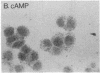
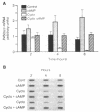
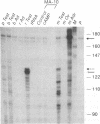
Abstract
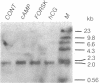
Mouse MA-10 Leydig tumor cells synthesize and secrete progesterone in response to human chorionic gonadotropin, luteinizing hormone, and cAMP but may not synthesize androgens. Maximal doses of human chorionic gonadotropin, ovine luteinizing hormone, forskolin, or 8-bromoadenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate, stimulated cytochrome P450scc mRNA accumulation 1.5- to 3-fold and progesterone secretion 10- to 100-fold in MA-10 cells. P450scc mRNA increased by 2 hr and was maximal by 8 hr; polymerase run-on experiments showed this was due to increased P450scc gene transcription. MA-10 cells are a hormonally homogeneous population, as all cells expressed P450scc mRNA and responded to cAMP equally. cAMP-stimulated accumulation of P450scc mRNA continued in the presence of cycloheximide. Gonadotropins stimulated testicular steroidogenesis by coordinate cAMP-induced increases in P450scc gene transcription, mRNA accumulation, and P450scc activity. We cloned rat P450c17 cDNA and showed it detected no P450c17 mRNA in control or cAMP-stimulated MA-10 cells by RNA transfer blots or RNase protection assays. Similarly, HPLC detected no 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone or testosterone synthesis in MA-10 cells. Thus MA-10 cells, unlike untransformed Leydig cells, do not express detectable amounts of P450c17 mRNA or P450c17 activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anakwe O. O., Payne A. H. Noncoordinate regulation of de novo synthesis of cytochrome P-450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage and cytochrome P-450 17 alpha-hydroxylase/C17-20 lyase in mouse Leydig cell cultures: relation to steroid production. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Sep;1(9):595–603. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-9-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. M., Mendelson C. R. Regulation of the synthesis of cholesterol side-chain cleavage cytochrome P-450 and adrenodoxin in rat Leydig cells in culture. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;438:259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb38291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli M. Characterization of several clonal lines of cultured Leydig tumor cells: gonadotropin receptors and steroidogenic responses. Endocrinology. 1981 Jan;108(1):88–95. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-1-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli M., Euffa J., Segaloff D. L. Epidermal growth factor activates steroid biosynthesis in cultured Leydig tumor cells without affecting the levels of cAMP and potentiates the activation of steroid biosynthesis by choriogonadotropin and cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9196–9203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Voutilainen R., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8962–8966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Picado-Leonard J., Haniu M., Bienkowski M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E., Miller W. L. Cytochrome P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): cloning of human adrenal and testis cDNAs indicates the same gene is expressed in both tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):407–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper C. F., Mellon S. H., Cumin F., Baxter J. D., Ganong W. F. Analysis by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization of renin and its mRNA in kidney, testis, adrenal, and pituitary of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7552–7556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Blasio A. M., Voutilainen R., Jaffe R. B., Miller W. L. Hormonal regulation of messenger ribonucleic acids for P450scc (cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme) and P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase) in cultured human fetal adrenal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jul;65(1):170–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-1-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Neaves W. B., Flores M. N. Comparative observations on intertubular lymphatics and the organization of the interstitial tissue of the mammalian testis. Biol Reprod. 1973 Dec;9(5):500–532. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/9.5.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring N. B., Durica J. M., Lifka J., Hedin L., Ratoosh S. L., Miller W. L., Orly J., Richards J. S. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage P450 messenger ribonucleic acid: evidence for hormonal regulation in rat ovarian follicles and constitutive expression in corpora lutea. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):1942–1950. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golos T. G., Miller W. L., Strauss J. F., 3rd Human chorionic gonadotropin and 8-bromo cyclic adenosine monophosphate promote an acute increase in cytochrome P450scc and adrenodoxin messenger RNAs in cultured human granulosa cells by a cycloheximide-insensitive mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):896–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI113149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivarie R., Morris J. Phenotypic switching in GH3 rat pituitary tumor cells: linked expression of growth hormone and another hormonally responsive protein. DNA. 1983;2(2):113–120. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M. E., John M. C., Boggaram V., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Transcriptional regulation of steroid hydroxylase genes by corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4715–4719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Eberhardt N. L., Mellon S. H., Malich N., Richards R. I., Slater E. P., Barta A., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D., Cathala G. Expression and hormonal regulation of the rat growth hormone gene in transfected mouse L cells. DNA. 1984;3(2):147–155. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. W., Deyman M. E. Simultaneous quantification of natural glucocorticoids and progestins in serum. J Chromatogr. 1987 Oct 9;421(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix A., Ascoli M., Puett D., McKenna T. J. Steroidogenesis in HCG-responsive Leydig cell tumor variants. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jun;10(6):669–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90520-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. I., MacDonald A. A., Laptook A. The activity and biosynthesis of cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme in cultured immature pig testis cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 4;795(3):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Molecular biology of steroid hormone synthesis. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):295–318. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Hall P. F. Microsomal cytochrome P-450 from neonatal pig testis. Purification and properties of A C21 steroid side-chain cleavage system (17 alpha-hydroxylase-C17,20 lyase). J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3871–3876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Miller W. L. Cloning and sequence of the human gene for P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): similarity with the gene for P450c21. DNA. 1987 Oct;6(5):439–448. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Miller W. L. Homologous sequences in steroidogenic enzymes, steroid receptors and a steroid binding protein suggest a consensus steroid-binding sequence. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Nov;2(11):1145–1150. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-11-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Voutilainen R., Kao L. C., Chung B. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin: cloning of three cDNAs and cycloheximide enhancement in JEG-3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3240–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler G. E., Kao L. C., Miller W. L., Strauss J. F., 3rd Effects of 8-bromo-cAMP on expression of endocrine functions by cultured human trophoblast cells. Regulation of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;61(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers R. J., Waterman M. R., Simpson E. R. Levels of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding cholesterol side-chain cleavage cytochrome P-450, 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450, adrenodoxin, and low density lipoprotein receptor in bovine follicles and corpora lutea throughout the ovarian cycle. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Mar;1(3):274–279. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-3-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler S. R., Mellon S. H., Baxter J. D. Growth hormone gene transcription is regulated by thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones in cultured rat pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11627–11632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Coordinate tropic hormone regulation of mRNAs for insulin-like growth factor II and the cholesterol side-chain-cleavage enzyme, P450scc [corrected], in human steroidogenic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Developmental and hormonal regulation of mRNAs for insulin-like growth factor II and steroidogenic enzymes in human fetal adrenals and gonads. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):9–15. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Tapanainen J., Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Hormonal regulation of P450scc (20,22-desmolase) and P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase) in cultured human granulosa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):202–207. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., John M. E., Okamura T., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Bovine adrenocortical cytochrome P-450(17 alpha). Regulation of gene expression by ACTH and elucidation of primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Expression of bovine 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 cDNA in nonsteroidogenic (COS 1) cells. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1258–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.3535074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]