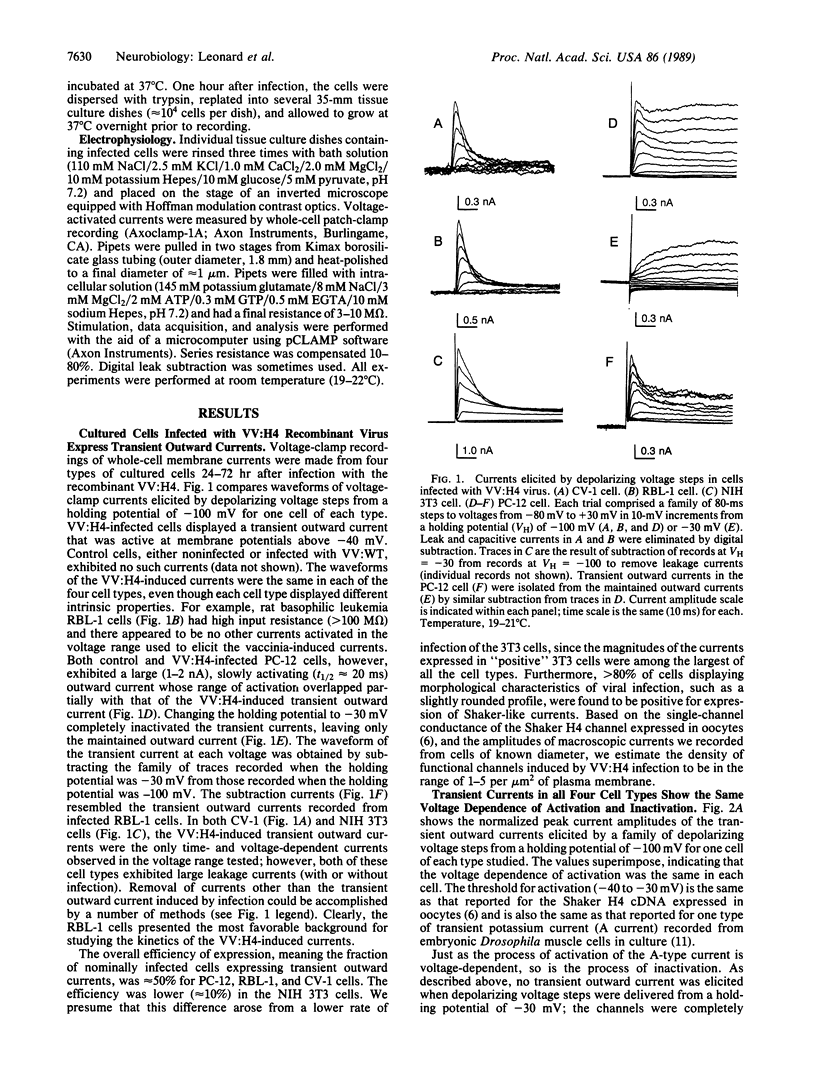
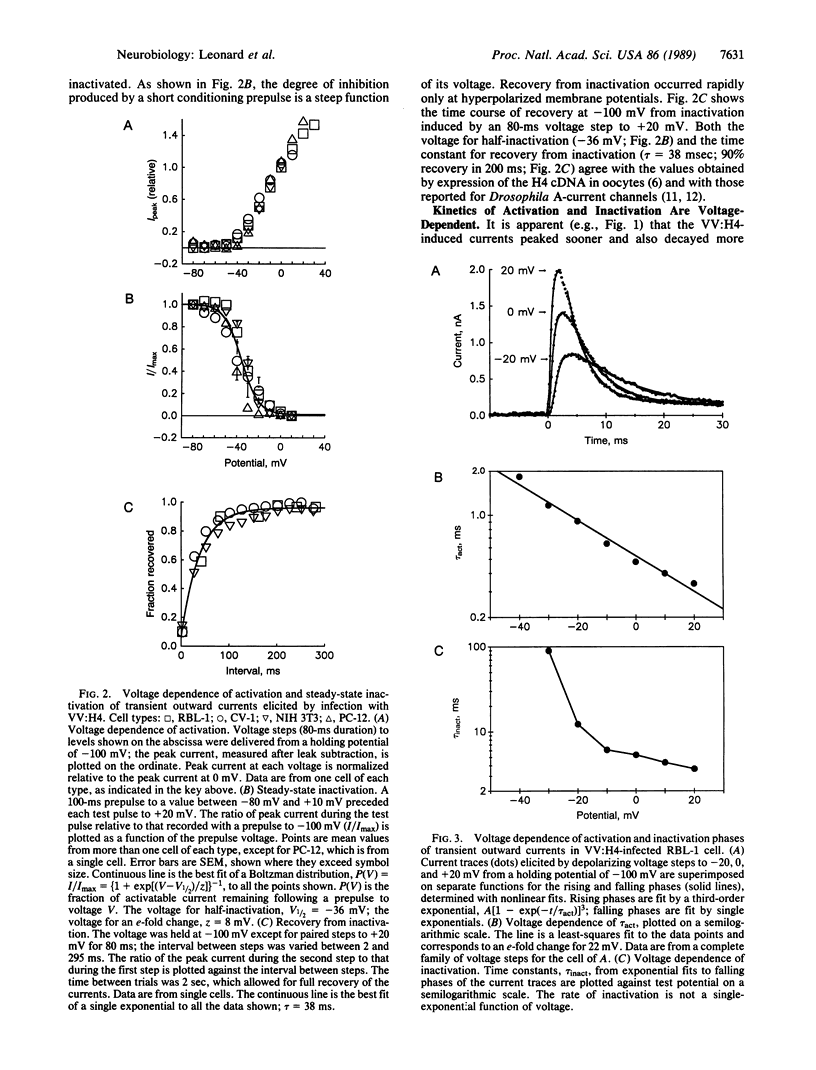
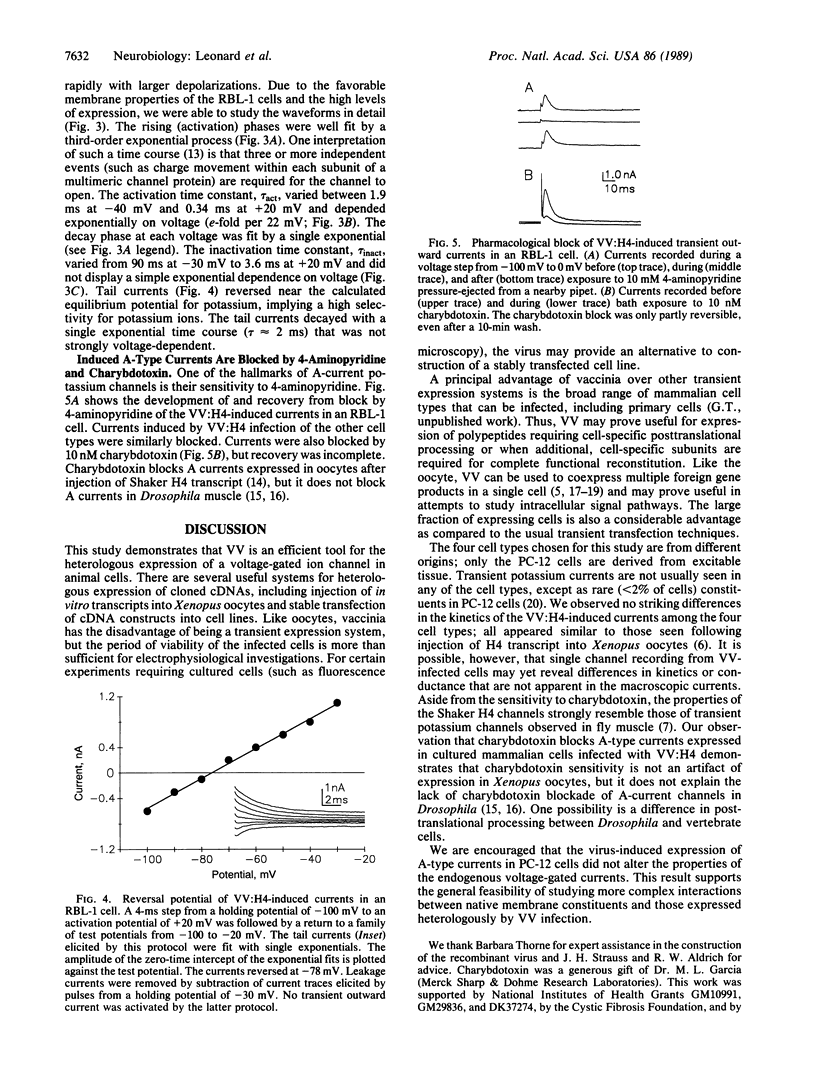
Abstract
A recombinant vaccinia virus containing a Drosophila potassium channel (Shaker H4) cDNA was constructed by homologous recombination between wild-type vaccinia virus DNA and a transfer plasmid. The new virus was used to infect four types of mammalian cells in culture. Electrophysiological recording 24-72 hr after infection revealed the expression of voltage-gated transient potassium channels in all four cell types. The properties of the induced currents were identical to those previously observed following injection of the Shaker H4 transcript into oocytes. Vaccinia promises to be an effective vehicle for the heterologous expression of transmembrane ion channels in a variety of cell types.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coupar B. E., Andrew M. E., Boyle D. B. A general method for the construction of recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing multiple foreign genes. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90593-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins T., Ganetzky B., Wu C. F. A Drosophila mutation that eliminates a calcium-dependent potassium current. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8415–8419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Voltage-dependent K+ currents and underlying single K+ channels in pheochromocytoma cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):73–106. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson L. E., Tanouye M. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Rudy B. A-type potassium channels expressed from Shaker locus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5723–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. Heterologous expression of excitability proteins: route to more specific drugs? Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1057–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.2457947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Reinhart P. H., White M. M. Charybdotoxin block of Shaker K+ channels suggests that different types of K+ channels share common structural features. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):997–1001. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccini A., Perkus M. E., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus as an expression vector. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:545–563. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Franke C. A., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Expression of Sindbis virus structural proteins via recombinant vaccinia virus: synthesis, processing, and incorporation into mature Sindbis virions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):227–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.227-239.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solc C. K., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Single-channel and genetic analyses reveal two distinct A-type potassium channels in Drosophila. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1094–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.2437657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Herbert E., Hruby D. E. Expression and cell type--specific processing of human preproenkephalin with a vaccinia recombinant. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1641–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.3754979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Thorne B. A., Thomas L., Allen R. G., Hruby D. E., Fuller R., Thorner J. Yeast KEX2 endopeptidase correctly cleaves a neuroendocrine prohormone in mammalian cells. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):226–230. doi: 10.1126/science.3291117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Berg P. Hybridization in situ of SV40 plaques: detection of recombinant SV40 virus carrying specific sequences of nonviral DNA. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):183–185. doi: 10.1126/science.191907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Brainard M. S., Aldrich R. W. Single-channel analysis of four distinct classes of potassium channels in Drosophila muscle. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4765–4779. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Gating of single Shaker potassium channels in Drosophila muscle and in Xenopus oocytes injected with Shaker mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7243–7247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


