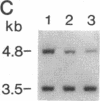
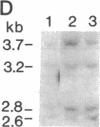
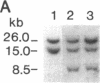
Abstract
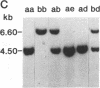
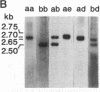
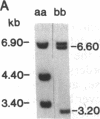
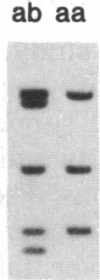
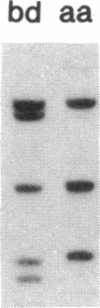
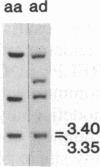
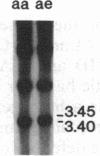
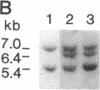
IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency are heritable disorders that can occur within the same family. Both immunodeficiencies are characterized by arrests in B-cell differentiation that vary in the extent of the immunoglobulin isotypes involved. A high frequency of major histocompatibility complex supratypes associated with a null allele of the gene encoding the C4A isotype of complement component C4 has been observed in IgA-deficient individuals. In search of a genetic linkage between the two immunodeficiencies, we examined the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III genes encoding complement components C2, C4A, and C4B and steroid 21-hydroxylase in addition to the HLA serotypes in individuals with either common variable immunodeficiency or IgA deficiency. Twelve of 19 patients with common variable immunodeficiency (63%, P less than 0.001) and 9 of 16 patients with IgA deficiency (56%, P less than 0.01) had rare C2 alleles and/or C4A and 21-hydroxylase A deletions, whereas these gene features were seen in only 5 of 34 healthy individuals (15%) in the control group. Nine of 11 patients with C4A deletion had an HLA haplotype consistent with the MHC supratype HLA-A1, Cw7, B8, C4AQ0, C4B1, BfS, DR3 previously found to be associated with IgA deficiency. The data support the hypothesis that common variable immunodeficiency and IgA deficiency are related disorders, susceptibility to which is determined by a gene(s) within or near the MHC class III gene region on chromosome 6.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Awdeh Z. L., Yunis E. J. Complotypes, extended haplotypes, male segregation distortion, and disease markers. Hum Immunol. 1986 Apr;15(4):366–373. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrus M., Hernádi E., Bajtai G. Prevalence of HLA-A1 and HLA-B8 antigens in selective IgA deficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 May;7(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. R., Campbell R. D., Cross S. J. DNA polymorphism of the C2 locus. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(4):377–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00430921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Palsdottir A., Belt K. T., Porter R. R. Deletion of complement C4 and steroid 21-hydroxylase genes in the HLA class III region. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2547–2552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy J. T., Oldham G., Platts-Mills T. A. Functional assessment of a B cell defect in patients with selective IgA deficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Feb;35(2):296–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland L. G., Bell D. A. The occurrence of systemic lupus erythematosus in two kindreds in association with selective IGA deficiency. J Rheumatol. 1978 Fall;5(3):288–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Cooper M. D. Immature IgA B cells in IgA-deficient patients. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 27;305(9):495–497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108273050905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R., Bockman D. E. Agammaglobulinaemia with B lymphocytes. Specific defect of plasma-cell differentiation. Lancet. 1971 Oct 9;2(7728):791–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92742-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham I., Sargent C. A., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Molecular mapping of the human major histocompatibility complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielder A. H., Walport M. J., Batchelor J. R., Rynes R. I., Black C. M., Dodi I. A., Hughes G. R. Family study of the major histocompatibility complex in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: importance of null alleles of C4A and C4B in determining disease susceptibility. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 5;286(6363):425–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilhus N. E., Aarli J. A., Thorsby E. HLA antigens in epileptic patients with drug-induced immunodeficiency. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1982;4(6):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(82)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. HLA-A, B, C and DR antigens in immunoglobulin A deficiency. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Jan;21(1):75–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Kidd V. J., Volanakis J. E. cDNA cloning and expression of human complement component C2. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2105–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Boss J. M., Spies T., Sorrentino R., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Genetic complexity and expression of human class II histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:45–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay A., Gartland G. L., Abo T., Cooper M. D. Enumeration of human lymphocyte subpopulations by immunofluorescence: a comparative study using automated flow microfluorometry and fluorescence microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Mar 25;58(3):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Carroll M. C., Steinmetz M., Meo T. A previously undetected MHC gene with an unusual periodic structure. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.3353717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Wolff R., Holm T., Culver M., Martin C., Fujimoto E., Hoff M., Kumlin E. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1616–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.3029872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A., Laurell A. B., Lindquist B., Golebiowska H., Axelsson U., Björkander J., Hanson L. A. IgG subclasses in selective IgA deficiency: importance of IgG2-IgA deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1476–1477. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl E. R., Vogler L. B., Okos A. J., Crist W. M., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. B lymphocyte precursors in human bone marrow: an analysis of normal individuals and patients with antibody-deficiency states. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1169–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira S., Webster D., Platts-Mills T. Immature B cells in fetal development and immunodeficiency: studies of IgM, IgG, IgA and IgD production in vitro using Epstein-Barr virus activation. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jul;12(7):540–546. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'Homme J. L., Griscelli C., Seligmann M. Immunoglobulins on the surface of lymphocytes in fifty patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Jan;1(2):241–256. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Cooper M. D., Schlossman S. F., Rosen F. S. Abnormalities of T cell maturation and regulation in human beings with immunodeficiency disorders. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):699–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI110305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Geha R., Wohl M. E., Morimoto C., Rosen F. S., Schlossman S. F. Immunodeficiency associated with loss of T4+ inducer T-cell function. N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 2;304(14):811–816. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198104023041403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Cooper M. D., Wedgwood R. J. The primary immunodeficiencies (1). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 26;311(4):235–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407263110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Campbell R. D. Identification of multiple HTF-island associated genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Human major histocompatibility complex contains genes for the major heat shock protein HSP70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Ng Y. C., Peters D. K. The role of complement and its receptor in the elimination of immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 21;315(8):488–495. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608213150805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M., Good R. A. Role of helper, suppressor and B-cell defects in the pathogenesis of the hypogammaglobulinemias. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 27;299(4):172–178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807272990404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Blanck G., Bresnahan M., Sands J., Strominger J. L. A new cluster of genes within the human major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):214–217. doi: 10.1126/science.2911734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C. DNA in heritable disease. Lancet. 1983 Oct 1;2(8353):787–788. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Bernoco D., Park M. S., Ozturk G., Iwaki Y. Microdroplet testing for HLA-A, -B, -C, and -D antigens. The Phillip Levine Award Lecture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;69(2):103–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLHEIM F. A., BELFRAGE S., COESTER C., LINDHOLM H. PRIMARY "ACQUIRED" HYPOGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA; CLINICAL AND GENETIC ASPECTS OF NINE CASES. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Jul;176:1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton A. N., Cobain T. J., Dawkins R. L. Family studies of IgA deficiency. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):333–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00430799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Edge M. D., Colten H. R. Isolation of a complementary DNA clone for the human complement protein C2 and its use in the identification of a restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):634–638. doi: 10.1172/JCI111461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. Y., Campbell R. D. Definitive RFLPs to distinguish between the human complement C4A/C4B isotypes and the major Rodgers/Chido determinants: application to the study of C4 null alleles. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(6):383–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00396104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]