Abstract
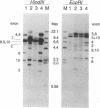
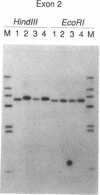
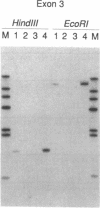
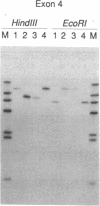
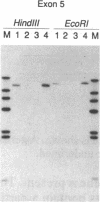
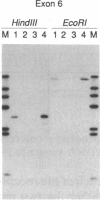
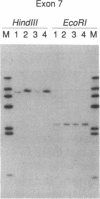
Laron-type dwarfism is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that is characterized by high levels of growth hormone and low levels of insulin-like growth factor I in the circulation. Several lines of evidence suggest that this disease is caused by a defect in the growth hormone receptor. In order to analyze the receptor gene in patients with Laron-type dwarfism and with other growth disorders, we have first determined the gene structure in normal individuals. There are nine exons that encode the receptor and several additional exons in the 5' untranslated region. The coding exons span at least 87 kilobase pairs of chromosome 5. Characterization of the growth hormone receptor gene from nine patients with Laron-type dwarfism shows that two individuals have a deletion of a large portion of the extracellular, hormone binding domain of the receptor gene. Interestingly, this deletion includes nonconsecutive exons, suggesting that an unusual rearrangement may have occurred. Thus, we provide direct evidence that Laron-type dwarfism can result from a defect in the structural gene for the growth hormone receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnard R., Waters M. J. Serum and liver cytosolic growth-hormone-binding proteins are antigenically identical with liver membrane 'receptor' types 1 and 2. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):885–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2370885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann G., Shaw M. A., Winter R. J. Absence of the plasma growth hormone-binding protein in Laron-type dwarfism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Oct;65(4):814–816. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-4-814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann G., Stolar M. W., Amburn K., Barsano C. P., DeVries B. C. A specific growth hormone-binding protein in human plasma: initial characterization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jan;62(1):134–141. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-1-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin J. M., Jolicoeur C., Okamura H., Gagnon J., Edery M., Shirota M., Banville D., Dusanter-Fourt I., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Cloning and expression of the rat prolactin receptor, a member of the growth hormone/prolactin receptor gene family. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Trivedi B. Absence of serum growth hormone binding protein in patients with growth hormone receptor deficiency (Laron dwarfism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4636–4640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. A., Linzer D. I. Expression of multiple forms of the prolactin receptor in mouse liver. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Apr;3(4):674–680. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-4-674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery M., Jolicoeur C., Levi-Meyrueis C., Dusanter-Fourt I., Pétridou B., Boutin J. M., Lesueur L., Kelly P. A., Djiane J. Identification and sequence analysis of a second form of prolactin receptor by molecular cloning of complementary DNA from rabbit mammary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshet R., Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Arnon R., Dintzman M. Defect of human growth hormone receptors in the liver of two patients with Laron-type dwarfism. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Jan;20(1):8–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffner M. E., Golde D. W., Lippe B. M., Kaplan S. A., Bersch N., Li C. H. Tissues of the Laron dwarf are sensitive to insulin-like growth factor I but not to growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 May;64(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-5-1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Tuddenham E. G., Shuman M. A., Goralka T. M., Chen E. Y., Lawn R. M. Detection and sequence of mutations in the factor VIII gene of haemophiliacs. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):427–430. doi: 10.1038/315427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath-Monnig E., Wohltmann H. J., Mills-Dunlap B., Daughaday W. H. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) responsiveness of fibroblasts of children with short stature: identification of a patient with IGF-I resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Mar;64(3):501–507. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Ymer S., Roupas P., Stevenson J. Growth hormone-binding proteins in high-speed cytosols of multiple tissues of the rabbit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 11;881(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Ymer S., Stevenson J. Identification and characterization of specific binding proteins for growth hormone in normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1817–1823. doi: 10.1172/JCI112507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. P., Friesen H. G. The nature and regulation of the receptors for pituitary growth hormone. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:469–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Edén S., Jansson J. O. Mode of action of pituitary growth hormone on target cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:483–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boehm C. D. Molecular basis and prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Kelijman M., Pertzelan A., Keret R., Shoffner J. M., Parks J. S. Human growth hormone gene deletion without antibody formation or growth arrest during treatment--a new disease entity? Isr J Med Sci. 1985 Dec;21(12):999–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Karp M. Pituitary dwarfism with high serum levels of growth hormone. Isr J Med Sci. 1968 Jul-Aug;4(4):883–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Mannheimer S. Genetic pituitary dwarfism with high serum concentation of growth hormone--a new inborn error of metabolism? Isr J Med Sci. 1966 Mar-Apr;2(2):152–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. A., 3rd, Hjelle B. L., Seeburg P. H., Zachmann M. Molecular basis for familial isolated growth hormone deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6372–6375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I., Kelly P. A., Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Studies of insulin, growth hormone and prolactin binding: tissue distribution, species variation and characterization. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):521–531. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P., Roth J. Hormonal regulation of human growth. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):941–943. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Kuniyoshi J., Talamantes F. Mouse serum growth hormone (GH) binding protein has GH receptor extracellular and substituted transmembrane domains. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;3(6):984–990. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-6-984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Linzer D. I., Talamantes F. Detection of two growth hormone receptor mRNAs and primary translation products in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9576–9579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. A., Hammonds R. G., Henzel W. J., Rodriguez H., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Rabbit liver growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein. Purification, characterization, and sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7862–7867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Capon D. J., Simonsen C. C., Eaton D. L., Gitschier J., Keyt B., Seeburg P. H., Smith D. H., Hollingshead P., Wion K. L. Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):330–337. doi: 10.1038/312330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S. I., Herington A. C. Evidence for the specific binding of growth hormone to a receptor-like protein in rabbit serum. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Jul;41(2-3):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]