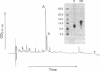
Abstract
Applaggin (Agkistrodon piscivorus piscivorus platelet aggregation inhibitor) is a potent inhibitor of platelet activation. The protein is isolated from the venom of the North American water moccasin snake in three steps, including gel filtration, cation exchange, and reverse-phase HPLC procedures. The purified protein migrates as a 17,700-Da polypeptide by SDS/PAGE under nonreducing conditions and as a 9800-Da peptide in the presence of thiol. The behavior of applaggin on SDS/PAGE would indicate that the protein is a disulfide-linked dimer. Applaggin has been completely sequenced by Edman degradation and consists of 71 amino acids. The sequence is rich in cysteine and contains Arg-Gly-Asp at residues 50-52. Applaggin blocks platelet aggregation induced by ADP, collagen, thrombin, or arachidonic acid with IC50 values ranging from 12 to 128 nM (0.2-2.3 micrograms/ml) depending on the agonist and its concentration. This inhibition is found to correlate with inhibition of thromboxane A2 generation and of dense granule release of serotonin. Inhibition by applaggin of serotonin release induced by ADP, gamma-thrombin, and collagen was monitored in plasma under stirred conditions with [3H]serotonin-loaded platelets, and IC50 values for inhibition are found to range from less than 10 to 145 nM. At saturating concentrations, 125I-labeled applaggin (125I-applaggin) binds to 28,500 sites per unstimulated, washed platelet with a Kd of 1.22 x 10(-7) M. Binding of 125I-applaggin to platelets is inhibited by the synthetic undecapeptide Arg8-Gly-Asp-Val at 200 microM.
Full text
PDF

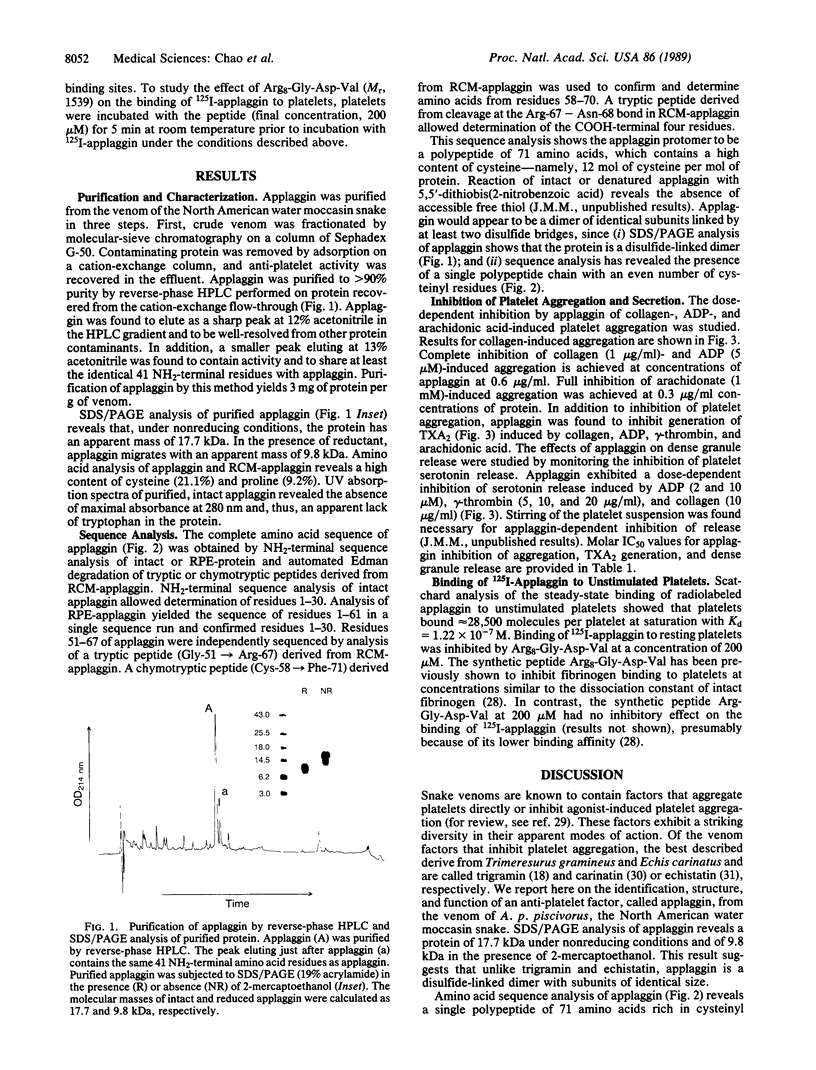
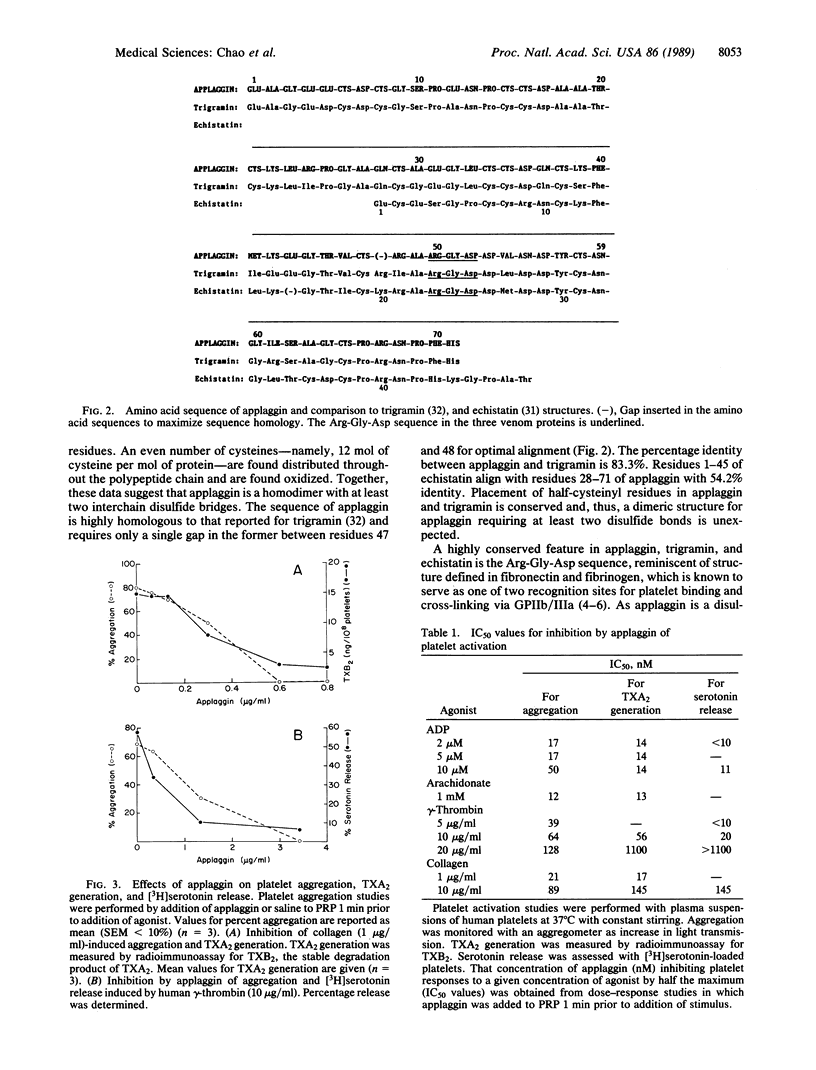

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. S., Hoxie J. A., Leitman S. F., Vilaire G., Cines D. B. Inhibition of fibrinogen binding to stimulated human platelets by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2417–2421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Folts J. D., Scudder L. E., Smith S. R. Antithrombotic effect of a monoclonal antibody to the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor in an experimental animal model. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):783–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Scudder L. E., Berger H. J., Iuliucci J. D. Inhibition of human platelet function in vivo with a monoclonal antibody. With observations on the newly dead as experimental subjects. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Oct 15;109(8):635–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-8-635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldor A., Vlodavsky I., Martinowicz U., Fuks Z., Coller B. S. Platelet interaction with subendothelial extracellular matrix: platelet-fibrinogen interactions are essential for platelet aggregation but not for the matrix-induced release reaction. Blood. 1985 Jun;65(6):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M., Krull L. H., Cavins J. F. The chromatographic determination of cystine and cysteine residues in proteins as s-beta-(4-pyridylethyl)cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3868–3871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan Z. R., Gould R. J., Jacobs J. W., Friedman P. A., Polokoff M. A. Echistatin. A potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from the venom of the viper, Echis carinatus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19827–19832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Loftus J. C., Plow E. F. Cytoadhesins, integrins, and platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson S. R., Pareti F. I., Ruggeri Z. M., Marzec U. M., Kunicki T. J., Montgomery R. R., Zimmerman T. S., Harker L. A. Effects of monoclonal antibodies against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on thrombosis and hemostasis in the baboon. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI113286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Timmons S., Kloczewiak M., Strong D. D., Doolittle R. F. gamma and alpha chains of human fibrinogen possess sites reactive with human platelet receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2068–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A. Evidence that the platelet plasma membrane is impermeable to calcium and magnesium complexes of A23187. A23187-induced secretion is inhibited by MG2+ and Ca2+, and requires aggregation and active cyclooxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10449–10452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Kirby E. P., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin: primary structure and its inhibition of von Willebrand factor binding to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on human platelets. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):661–666. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Lukasiewicz H., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin. A low molecular weight peptide inhibiting fibrinogen interaction with platelet receptors expressed on glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16157–16163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski J. A., Stampfer M. J., Vaillancourt R., Deykin D. Cumulative antiplatelet effect of low-dose enteric coated aspirin. Br J Haematol. 1985 Aug;60(4):635–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Lukas T. J., Hawiger J. Platelet receptor recognition site on human fibrinogen. Synthesis and structure-function relationship of peptides corresponding to the carboxy-terminal segment of the gamma chain. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornecki E., Tuszynski G. P., Niewiarowski S. Inhibition of fibrinogen receptor-mediated platelet aggregation by heterologous anti-human platelet membrane antibody. Significance of an Mr = 66,000 protein derived from glycoprotein IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9349–9356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo V. T., Hodson E., Roberts J. R., Kunicki T. J., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Independent modulation of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen binding to the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex as demonstrated by monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1950–1958. doi: 10.1172/JCI112193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5357–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang C. H., Ma Y. H., Jih H. C., Teng C. M. Characterization of the platelet aggregation inducer and inhibitor from Echis carinatus snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 26;841(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jenkins C. S., Lüscher E. F., Larrieu M. Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):599–600. doi: 10.1038/257599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G. A. Induction of the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by epinephrine and the combination of epinephrine and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10971–10977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Houghten R. A., Russell S. R., Zimmerman T. S. Inhibition of platelet function with synthetic peptides designed to be high-affinity antagonists of fibrinogen binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5708–5712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Hoxie J. A., Cunningham M., Brass L. F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11107–11114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda T., Gold H. K., Fallon J. T., Leinbach R. C., Guerrero J. L., Scudder L. E., Kanke M., Shealy D., Ross M. J., Collen D. Monoclonal antibody against the platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor prevents coronary artery reocclusion after reperfusion with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1284–1291. doi: 10.1172/JCI113446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]