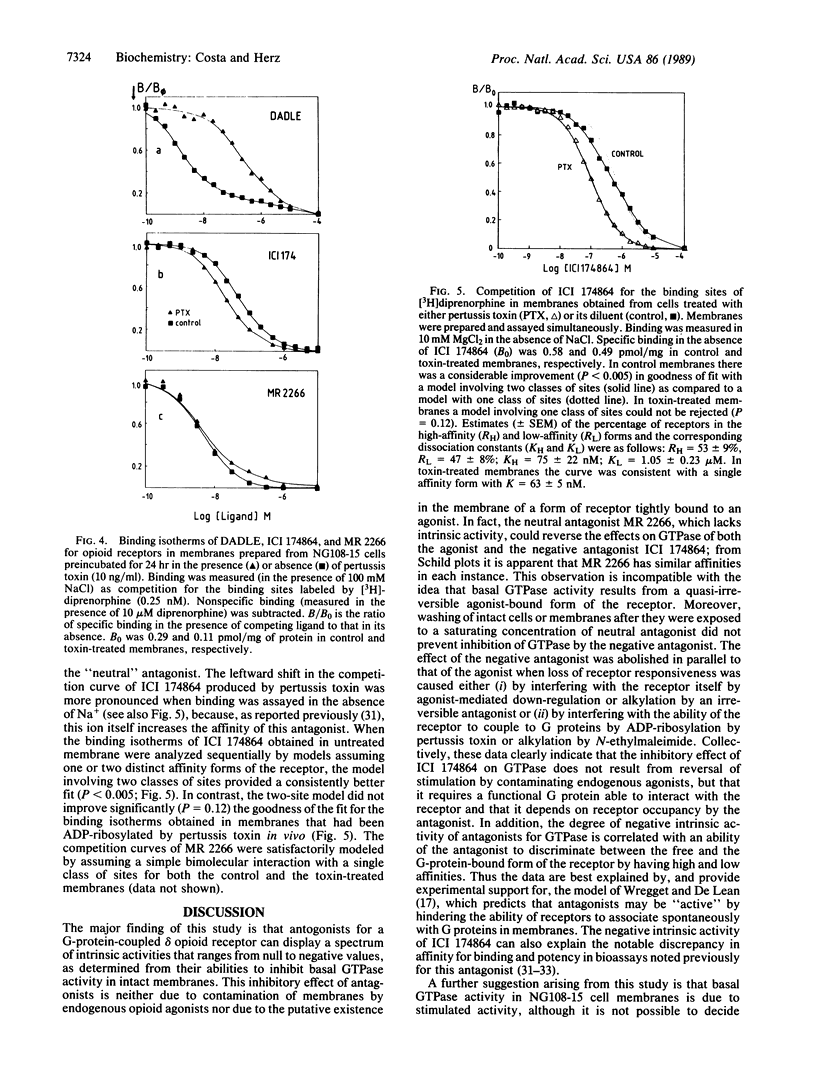
Abstract
According to classical models of drug-receptor interactions, competitive antagonists share with agonists the ability to bind to a common site on the receptor molecule. However, they are different from agonists, as they cannot trigger the "stimulus" that leads to biological responses--i.e., they lack intrinsic activity. For those receptors whose signals are transduced to effector systems by GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins), a mechanistic equivalent of such a stimulus is an increased ability of agonist-bound receptor to accelerate nucleotide exchange and thus GTPase activity on the G-protein molecule. Here we show that for a member of this family of receptors (delta opioid receptors in membranes of NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma cells), two types of competitive antagonists can be distinguished. One type has no intrinsic activity, since it neither stimulates nor inhibits the GTPase activity of G proteins and its apparent affinity for the receptor is not altered by pertussis toxin-mediated uncoupling of receptor and G protein. The second type, however, can inhibit GTPase and thus exhibits negative intrinsic activity; its affinity for receptors is increased following uncoupling from G proteins. The existence of antagonists with negative intrinsic activity may be a general feature of several classes of neurotransmitters or hormone receptors and calls for a reevaluation of biological effects produced by competitive antagonists.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Schultz G., Jakobs K. H. Stimulation of a low Km GTPase by inhibitors of adipocyte adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;21(2):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelmans N., Carroll J. A., Rance M. J., Simon E. J., Traynor J. R. Sodium ions increase the binding of the antagonist peptide ICI 174864 to the delta-opiate receptor. Neuropeptides. 1986 Feb-Mar;7(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(86)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Uncoupling of gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors from GTP-binding proteins by N-ethylmaleimide: effect of N-ethylmaleimide on purified GTP-binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;29(3):244–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Pedersen S. E., Scott C. W., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of catecholamine-stimulated binding of guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) to the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5460–5467. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Schmiechen R., Neef G., Nielsen M., Petersen E. N. Interaction of convulsive ligands with benzodiazepine receptors. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1241–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.6281892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgisser E., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. Reciprocal modulation of agonist and antagonist binding to muscarinic cholinergic receptor by guanine nucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1732–1736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Birnbaumer L., Caron M. G. The mammalian beta 2-adrenergic receptor: reconstitution of functional interactions between pure receptor and pure stimulatory nucleotide binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4519–4525. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Eckel R. W., Blanchard S. G. Opioid peptides induce reduction of enkephalin receptors in cultured neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):446–448. doi: 10.1038/296446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., McKnight A. T., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Selectivities of opioid peptide analogues as agonists and antagonists at the delta-receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):271–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Klinz F. J., Vachon L., Herz A. Opioid receptors are coupled tightly to G proteins but loosely to adenylate cyclase in NG108-15 cell membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):744–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R., Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Rance M. J., Traynor J. R. The use of [3H]-[D-Pen2,D-Pen5]enkephalin as a highly selective ligand for the delta-binding site. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;84(4):927–932. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb17387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Kilpatrick B. F., Caron M. G. Dopamine receptor of the porcine anterior pituitary gland. Evidence for two affinity states discriminated by both agonists and antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Hübner K., Hamprecht B. Neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells synthesize enkephalin-like opioid peptides. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):59–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. D. Reciprocal modulation of agonist and antagonist binding to inhibitory adenosine receptors by 5'-guanylylimidodiphosphate and monovalent cations. J Neurosci. 1984 Oct;4(10):2472–2476. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-10-02472.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga K., Haga T., Ichiyama A. Reconstitution of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Guanine nucleotide-sensitive high affinity binding of agonists to purified muscarinic receptors reconstituted with GTP-binding proteins (Gi and Go). J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10133–10140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Streaty R. A., Klee W. A. Modulation of sodium-sensitive GTPase by partial opiate agonists. An explanation for the dual requirement for Na+ and GTP in inhibitory regulation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14035–14040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Katada T., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Ui M. Functional interaction of purified muscarinic receptors with purified inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6423–6428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mullikin D., Caron M. G. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by guanyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate and other purine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-induced increase in apparent beta-adrenergic receptor size. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):228–232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. An agonist-specific effect of guanine nucleotides on binding to the beta adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;12(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Ross E. M. Functional activation of beta-adrenergic receptors by thiols in the presence or absence of agonists. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14150–14157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Nakata H., DeMarinis R. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Purification and characterization of the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3894–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Benovic J. L., Amlaiky N., Unson C., Milligan G., Vinitsky R., Spiegel A. M., Caron M. G. The D2-dopamine receptor of anterior pituitary is functionally associated with a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4860–4867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Harada H., Nozaki M., Katada T., Ui M., Satoh M., Takagi H. Reconstitution of rat brain mu opioid receptors with purified guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins, Gi and Go. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7013–7017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon L., Costa T., Herz A. GTPase and adenylate cyclase desensitize at different rates in NG108-15 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;31(2):159–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow J. W., Bradley J. D., Smith J. A., Neer E. J. Reactive sulfhydryl groups of alpha 39, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein from brain. Location and function. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4501–4507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreggett K. A., De Léan A. The ternary complex model. Its properties and application to ligand interactions with the D2-dopamine receptor of the anterior pituitary gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):214–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



