Abstract
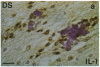
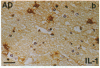
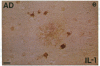
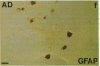
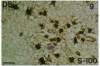
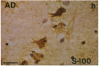
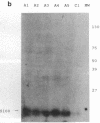
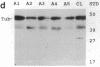
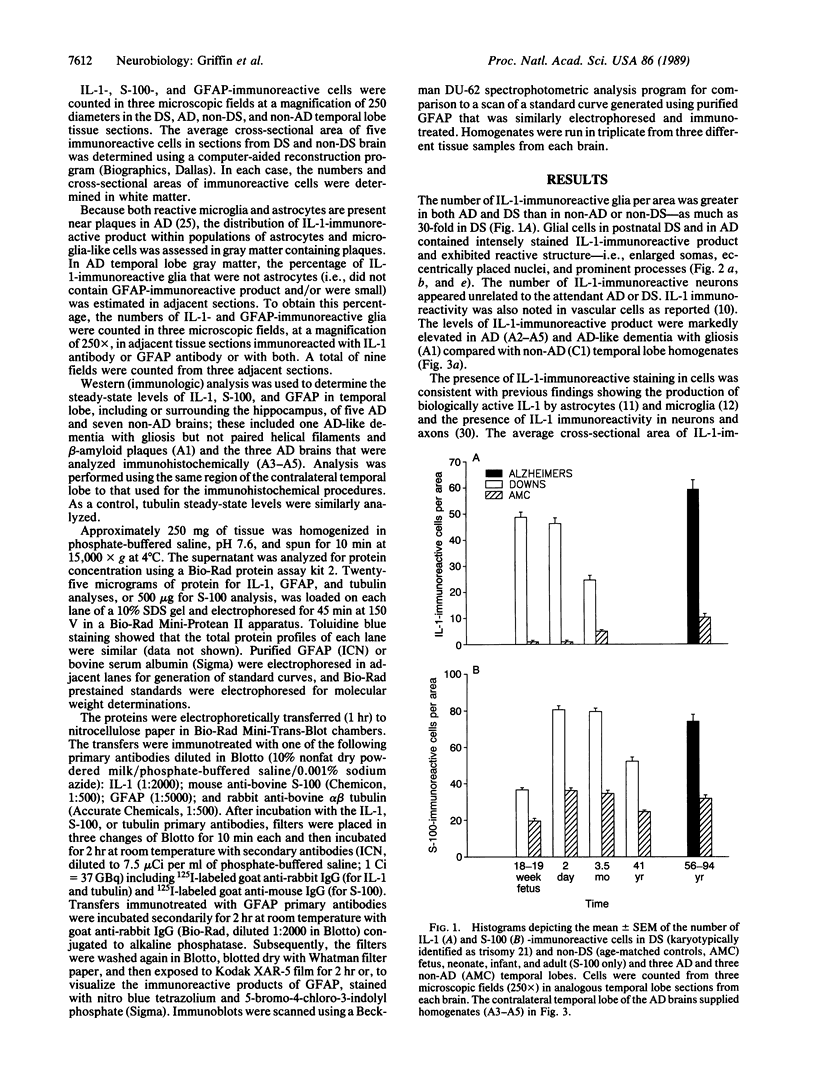
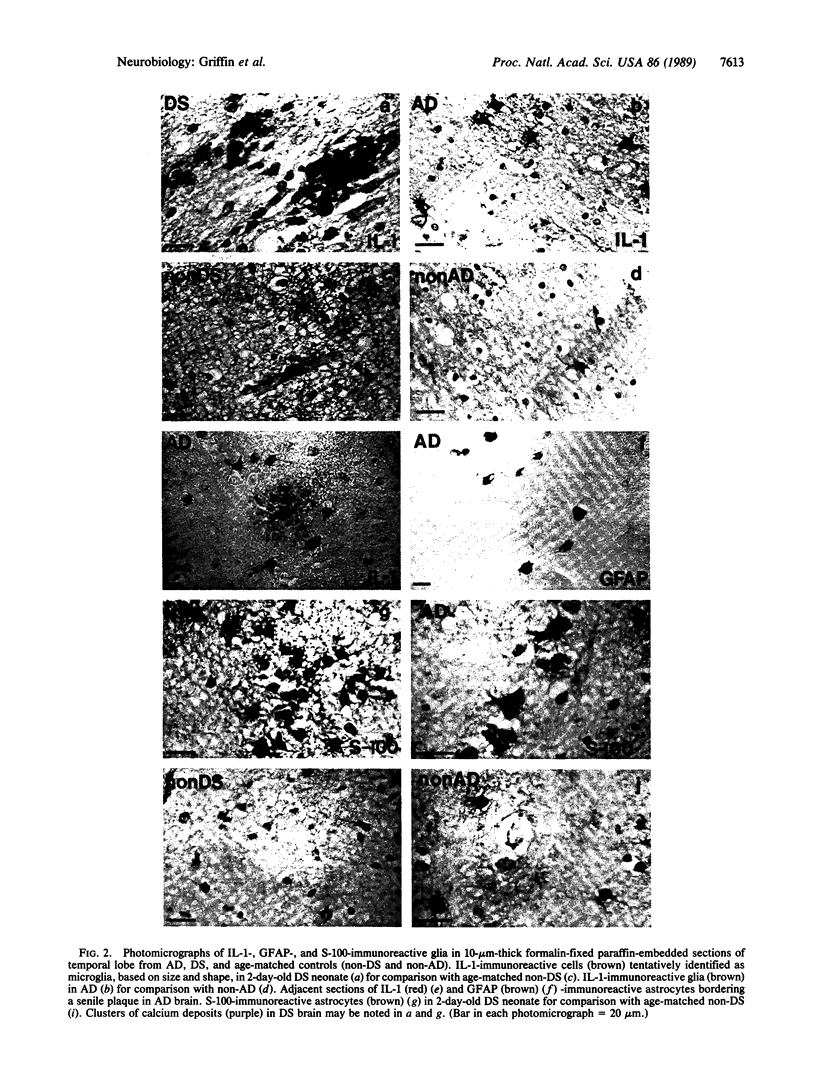
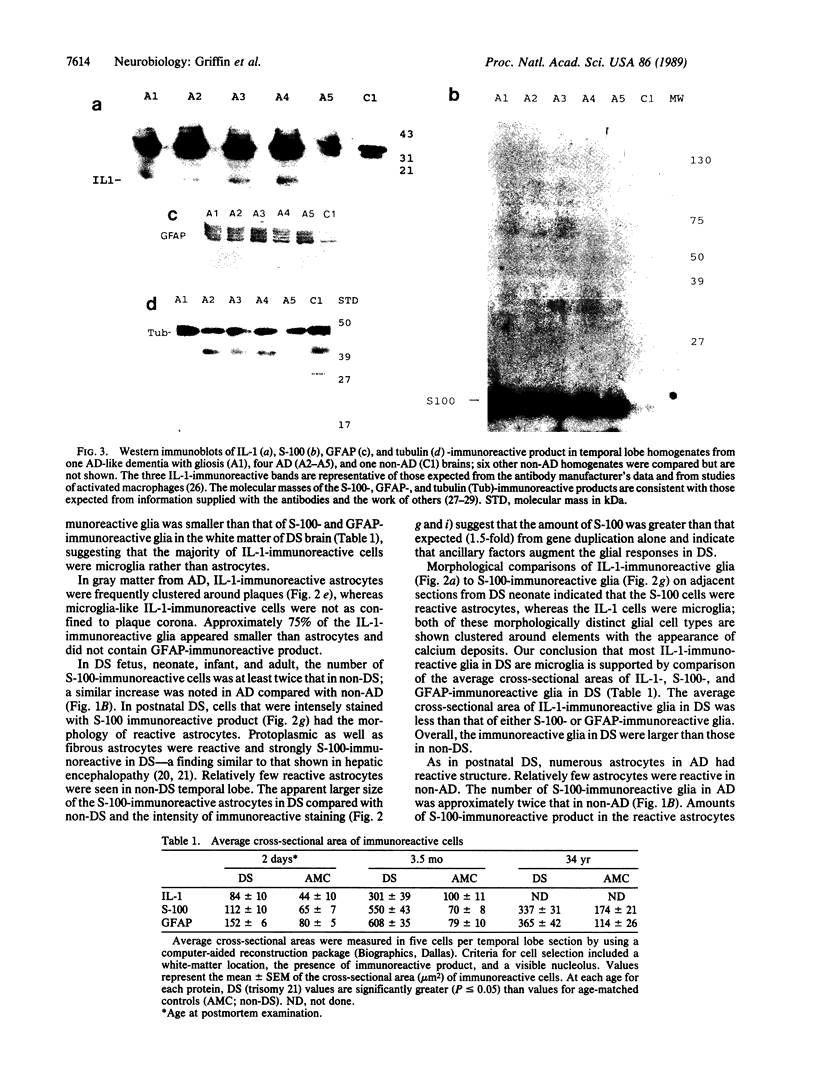
Interleukin 1, an immune response-generated cytokine that stimulates astrocyte proliferation and reactivity (astrogliosis), was present in up to 30 times as many glial cells in tissue sections of brain from patients with Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease compared with age-matched control subjects. Most interleukin 1-immunoreactive glia in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease were classified as microglia. The number of interleukin 1 immunoreactive neurons did not appear to differ in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease compared with control brain. Numerous temporal lobe astrocytes in Alzheimer disease and postnatal Down syndrome were intensely interleukin 1-, S-100-, and glial fibrillary acidic protein-immunoreactive and had reactive structure. Interleukin 1 levels in Alzheimer disease temporal lobe homogenates were elevated, as were the levels of S-100 and glial fibrillary acidic protein, two proteins reportedly elevated in reactive astrocytes. These data suggest that increased expression of S-100 in Down syndrome, resulting from duplication of the gene on chromosome 21 that encodes the beta subunit of S-100, may be augmented by elevation of interleukin 1. As a corollary, the astrogliosis in Alzheimer disease may be promoted by elevation of interleukin 1.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allore R., O'Hanlon D., Price R., Neilson K., Willard H. F., Cox D. R., Marks A., Dunn R. J. Gene encoding the beta subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implications for Down syndrome. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2964086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes B. E., Kim S. U., Lee V., Sung S. C. Immunohistochemical co-localization of S-100b and the glial fibrillary acidic protein in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1986 Mar;17(3):857–865. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Wilson L. Are cytoplasmic microtubules heteropolymers? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1762–1766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D. Glial fibrillary acidic protein from bovine and rat brain. Degradation in tissues and homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 20;420(1):142–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90353-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy P. E., Rapport M., Graf L. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and Alzheimer-type senile dementia. Neurology. 1980 Jul;30(7 Pt 1):778–782. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.7.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. G., McCulloch J. R., Corley C. L. Presenile dementia in Down's syndrome. Ultrastructural identity with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1974 Feb;24(2):101–106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J., Shih L. C., Lachman L. B. Interleukin 1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):594–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3872478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Woodward J., Young D. G., Krebs J. F., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 injected into mammalian brain stimulates astrogliosis and neovascularization. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2485–2490. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02485.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Harris H. W., Hla T., Maciag T., Donnelly R. J., Jacobsen J. S., Vitek M. P., Gajdusek D. C. Interleukin 1 regulates synthesis of amyloid beta-protein precursor mRNA in human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7606–7610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Takahashi K., Okuyama T. S100a0 (alpha alpha) protein is present in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1494–1496. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Marshak D. R., Anderson C., Lukas T. J., Watterson D. M. Characterization of human brain S100 protein fraction: amino acid sequence of S100 beta. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):700–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Kimura S. S100ao (alpha alpha) protein is mainly located in the heart and striated muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 17;842(2-3):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Budka H. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and S-100 protein in human hepatic encephalopathy: immunocytochemical demonstration of dissociation of two glia-associated proteins. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;70(1):17–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00689509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancardi G. L., Liwnicz B. H., Mandybur T. I. Fibrous astrocytes in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia of Alzheimer's type. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;61(1):76–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00688390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M. The pathological association between Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 1988 May;43(2):99–136. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(88)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Studies on the purification and structure-functional relationships of murine lymphocyte activating factor (Interleukin 1). Mol Immunol. 1980 May;17(5):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossakowski M. J., Weinrauder H. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and S100 protein in abnormal astrocytes in Wilson's disease. Neuropatol Pol. 1986;24(3):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Down's syndrome. The possibility of a pathogenetic segment on chromosome no. 21. Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):99–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00278575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozemuller J. M., Eikelenboom P., Pals S. T., Stam F. C. Microglial cells around amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease express leucocyte adhesion molecules of the LFA-1 family. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 3;101(3):288–292. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumble B., Retallack R., Hilbich C., Simms G., Multhaup G., Martins R., Hockey A., Montgomery P., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. Amyloid A4 protein and its precursor in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 1;320(22):1446–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906013202203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel-Sulkowska E. M., Majocha R. E., Salim M., Zain S. B., Marotta C. A. The postmortem Alzheimer brain is a source of structurally and functionally intact astrocytic messenger RNA. J Neurosci Methods. 1988 Mar;23(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(88)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter R., Yen S. H., Terry R. D. Fibrous Astrocytes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Mar;40(2):95–101. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198103000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A. C., Collins K. L., Auron P. E., Eddy R. L., Nakai H., Byers M. G., Haley L. L., Henry W. M., Shows T. B. Interleukin-1 gene (IL1) assigned to long arm of human chromosome 2. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Spring;5(2):77–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski K. E., Wisniewski H. M., Wen G. Y. Occurrence of neuropathological changes and dementia of Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):278–282. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]