Abstract
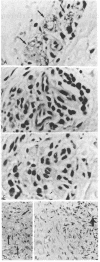
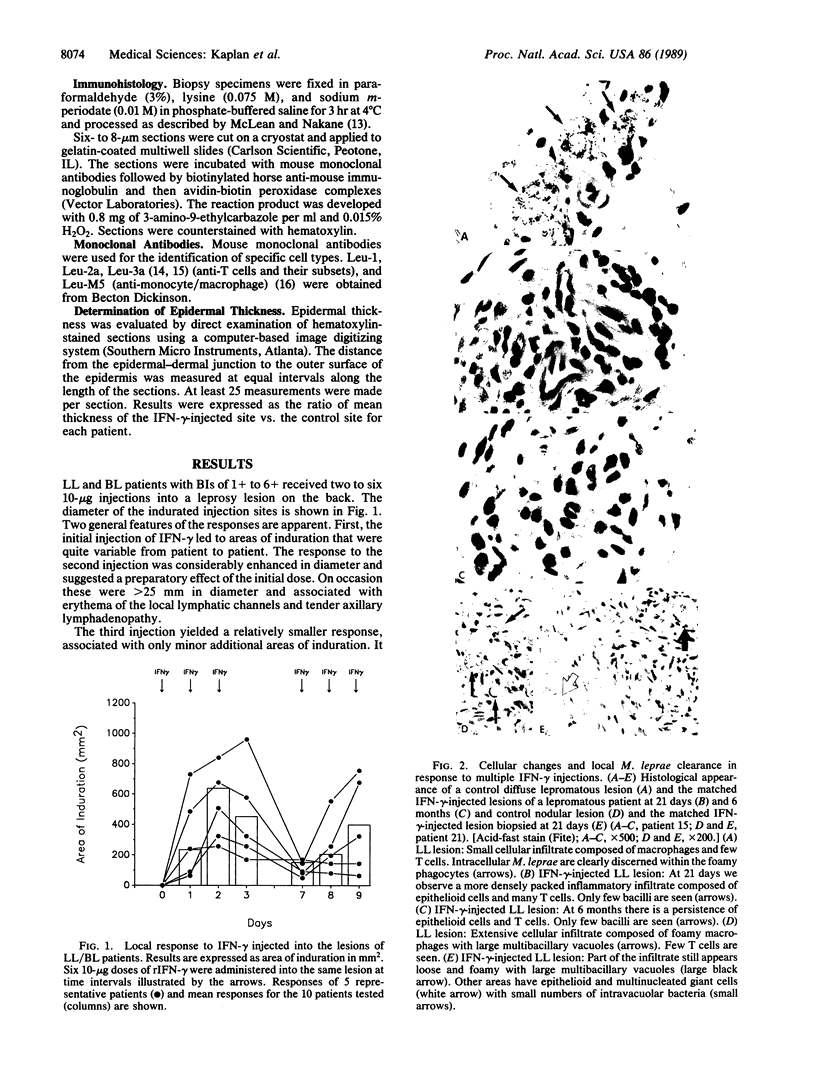
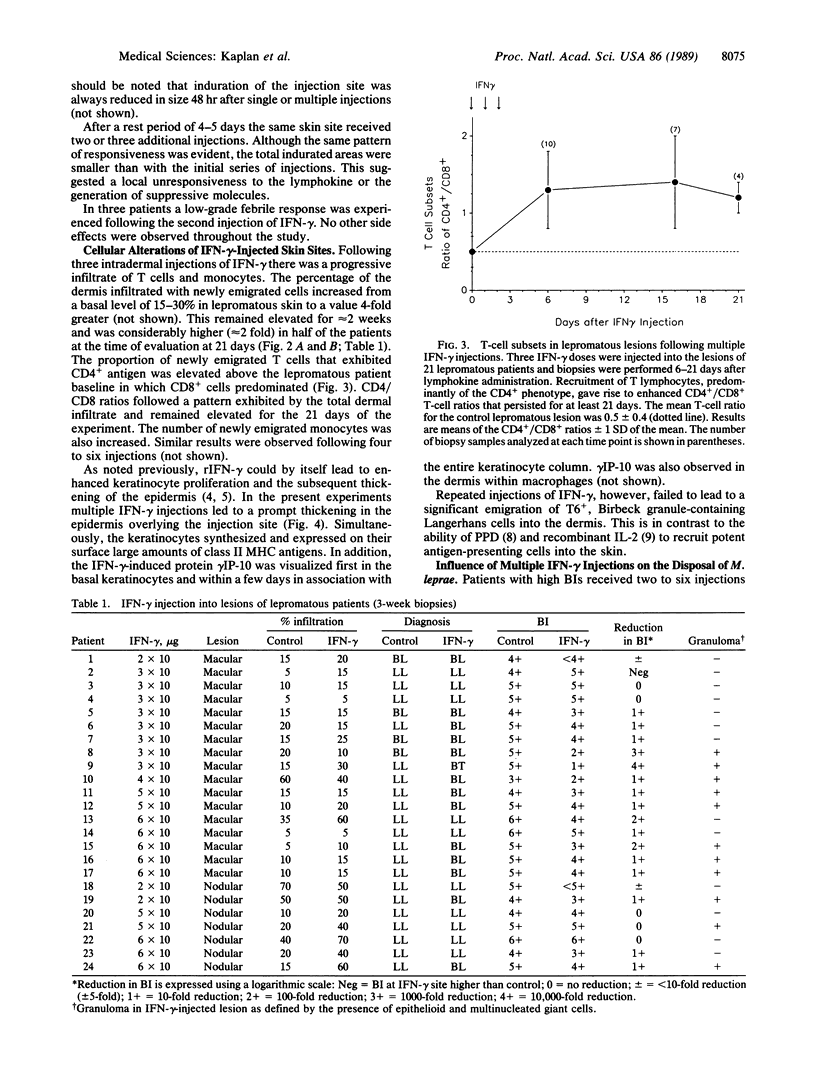
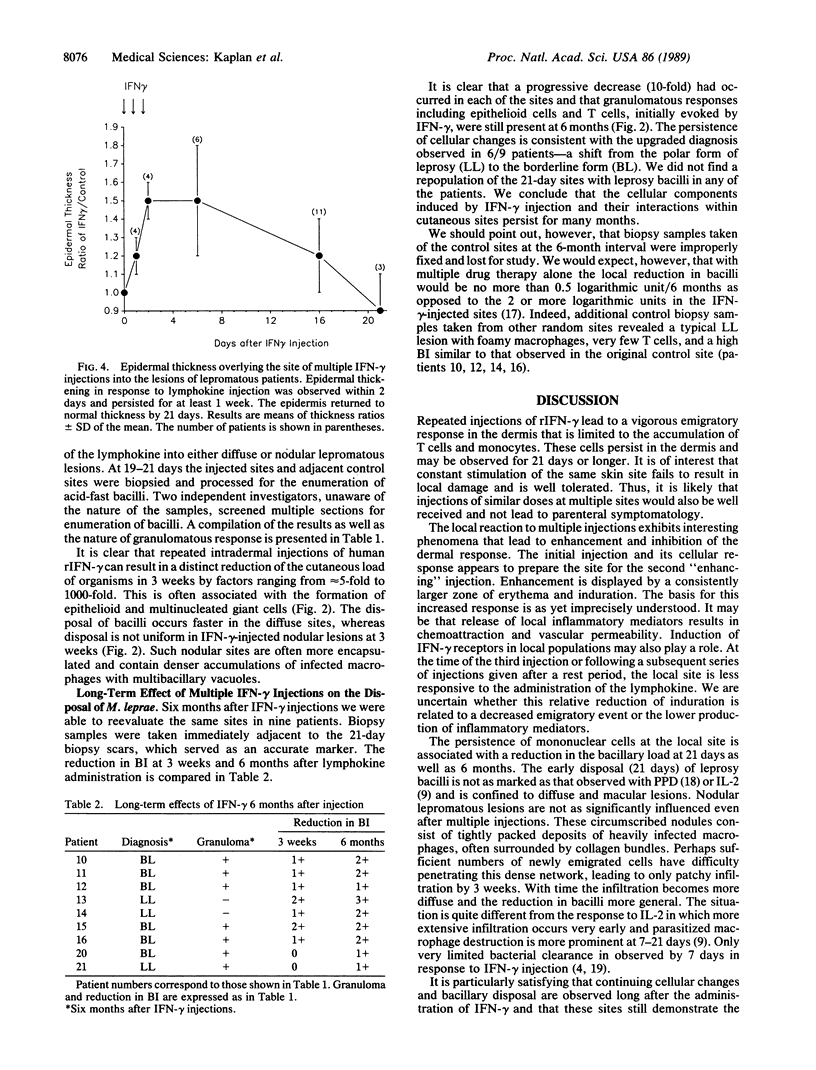
The effect of multiple intradermal injections (four to six) of 10 micrograms of interferon gamma on the number of Mycobacterium leprae in the skin of patients with polar lepromatous leprosy and borderline lepromatous leprosy was evaluated. To achieve a maximum zone of induration and cell emigration a preparatory dose of the lymphokine was required. A second group of three injections, given 3-4 days after the initial series, resulted in lesser degrees of induration and was more in keeping with a partial local hyporesponsive state. A marked emigration of T cells and monocytes into the dermis resulted from injections of interferon gamma and persisted for greater than 21 days. A preponderance of CD4+ cells in the infiltrate was seen within a few days and CD4/CD8 ratios remained elevated for greater than 5 weeks. The bacillary load of injected sites evaluated 21 days after lymphokine administration was reduced in 14/17 patients by factors ranging from 5- to 1000-fold. This occurred predominantly within diffuse lesions and occurred rarely in nodular sites. Biopsy samples of injected sites taken 6 months later demonstrated progressive 10-fold reductions in bacilli and the continued presence of a granulomatous response.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engleman E. G., Warnke R., Fox R. I., Dilley J., Benike C. J., Levy R. Studies of a human T lymphocyte antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1791–1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Wall D. W., Platsoucas C. D., Siegal F. P., Fikrig S. M., Testa C. M., Good R. A. Thymus-dependent membrane antigens in man: inhibition of cell-mediated lympholysis by monoclonal antibodies to TH2 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):544–548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T. Immunological aspects of leprosy--present status. Prog Allergy. 1978;25:211–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Levis W. R., Cohn Z. A. Defective production of monocyte-activating cytokines in lepromatous leprosy. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):666–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job C. K., Chacko C. J. A simplified 6 group classification of leprosy. Lepr India. 1982 Jan;54(1):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Kiessling R., Teklemariam S., Hancock G., Sheftel G., Job C. K., Converse P., Ottenhoff T. H., Becx-Bleumink M., Dietz M. The reconstitution of cell-mediated immunity in the cutaneous lesions of lepromatous leprosy by recombinant interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):893–907. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Laal S., Sheftel G., Nusrat A., Nath I., Mathur N. K., Mishra R. S., Cohn Z. A. The nature and kinetics of a delayed immune response to purified protein derivative of tuberculin in the skin of lepromatous leprosy patients. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Luster A. D., Hancock G., Cohn Z. A. The expression of a gamma interferon-induced protein (IP-10) in delayed immune responses in human skin. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1098–1108. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Nusrat A., Sarno E. N., Job C. K., McElrath J., Porto J. A., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Cellular responses to the intradermal injection of recombinant human gamma-interferon in lepromatous leprosy patients. Am J Pathol. 1987 Aug;128(2):345–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Nath I., Cohn Z. A. Distribution and turnover of Langerhans cells during delayed immune responses in human skin. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):763–776. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Sheftel G., Job C. K., Mathur N. K., Nath I., Cohn Z. A. Efficacy of a cell-mediated reaction to the purified protein derivative of tuberculin in the disposal of Mycobacterium leprae from human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5210–5214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Van Voorhis W. C., Sarno E. N., Nogueira N., Cohn Z. A. The cutaneous infiltrates of leprosy. A transmission electron microscopy study. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1145–1159. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., DePamphilis J., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S. Circulating interferon-gamma in AIDS patients treated with interleukin-2. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1538–1539. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma, the activated macrophage, and host defense against microbial challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):595–608. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Kaplan G., Levy E., Sarno E. N., Kushner P., Granelli-Piperno A., Vieira L., Colomer Gould V., Levis W., Steinman R. Defective gamma interferon production in leprosy. Reversal with antigen and interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2165–2170. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S. A logarithmic index of bacilli in biopsies. 2. Evaluation. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1967 Apr-Jun;35(2):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Hilson G. R. A logarithmic index of bacilli in biopsies. I. Method. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1967 Apr-Jun;35(2):184–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel N. M., Grange J. M., Samuel S., Lucas S., Owilli O. M., Adalla S., Leigh I. M., Navarrette C. A study of the effects of intradermal administration of recombinant gamma interferon in lepromatous leprosy patients. Lepr Rev. 1987 Dec;58(4):389–400. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19870041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Stein H., Wang C. Y. The monoclonal antibodies alpha S-HCL 1 (alpha Leu-14) and alpha S-HCL 3 (alpha Leu-M5) allow the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):974–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]