Abstract
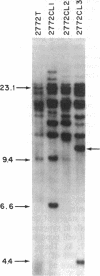
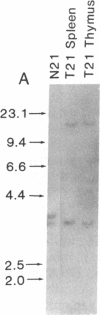
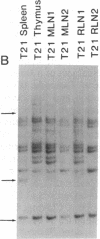
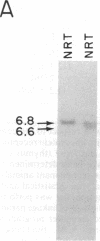
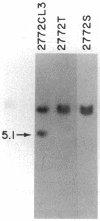
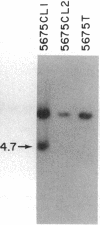
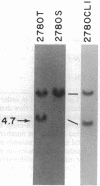
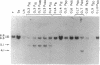
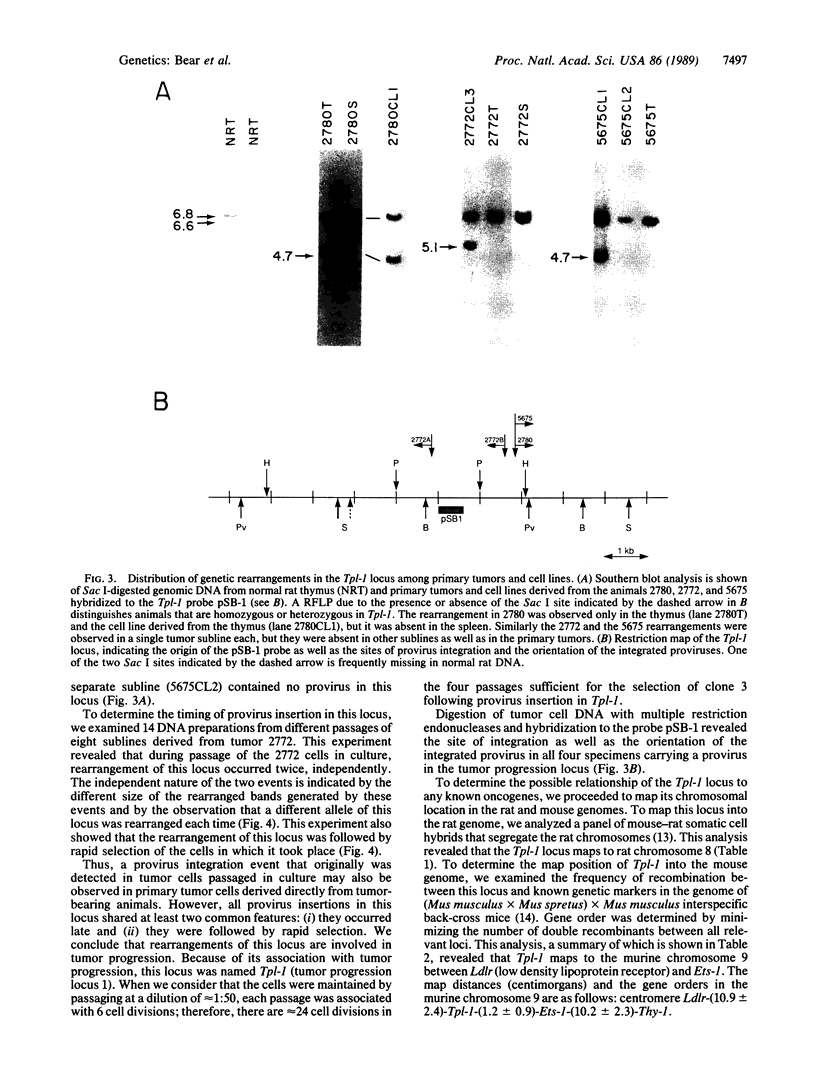
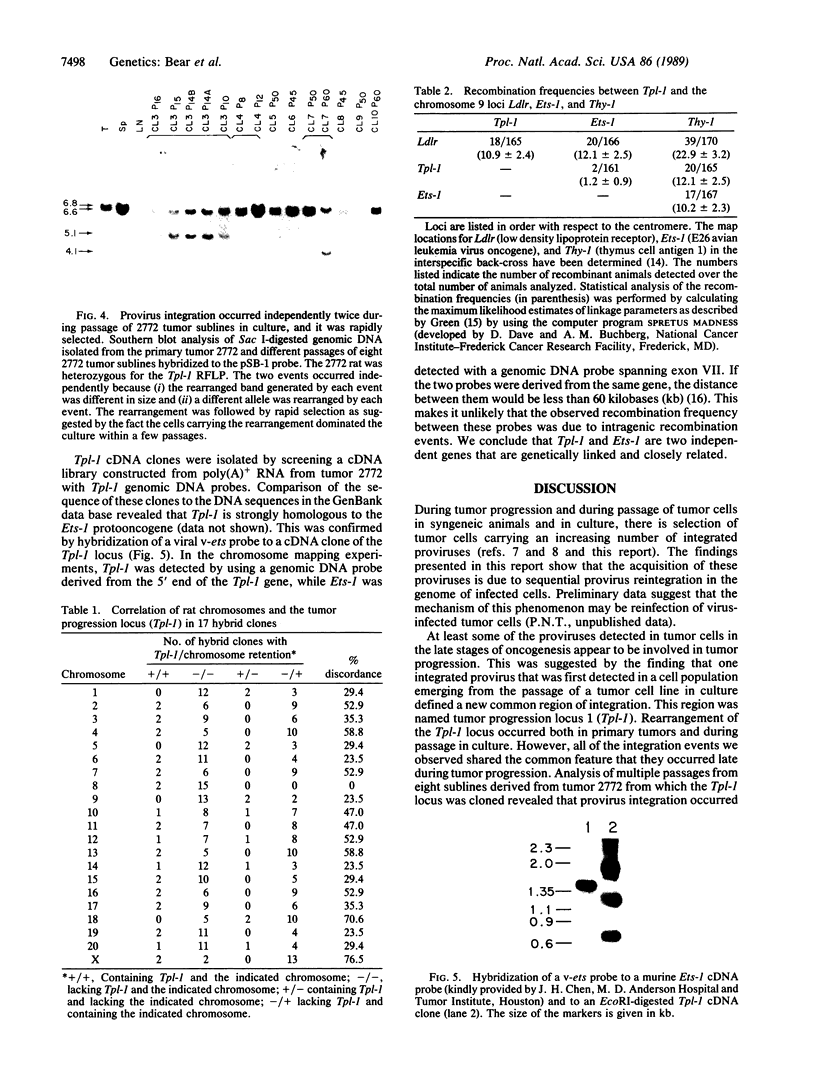
T-cell lymphomas induced in rats by Moloney murine leukemia virus acquire increasing numbers of proviruses in their genome during tumor progression in vivo and passage of tumor cells in vitro. To determine whether the proviruses progressively acquired during tumor progression play a causal role in this process, we cloned one of them from a cell line derived from the primary tumor 2772. A probe from the cellular DNA flanking the provirus was used to analyze 79 DNA samples from primary tumor tissues of 28 tumor-bearing rats and 80 DNA samples from 30 independent tumor cell lines. This analysis revealed a rearrangement in this region in the primary tumor derived from the thymus of one animal but not in a clone of the same tumor segregating in the spleen. Of the cell line DNA samples, three carried a provirus in this region. Two of these integration events had occurred independently in two clonally related sublines derived from tumor 2772, and they were followed by rapid selection in culture. On the basis of these findings this locus was named Tpl-1 (tumor progression locus 1). The Tpl-1 locus was mapped to rat chromosome 8 and to mouse chromosome 9 at a genetic distance of 1.2 +/- 0.9 centimorgans from the Ets-1 protooncogene. Although the genetic distance between Tpl-1 and Ets-1 indicates that they are different genes, analysis of Tpl-1 cDNA clones revealed that the two are closely related.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. Oncogenes and human cancer: cause or consequence? Carcinogenesis. 1986 Jul;7(7):1037–1042. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.7.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Colston E. M., Cole M. D. Integration of the BALB/c ecotropic provirus into the colony-stimulating factor-1 growth factor locus in a myc retrovirus-induced murine monocyte tumor. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3151–3155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3151-3155.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L. Isolation of cytoplasmic RNA: ribonucleoside-vanadyl complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:227–234. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer M. L., Cuypers H. T., Berns A. Evidence for the involvement of pim-2, a new common proviral insertion site, in progression of lymphomas. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):743–748. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G. C., Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Melief C. J., Berns A. J. Tumor progression in murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas: monitoring clonal selections with viral and cellular probes. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):230–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.230-241.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haluska F. G., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Oncogene activation by chromosome translocation in human malignancy. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:321–345. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:254–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Tumor cell instability, diversification, and progression to the metastatic phenotype: from oncogene to oncofetal expression. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1473–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Kozak C., Jolicoeur P. Identification of a common helper provirus integration site in Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced lymphoma DNA. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3985–3992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3985-3992.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Papas T. S., Reddy E. S. erg, a human ets-related gene on chromosome 21: alternative splicing, polyadenylation, and translation. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):635–639. doi: 10.1126/science.3299708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Lohse M. A., Szpirer C., Szpirer J., Levan G. Cellular DNA regions involved in the induction of rat thymic lymphomas (Mlvi-1, Mlvi-2, Mlvi-3, and c-myc) represent independent loci as determined by their chromosomal map location in the rat. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.938-942.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N. Oncogenesis by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Anticancer Res. 1987 Mar-Apr;7(2):171–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
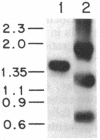
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Papas T. S. Molecular organization of the chicken ets locus. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90624-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]