Abstract
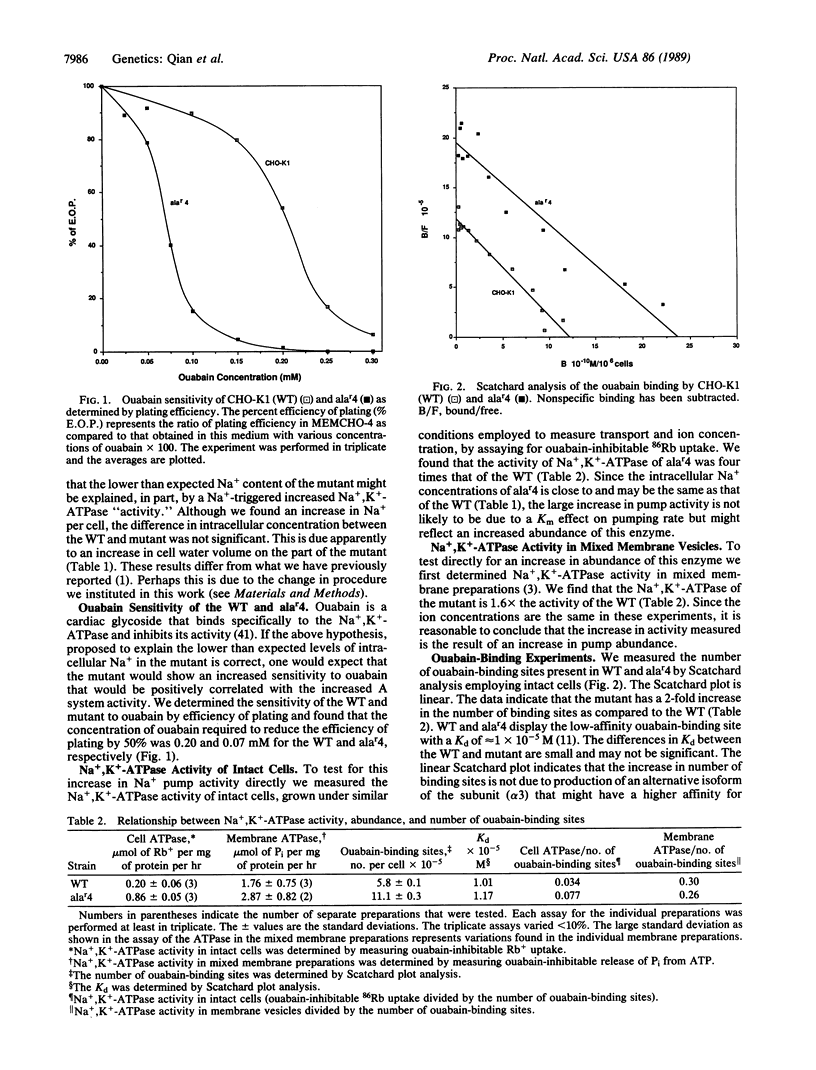
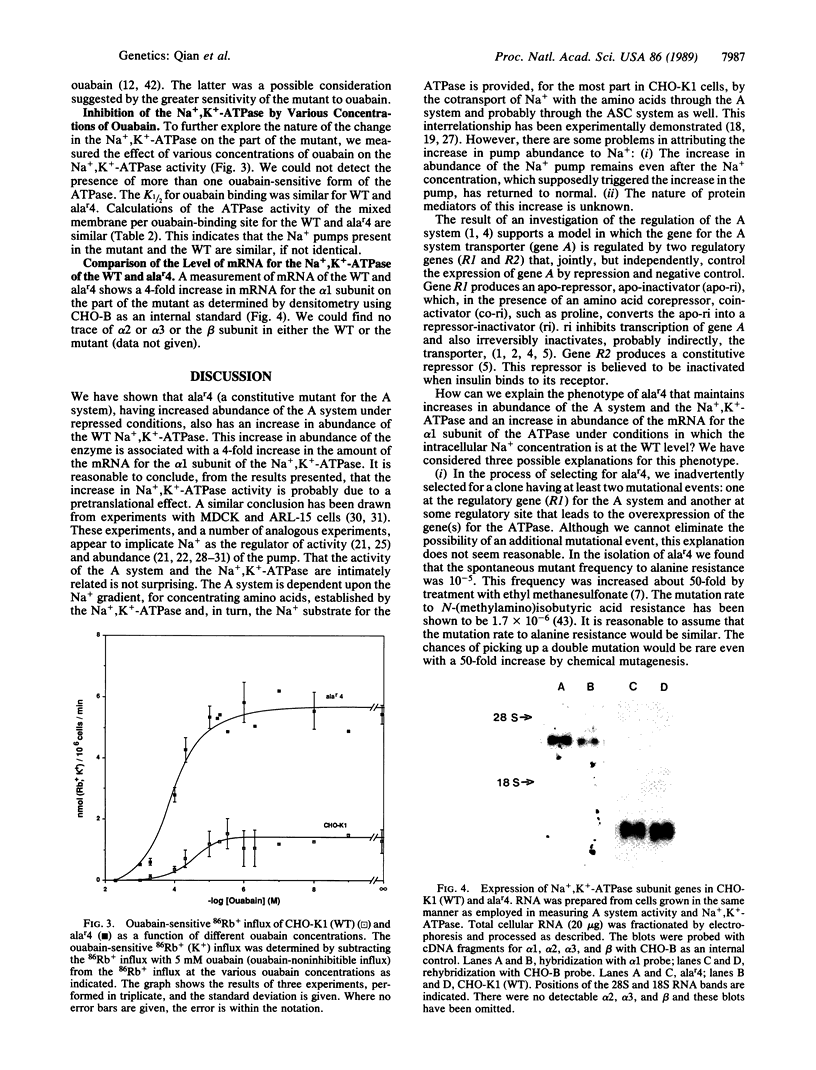
A constitutive mutant, alar4, for the A system of amino acid transport, has increased activity and amount of the A system. This is accompanied by increased sensitivity to ouabain, as measured by efficiency of plating, and increased activity and abundance of the Na+,K+-ATPase that is present in the parental cell line, CHO-K1 (wild type). The latter was shown by increases in (i) ouabain-inhibitable 86Rb uptake in intact cells, (ii) ouabain-inhibitable ATPase activity in mixed membrane vesicles, and (iii) number of ouabain-binding sites and by similar Kd values for ouabain binding and K1/2 for ouabain inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase as compared to the wild type. The increase in abundance of the Na+ pump is associated with a 4-fold increase in abundance of the mRNA for the alpha 1 subunit of the Na+,K+-ATPase. We could not detect mRNA for alpha 2 or alpha 3 or for the beta subunits. The increase in abundance of the A system and Na+,K+-ATPase is associated with a negligible increase in intracellular Na+ concentration. We propose that the increase in the abundance of the A system and the Na+,K+-ATPase is the result of a mutation in regulatory gene R1 that controls the A system and the Na+,K+-ATPase and is not due to a primary effect of a possible initial increase in Na+ concentration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiton J. F., Lamb J. F. Effect of the serum concentration of the growth medium on the sodium pump site density of cultured HeLa cells. Q J Exp Physiol. 1984 Jan;69(1):97–115. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1984.sp002799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman L., Huett M., Lamb J. F., Newton J. P., Polson J. M. Evidence for the genetic control of the sodium pump density in HeLa cells. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(3):771–794. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen J. W., McDonough A. Pretranslational regulation of Na-K-ATPase in cultured canine kidney cells by low K+. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):C179–C189. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.2.C179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collarini E. J., Oxender D. L. Mechanisms of transport of amino acids across membranes. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:75–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R., Garetz S., Stone L., Levenson R. Differential expression of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit mRNAs in rat tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9030–9034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Moffett J. A genetic approach to the study of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells in culture. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(3):199–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01868814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertsey R., Englesberg E. Recessive 2-(methylamino)-isobutyrate (MeAIB)-resistant mutant of Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-K1) with increased transport through ASC system. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Mar;10(2):171–182. doi: 10.1007/BF01534906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. S., Wheeler D. D. Increase in K+ and alpha-AIB active transport in CHO cells after low [K+] treatment. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C124–C132. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. Interaction of cardiac glycosides with (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. A biochemical link to digitalis-induced inotropy. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Sep;36(3):143–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert J. J., Schenk D. B., Skelly H., Leffert H. L. Rat hepatic (Na+, K+)-ATPase: alpha-subunit isolation by immunoaffinity chromatography and structural analysis by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4156–4163. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Pressley T. A., Haber R. S., Gick G. G., Loeb J. N., Edelman I. S. Kinetic analysis of Na,K-activated adenosine triphosphatase induced by low external K+ in a rat liver cell line. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8162–8167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B. G., Lever J. E. Regulation of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in MDCK kidney epithelial cell cultures: role of growth state, cyclic AMP, and chemical inducers of dome formation and differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):51–63. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D., Marsh J. D., Barry W. H., Smith T. W. Effects of growth in low potassium medium or ouabain on membrane Na,K-ATPase, cation transport, and contractility in cultured chick heart cells. Circ Res. 1984 Jul;55(1):39–48. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Pariza M. W., Becker J. E., Potter V. R. A method using 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture. Anal Biochem. 1975 Oct;68(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Lin J. C., Guidotti G. Identification of two molecular forms of (Na+,K+)-ATPase in rat adipocytes. Relation to insulin stimulation of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1177–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendiaz E., Mamounas M., Moffett J., Englesberg E. A defined medium for and the effect of insulin on the growth, amino acid transport, and morphology of Chinese hamster ovary cells, CHO-K1 (CCL 61) and the isolation of insulin "independent" mutants. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;22(2):66–74. doi: 10.1007/BF02623535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza S. A., Wigglesworth N. M., Pohjanpelto P., Rozengurt E. Na entry and Na-K pump activity in murine, hamster, and human cells--effect of monensin, serum, platelet extract, and viral transformation. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Apr;103(1):17–27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Curriden S., Ertsey R., Mendiaz E., Englesberg E. Alanine-resistant mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells, CHO-K1, producing increases in velocity of proline transport through the A, ASC, and P systems. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Mar;9(2):189–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01543177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Englesberg E. Recessive constitutive mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-K1) with an altered A system for amino acid transport and the mechanism of gene regulation of the A system. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):799–808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Englesberg E. Regulation of the A system of amino acid transport in Chinese hamster ovary cells, CHO-K1: the difference in specificity between the apo-repressor inactivator (apo-ri) and the transporter and the characterization of the proposed apo-ri. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Mar;126(3):421–429. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Jones M., Englesberg E. Amino acid transport in membrane vesicles from CHO-K1 and alanine-resistant transport mutants. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2487–2494. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Mendiaz E., Jones M., Englesberg E. Two membrane-bound proteins associated with alanine resistance and increased A-system amino acid transport in mutants of CHO-K1. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jan;14(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01535044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Périer F., Jones M., Englesberg E. Control of A-system amino acid transport by a second regulatory gene R2 in Chinese hamster ovary cells CHO-K1 and the possible connection of this gene with insulin activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8040–8043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Lingrel J. B. Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rat Na,K-ATPase catalytic alpha isoform and beta subunit mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10436–10442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen A. J., 3rd, Geyer R. P., Antoniades H. N. Human platelet-derived growth factor stimulates amino acid transport and protein synthesis by human diploid fibroblasts in plasma-free media. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressley T. A., Haber R. S., Loeb J. N., Edelman I. S., Ismail-Beigi F. Stimulation of Na,K-activated adenosine triphosphatase and active transport by low external K+ in a rat liver cell line. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Apr;87(4):591–606. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.4.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznik V. M., Shapiro R. J., Mendoza S. A. Vasopressin stimulates DNA synthesis and ion transport in quiescent epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C267–C270. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznik V. M., Villela J., Mendoza S. A. Serum stimulates Na entry and the Na-K pump in quiescent cultures of epithelial cells (MDCK). J Cell Physiol. 1983 Nov;117(2):211–214. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosić N. K., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J. The mechanism of insulin stimulation of (Na+,K+)-ATPase transport activity in muscle. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6206–6212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt C. A., McDonough A. A. Developmental and thyroid hormone regulation of two molecular forms of Na+-K+-ATPase in brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10439–10444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Gilmore-Hebert M., Utset M. F., Lai C., Greene A., Benz E. J., Jr Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):284–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation, and difference in affinity for strophanthidin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6060–6067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Weinberger C., Lebo R., Evans R. M. Identification of a novel thyroid hormone receptor expressed in the mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1610–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.3629259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
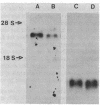
- Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. (Na,K)-ATPase-mediated cation pumping in cultured rat hepatocytes. Rapid modulation by alanine and taurocholate transport and characterization of its relationship to intracellular sodium concentration. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12912–12919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Schneider J. A., Rozengurt E. Ionic responses rapidly elicited by activation of protein kinase C in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2384–2388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolitzky B. A., Fambrough D. M. Regulation of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in cultured chick skeletal muscle. Modulation of expression by the demand for ion transport. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9990–9999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zibirre R., Poronnik P., Koch G. Na+-dependent amino acid transport is a major factor determining the rate of (Na+,K+)-ATPase mediated cation transport in intact HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Oct;129(1):85–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]