Abstract
Phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated production of inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol is stimulated by binding of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) to cell-surface receptors. Antibodies recognizing native PDGF receptors through peptide-domain epitopes coprecipitated 4-fold more PLC activity with receptors from PDGF-stimulated than from unstimulated BALB/c 3T3 cells, despite equivalent PDGF receptor recovery. Activity coprecipitated from unstimulated cells was comparable to nonspecific activity recovered with preimmune sera or in the presence of competing peptide immunogen. PLC activity coprecipitating with PDGF receptors represented 60% of anti-phosphotyrosine antibody-recovered activity from PDGF-stimulated cells. Coprecipitation was rapidly induced in cells treated with PDGF at 4 degrees C, reversibly lost with acid dissociation of PDGF from receptors, and recovered with PDGF readdition. PDGF concentrations effecting coprecipitation correlated with stimulation of intact-cell inositol phosphate production. Monoclonal antibodies to PLC gamma (145 kDa) coprecipitated from PDGF-stimulated cell lysates (but not from unstimulated cell lysates) tyrosine kinase activity that phosphorylated PDGF receptor and PLC gamma. Stable physical association of PDGF receptors with PLC may participate in coupling ligand binding to increased PLC activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Brown K. D. Inositol trisphosphate formation and calcium mobilization in Swiss 3T3 cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2220195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishayee S., Majumdar S., Scher C. D., Khan S. Characterization of a novel anti-peptide antibody that recognizes a specific conformation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3696–3702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishayee S., Ross A. H., Womer R., Scher C. D. Purified human platelet-derived growth factor receptor has ligand-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6756–6760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Methods for studying the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:69–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. O., Milfay D. F., Escobedo J., Williams L. T. Biosynthetic and glycosylation studies of cell surface platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9778–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Barr P. J., Williams L. T. Role of tyrosine kinase and membrane-spanning domains in signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5126–5131. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. A PDGF receptor domain essential for mitogenesis but not for many other responses to PDGF. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):85–87. doi: 10.1038/335085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackelton A. R., Jr, Tremble P. M., Williams L. T. Evidence for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor in vivo. Immunopurification using a monoclonal antibody to phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7909–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H., Lutz F., Sasaki T. Pathway of phospholipase C activation initiated with platelet-derived growth factor is different from that initiated with vasopressin and bombesin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12970–12976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshijima M., Ueda T., Hamamori Y., Ohmori T., Takai Y. Different sensitivity to phorbol esters and pertussis toxin of bombesin- and platelet-derived growth factor-induced, phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in NIH/3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80712-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Ives H. E. Guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotrisphosphate) potentiates both thrombin- and platelet-derived growth factor-induced inositol phosphate release in permeabilized vascular smooth muscle cells. Signaling mechanisms distinguished by sensitivity to pertussis toxin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4391–4397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn R. D., Posner M. R., Rayter S. I., Foulkes J. G., Frackelton A. R., Jr Cell lines and peripheral blood leukocytes derived from individuals with chronic myelogenous leukemia display virtually identical proteins phosphorylated on tyrosine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4408–4412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ives H. E., Daniel T. O. Interrelationship between growth factor-induced pH changes and intracellular Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Garrison J. C. Epidermal growth factor and angiotensin II stimulate formation of inositol 1,4,5- and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in hepatocytes. Differential inhibition by pertussis toxin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17285–17293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M. T., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Ligand activation causes a phosphorylation-dependent change in platelet-derived growth factor receptor conformation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12805–12808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letterio J. J., Coughlin S. R., Williams L. T. Pertussis toxin-sensitive pathway in the stimulation of c-myc expression and DNA synthesis by bombesin. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1117–1119. doi: 10.1126/science.3465038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Heidaran M., Miki T., Popescu N., La Rochelle W., Kraus M., Pierce J., Aaronson S. Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):800–804. doi: 10.1126/science.2536956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuoka K., Fukami K., Nakanishi O., Kawai S., Takenawa T. Mitogenesis in response to PDGF and bombesin abolished by microinjection of antibody to PIP2. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):640–643. doi: 10.1126/science.2829356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
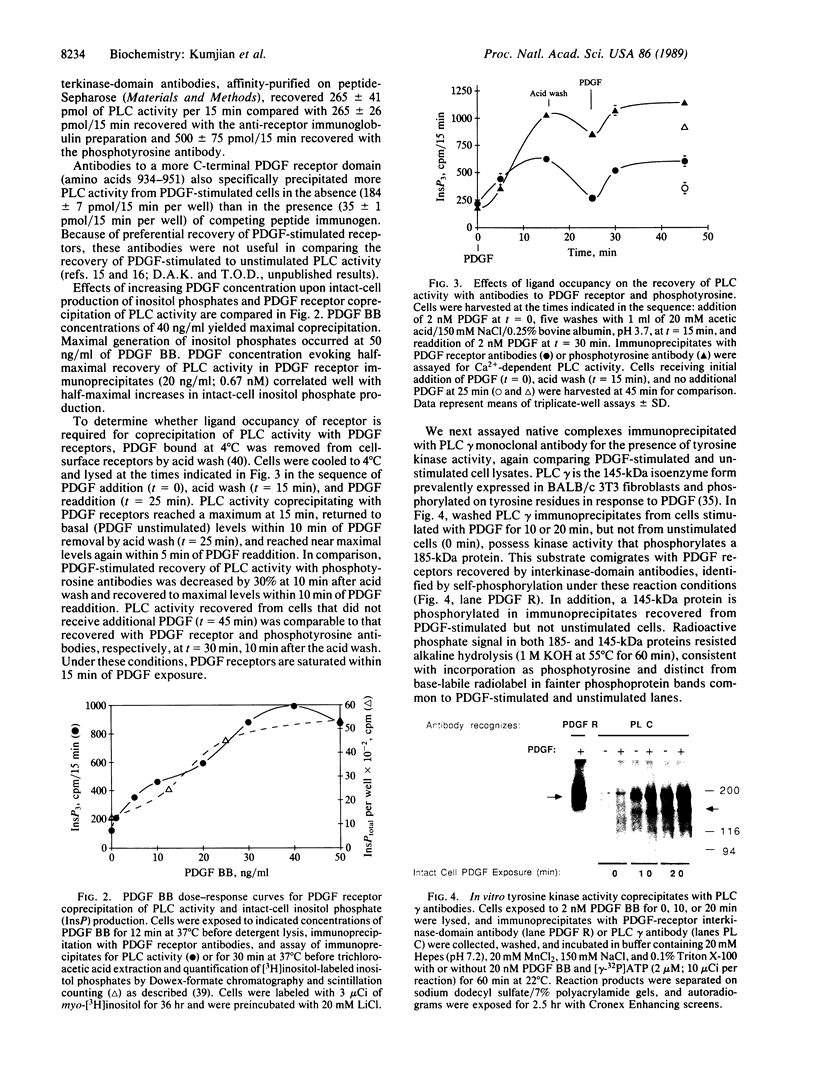
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W. Growth factors immediately raise cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8066–8069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nånberg E., Rozengurt E. Temporal relationship between inositol polyphosphate formation and increases in cytosolic Ca2+ in quiescent 3T3 cells stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor, bombesin and vasopressin. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2741–2747. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03128.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olashaw N. E., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor stimulates formation of inositol phosphates in BALB/c/3T3 cells pretreated with cholera toxin and isobutylmethylxanthine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1111–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Chambard J. C., Pouysségur J. Tyrosine kinase-activating growth factors potentiate thrombin- and AIF4- -induced phosphoinositide breakdown in hamster fibroblasts. Evidence for positive cross-talk between the two mitogenic signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12893–12900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturani E., Zippel R., Morello L., Brambillo R., Alberghina L. Dissociation of the ligand and dephosphorylation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jun 20;233(2):371–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Choi W. C., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Monoclonal antibodies to three phospholipase C isozymes from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14497–14504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Cloning and sequence of multiple forms of phospholipase C. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]