Abstract
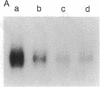
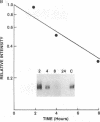
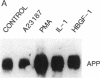
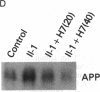
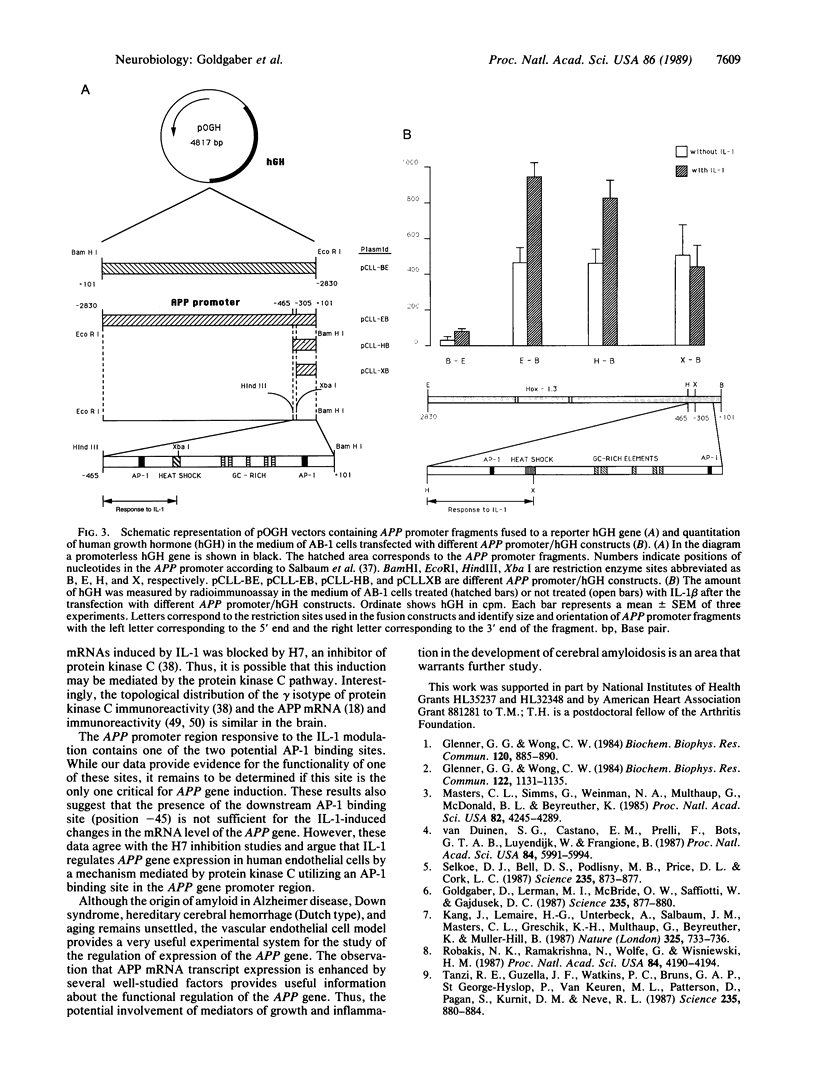
We have analyzed the modulation of amyloid beta-protein precursor (APP) gene expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). The level of the APP mRNA transcripts increased as HUVEC reached confluency. In confluent culture the half-life of the APP mRNA was 4 hr. Treatment of the cells with human-recombinant interleukin 1 (IL-1), phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, or heparin-binding growth factor 1 enhanced the expression of APP gene in these cells, but calcium ionophore A23187 and dexamethasone did not. The protein kinase C inhibitor 1-(isoquinolinsulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H7) inhibited IL-1-mediated increase of the level of APP transcripts. To map IL-1-responsive elements of the APP promoter, truncated portions of the APP promoter were fused to the human growth hormone reporter gene. The recombinant plasmids were transfected into mouse neuroblastoma cells, and the cell medium was assayed for the human growth hormone. A 180-base-pair region of the APP promoter located between position -485 and -305 upstream from the transcription start site was necessary for IL-1-mediated induction of the reporter gene. This region contains the upstream transcription factor AP-1 binding site. These results suggest that IL-1 upregulates APP gene expression in HUVEC through a pathway mediated by protein kinase C, utilizing the upstream AP-1 binding site of the APP promoter.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Meade R. P., Davis L. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the precursor protein for beta-amyloid in the rat central nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):835–846. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90131-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Krekoski C. A., Parhad I. M., Liston D., Julien J. P., Hoar D. I. Altered expression of genes for amyloid and cytoskeletal proteins in Alzheimer cortex. Ann Neurol. 1989 Apr;25(4):331–339. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Golde T. E., Usiak M. F., Younkin L. H., Younkin S. G. In situ hybridization of nucleus basalis neurons shows increased beta-amyloid mRNA in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R. J., Rasool C. G., Bartus R., Vitek S., Blume A. J., Vitek M. Multiple forms of beta-amyloid peptide precursor RNAs in a single cell type. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A. Astrocytes and lymphocytes: intercellular communication by growth factors. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):443–451. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3872478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M. Neuronal localization of amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA in normal human brain and in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3627–3632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin W. S., Stanley L. C., Ling C., White L., MacLeod V., Perrot L. J., White C. L., 3rd, Araoz C. Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7611–7615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. N., Merz P., Bennett-Gray J., Menezes A. H., Goeken J. A., Schelper R. L., Wisniewski H. M. beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease is found in cerebral and spinal cord vascular malformations. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):167–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. A., Lewis D. A., Bahmanyar S., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Young W. G., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C. Differential regulation of amyloid-beta-protein mRNA expression within hippocampal neuronal subpopulations in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1297–1301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto N., Kobayashi K., Kosaka K. The formation of prostaglandins in the postmortem cerebral cortex of Alzheimer-type dementia patients. J Neurol. 1989 Feb;236(2):80–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00314401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. A., Pasinetti G. M., May P. C., Ponte P. A., Cordell B., Finch C. E. Selective reduction of mRNA for the beta-amyloid precursor protein that lacks a Kunitz-type protease inhibitor motif in cortex from Alzheimer brains. Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;102(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Higgins G. A., Young W. G., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Wilson M. C., Morrison J. H. Distribution of precursor amyloid-beta-protein messenger RNA in human cerebral cortex: relationship to neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1691–1695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Hoover G. A., Stemerman M. B., Weinstein R. Serial propagation of human endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):420–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning R. W., Reid C. M., Lampe R. A., Davis L. G. Identification in rodents and other species of an mRNA homologous to the human beta-amyloid precursor. Brain Res. 1988 Jun;427(3):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa T., Shimoji A., Kuramoto R., Higuchi Y. The relationship between senile plaques and cerebral blood vessels in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia. Morphological mechanism of senile plaque production. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;40(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF02932857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Finch E. A., Dawes L. R. Expression of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor gene transcripts in the human brain. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Golde T. E., Cohen M. L., Kovacs D. M., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Usiak M. F., Younkin L. H., Younkin S. G. Amyloid protein precursor messenger RNAs: differential expression in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1080–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.2457949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salbaum J. M., Weidemann A., Lemaire H. G., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. The promoter of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 precursor gene. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2807–2813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Goldgaber D., Burkhart D. S., Gilbert J. R., Gajdusek D. C., Roses A. D. Cellular localization of messenger RNA encoding amyloid-beta-protein in normal tissue and in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1988;2(2):96–111. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198802020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorer A. E., Moldow C. F., Rick M. E. Interleukin 1 or endotoxin increases the release of von Willebrand factor from human endothelial cells. Br J Haematol. 1987 Oct;67(2):193–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Bell D. S., Podlisny M. B., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Conservation of brain amyloid proteins in aged mammals and humans with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):873–877. doi: 10.1126/science.3544219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Nakamura S., Ueda K., Kameyama M., Shiojiri S., Takahashi Y., Kitaguchi N., Ito H. Three types of amyloid protein precursor mRNA in human brain: their differential expression in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):472–479. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate-Ostroff B., Majocha R. E., Marotta C. A. Identification of cellular and extracellular sites of amyloid precursor protein extracytoplasmic domain in normal and Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):745–749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M. P., Rasool C. G., de Sauvage F., Vitek S. M., Bartus R. T., Beer B., Ashton R. A., Macq A. F., Maloteaux J. M., Blume A. J. Absence of mutation in the beta-amyloid cDNAs cloned from the brains of three patients with sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1988 Sep;464(2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. A., Taylor J. M. Interleukin-1 and the acute-phase response: induction of mouse liver serum amyloid A mRNA by murine recombinant interleukin-1. J Trauma. 1987 Nov;27(11):1227–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkles J. A., Friesel R., Burgess W. H., Howk R., Mehlman T., Weinstein R., Maciag T. Human vascular smooth muscle cells both express and respond to heparin-binding growth factor I (endothelial cell growth factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S. B., Salim M., Chou W. G., Sajdel-Sulkowska E. M., Majocha R. E., Marotta C. A. Molecular cloning of amyloid cDNA derived from mRNA of the Alzheimer disease brain: coding and noncoding regions of the fetal precursor mRNA are expressed in the cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):929–933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duinen S. G., Castaño E. M., Prelli F., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis in patients of Dutch origin is related to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5991–5994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]