Abstract
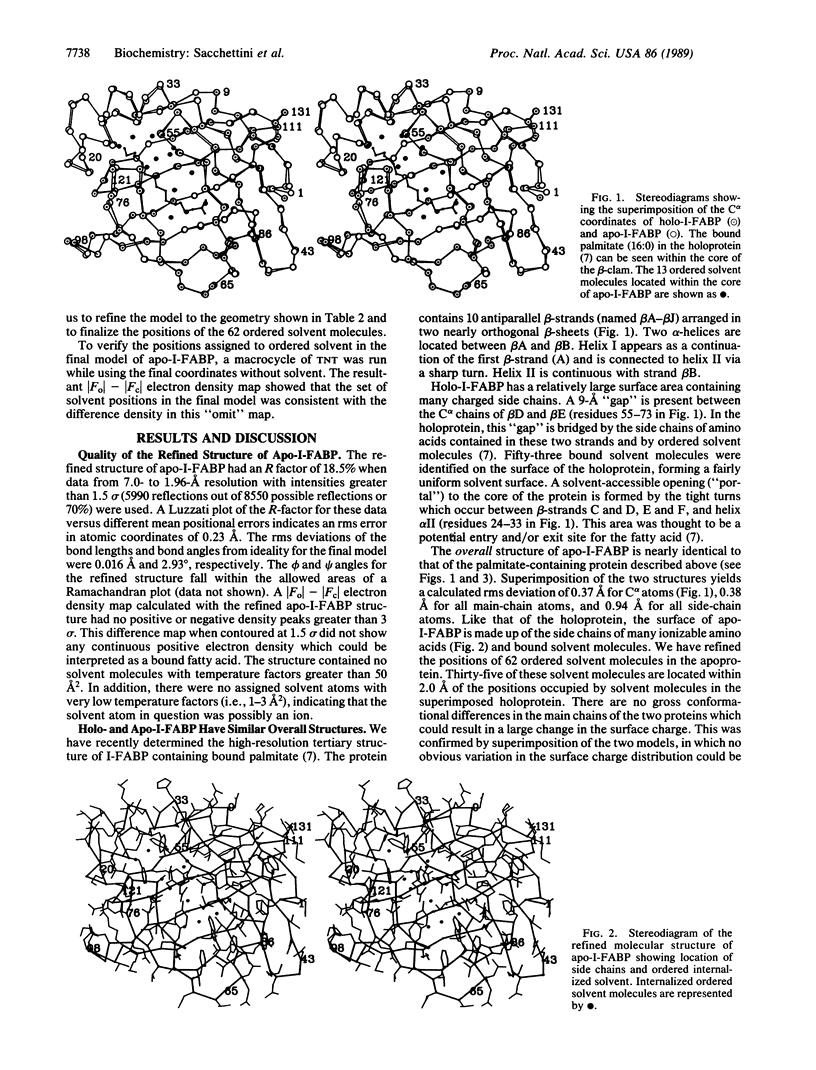
Rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) is a member of a family of cytoplasmic hydrophobic ligand-binding proteins. To gain insights about the contribution of bound fatty acid to I-FABP's conformation and mechanism of ligand binding, we have determined the structure of Escherichia coli-derived rat apo-I-FABP to 1.96-A resolution and compared it to the recently refined structure of I-FABP with bound palmitate. Both apo- and holo-I-FABP are composed primarily of anti-parallel beta-strands which form two nearly orthogonal beta-sheets ("beta-clam"). The overall structures of the apo- and holo-I-FABP are nearly identical, with a root mean square (rms) difference of 0.37 A between C alpha atoms, 0.38 A between all main-chain atoms, and 0.94 A between all side-chain atoms. However, rms differences of greater than 1.3 A were noted for the side chains of Ile-23, Lys-27, Arg-56, Leu-72, Ala-73, and Asp-74. The space occupied by bound ligand in the core of the holoprotein is occupied in the apo-protein by ordered solvent molecules. This results in an increase in the total number of internal ordered solvent molecules from 7 in the holoprotein to 13 in apo-I-FABP. This finding, together with observed differences in the side-chain orientations of two residues (Arg-56 and Lys-27) situated over a potential opening to the cores of the apo- and holoproteins, suggests that solvent molecules play a critical role in ligand binding. Moreover, the data indicate that the beta-clam structure is stable even in the absence of bound ligand.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aqvist J., Sandblom P., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., van Gunsteren W. F., Tapia O. Molecular dynamics simulations of the holo and apo forms of retinol binding protein. Structural and dynamical changes induced by retinol removal. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhmer F. D., Kraft R., Otto A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Kurtz A., Müller T., Rohde K., Etzold G., Lehmann W. Identification of a polypeptide growth inhibitor from bovine mammary gland. Sequence homology to fatty acid- and retinoid-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15137–15143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Rypniewski W. R., Law J. H., Rayment I. The molecular structure of insecticyanin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta L. at 2.6 A resolution. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Schneider M., Epp O., Mayr I., Messerschmidt A., Pflugrath J., Kayser H. Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and preliminary molecular model of the bilin binding protein from the insect Pieris brassicae. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Schneider M., Mayr I., Müller R., Deutzmann R., Suter F., Zuber H., Falk H., Kayser H. Molecular structure of the bilin binding protein (BBP) from Pieris brassicae after refinement at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):499–513. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Bergfors T., Sedzik J., Unge T. The three-dimensional structure of P2 myelin protein. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. B., Sacchettini J. C., Laposata M., McQuillan J. J., Gordon J. I. Expression of rat intestinal fatty acid-binding protein in Escherichia coli. Purification and comparison of ligand binding characteristics with that of Escherichia coli-derived rat liver fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5931–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco H. L., Zanotti G., Spadon P., Bolognesi M., Sawyer L., Eliopoulos E. E. Crystal structure of the trigonal form of bovine beta-lactoglobulin and of its complex with retinol at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90476-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A., Aqvist J., Sundelin J., Eriksson U., Rask L., Peterson P. A. The three-dimensional structure of retinol-binding protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1451–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiz M. Z., Sawyer L., Eliopoulos E. E., North A. C., Findlay J. B., Sivaprasadarao R., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., Kraulis P. J. The structure of beta-lactoglobulin and its similarity to plasma retinol-binding protein. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):383–385. doi: 10.1038/324383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchettini J. C., Gordon J. I., Banaszak L. J. Crystal structure of rat intestinal fatty-acid-binding protein. Refinement and analysis of the Escherichia coli-derived protein with bound palmitate. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchettini J. C., Gordon J. I., Banaszak L. J. The structure of crystalline Escherichia coli-derived rat intestinal fatty acid-binding protein at 2.5-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5815–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salemme F. R. Protein crystallization by free interface diffusion. Methods Enzymol. 1985;114:140–141. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)14013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Heuckeroth R. O., Gordon J. I. The metabolic significance of mammalian fatty-acid-binding proteins: abundant proteins in search of a function. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:337–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz D. A., Wider M. D., Snow J. W., Dass C., Desiderio D. M. The complete amino acid sequence of porcine gastrotropin, an ileal protein which stimulates gastric acid and pepsinogen secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14189–14195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



