Abstract
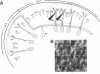
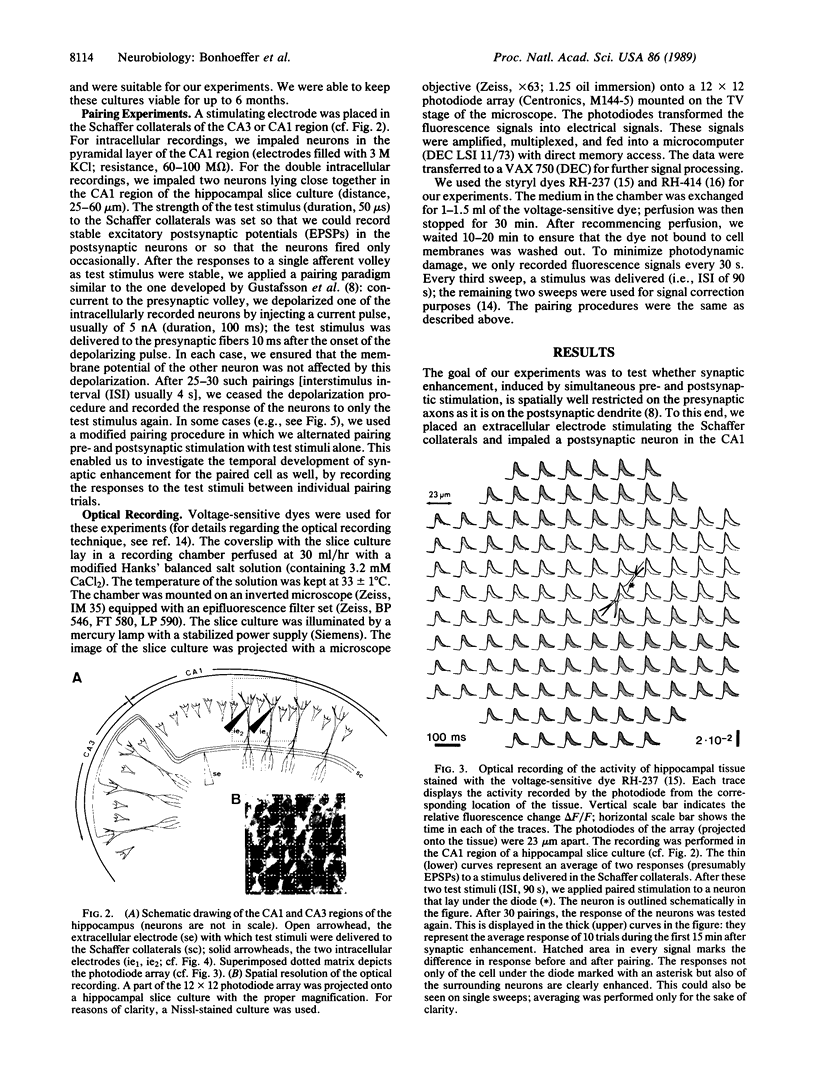
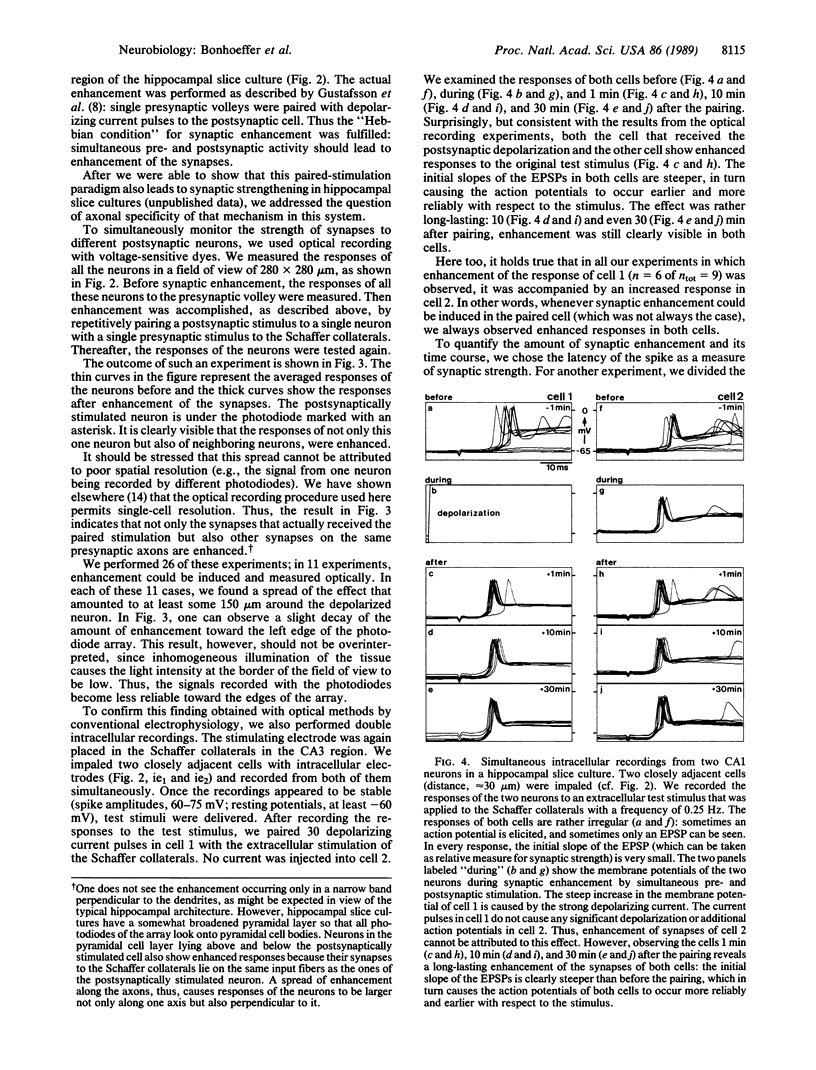
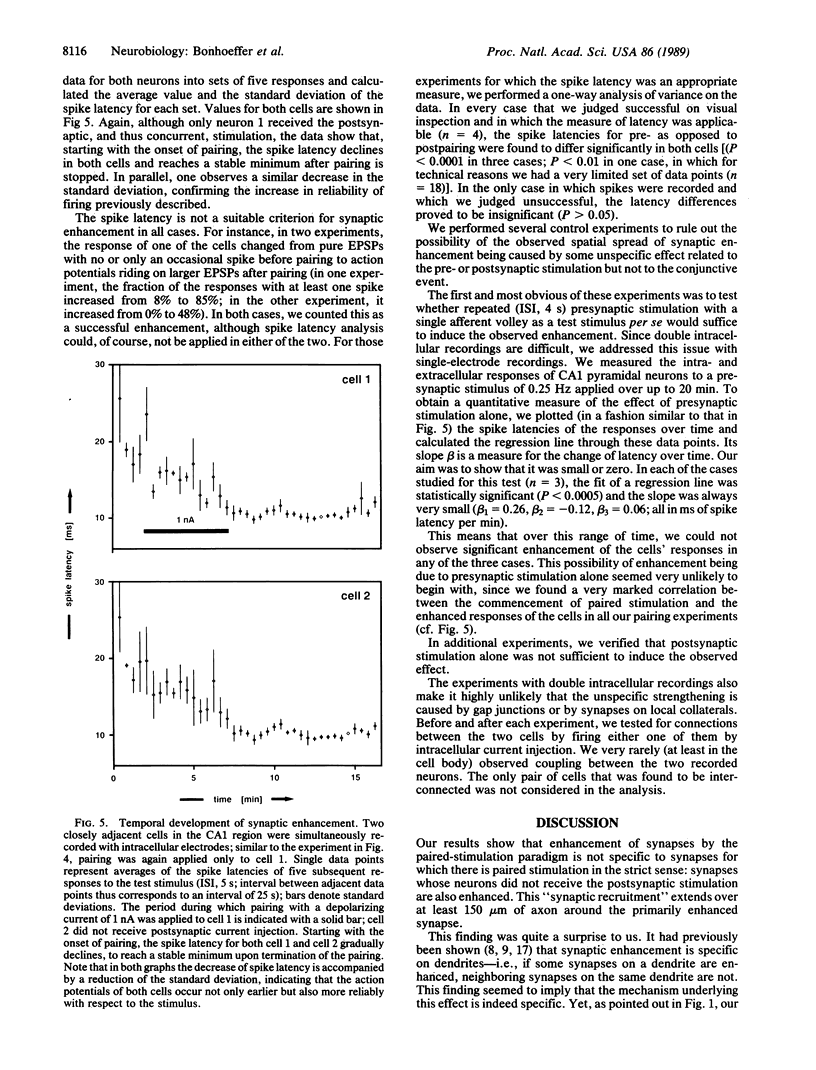
A central theme in neurobiology is the search for the mechanisms underlying learning and memory. Since the seminal work, first of Cajal and later of Hebb, the synapse is thought to be the basic "storing unit." Hebb proposed that information is stored by correlation: synapses between neurons, which are often coactive, are enhanced. Several recent findings suggest that such a mechanism is indeed operative in the central nervous system. Pairing of activity on presynaptic fibers with strong postsynaptic depolarization results in synaptic enhancement. While there is substantial evidence in favor of a postsynaptic locus for detection of the synchronous pre- and postsynaptic event and subsequent initiation of synaptic enhancement, the locus of this enhancement and its ensuing persistence is still disputed: both pre- and postsynaptic contributions have been suggested. In all previous studies, the enhancement was presumed to be specific to the synapses where synchronous pre- and postsynaptic stimulation was applied. We report here that two recording techniques--optical recording, using voltage-sensitive dyes, and double intracellular recordings--reveal that synaptic enhancement is not restricted to the stimulated cell. Although we paired single afferent volleys with intracellular stimulation confined to one postsynaptic cell, we found that strengthening also occurred on synapses between the stimulated presynaptic fibers and neighboring cells. This suggests that synaptic enhancement by the "paired-stimulation paradigm" is not local on the presynaptic axons and that, in fact, the synapses of many neighboring postsynaptic cells are enhanced.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Wigström H. Specific long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):736–737. doi: 10.1038/266736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Oliver M., Creager R., Wieraszko A., Lynch G. Increase in glutamate receptors following repetitive electrical stimulation in hippocampal slices. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 28;27(4):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindman L. J., Murphy K. P., Pockett S. Postsynaptic control of the induction of long-term changes in efficacy of transmission at neocortical synapses in slices of rat brain. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Sep;60(3):1053–1065. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.3.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhoeffer T., Staiger V. Optical recording with single cell resolution from monolayered slice cultures of rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Oct 17;92(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90599-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline H. T., Debski E. A., Constantine-Paton M. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist desegregates eye-specific stripes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4342–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. N., Lester R. A., Reymann K. G., Collingridge G. L. Temporally distinct pre- and post-synaptic mechanisms maintain long-term potentiation. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):500–503. doi: 10.1038/338500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R. N-methyl aspartate activates voltage-dependent calcium conductance in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:385–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Errington M. L., Bliss T. V. Long-term potentiation of the perforant path in vivo is associated with increased glutamate release. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):496–498. doi: 10.1038/297496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. M., Goddard G. V., Riives M. Inhibitory modulation of long-term potentiation: evidence for a postsynaptic locus of control. Brain Res. 1982 May 27;240(2):259–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fifková E., Van Harreveld A. Long-lasting morphological changes in dendritic spines of dentate granular cells following stimulation of the entorhinal area. J Neurocytol. 1977 Apr;6(2):211–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01261506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Anglister L., Freeman J. A., Hildesheim R., Manker A. Real-time optical imaging of naturally evoked electrical activity in intact frog brain. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):848–850. doi: 10.1038/308848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Hildesheim R., Farber I. C., Anglister L. Improved fluorescent probes for the measurement of rapid changes in membrane potential. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84520-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H., Abraham W. C., Huang Y. Y. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus using depolarizing current pulses as the conditioning stimulus to single volley synaptic potentials. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):774–780. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00774.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Development of the hippocampus in vitro: cell types, synapses and receptors. Neuroscience. 1984 Apr;11(4):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Organotypic monolayer cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Dec;4(4):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Slice cultures of cerebellar, hippocampal and hypothalamic tissue. Experientia. 1984 Mar 15;40(3):235–243. doi: 10.1007/BF01947561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer J. A., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A persistent postsynaptic modification mediates long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):911–917. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso S. R., Ganong A. H., Brown T. H. Hebbian synapses in hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5326–5330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen E. I. Experience alters the spatial tuning of auditory units in the optic tectum during a sensitive period in the barn owl. J Neurosci. 1985 Nov;5(11):3094–3109. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-03094.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. B., Steward O. Synapses as associative memory elements in the hippocampal formation. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 19;175(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G. S., Gribkoff V. K., Deadwyler S. A. Long term potentiation is accompanied by a reduction in dendritic responsiveness to glutamic acid. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):151–153. doi: 10.1038/263151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauschecker J. P., Singer W. The effects of early visual experience on the cat's visual cortex and their possible explanation by Hebb synapses. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:215–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter H. O., Stryker M. P. Neural plasticity without postsynaptic action potentials: less-active inputs become dominant when kitten visual cortical cells are pharmacologically inhibited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry B. R., Murali Mohan P., Goh J. W. A transient increase in the activity of CA3 neurons induces a long-lasting reduction in the excitability of Schaffer collateral terminals in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 7;53(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrede K. K., Malthe-Sørenssen D. Increased resting and evoked release of transmitter following repetitive electrical tetanization in hippocampus: a biochemical correlate to long-lasting synaptic potentiation. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 16;208(2):436–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90573-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stent G. S. A physiological mechanism for Hebb's postulate of learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):997–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Strengthening the synapses. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):460–461. doi: 10.1038/338460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryker M. P., Harris W. A. Binocular impulse blockade prevents the formation of ocular dominance columns in cat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2117–2133. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02117.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]