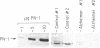Abstract
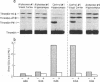
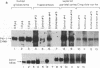
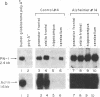
Protease nexin-1 (PN-1) is a cell-secreted protein that inhibits certain proteases, particularly thrombin, by forming SDS-stable complexes with the catalytic site serine of the protease. PN-1 was recently shown to be identical to a glial-derived neurite-promoting factor/glial-derived nexin present in rat brain. Its neurite outgrowth activity depends on inhibition of thrombin, presumably because thrombin brings about neurite retraction. Here we show that human brain contains PN-1 and that PN-1 activity in brains of individuals with Alzheimer disease (AD) was only 14% of control values (total of 14 AD patients and 7 control individuals). PN-1 activity in the hippocampus, a region with marked neuropathology in AD, was 15% of control values (10 AD patients and 4 control individuals). Western blot analysis indicated a large decrease in free PN-1 protein and an increase in PN-1-containing complexes that comigrated with PN-1-thrombin complexes. Northern blot analysis indicated that PN-1 mRNA levels were about equal in brains from AD patients and control individuals. Thus these results suggest that the decreases in PN-1 activity and free PN-1 protein are due to formation of PN-1-protease complexes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W. Alzheimer's disease. Enter a protease inhibitor. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):478–479. doi: 10.1038/331478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Defossez A., Persuy P., Peers M. C. Observation of morphological relationships between angiopathic blood vessels and degenerative neurites in Alzheimer's disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;411(3):199–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00735024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. H., Cunningham D. D. Glycosaminoglycans on fibroblasts accelerate thrombin inhibition by protease nexin-1. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):543–550. doi: 10.1042/bj2450543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. H., Cunningham D. D. Human fibroblasts accelerate the inhibition of thrombin by protease nexin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. H., Wagner S. L., Yuan R. H., Cunningham D. D. Localization of protease nexin-1 on the fibroblast extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):179–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041340203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor S., Odink K., Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity belongs to the protease nexins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):687–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90511-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D. Thrombin modulates and reverses neuroblastoma neurite outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. A., Mann D. M., Wester P., Winblad B. An integrative hypothesis concerning the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):489–502. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(86)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Seeds N. W. Peripheral neurons and Schwann cells secrete plasminogen activator. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):773–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R. Thrombin inactivates acidic fibroblast growth factor but not basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2572–2578. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low D. A., Baker J. B., Koonce W. C., Cunningham D. D. Released protease-nexin regulates cellular binding, internalization, and degradation of serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney M., Snider R. M., Richelson E. Thrombin binding to human brain and spinal cord. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983 Dec;58(12):829–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means E. D., Anderson D. K. Thrombin interactions with central nervous system tissue and implications of these interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;485:314–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Niday E., Limat A., Solomon F. Inhibition of protease activity can lead to neurite extension in neuroblastoma cells. Prog Brain Res. 1983;58:359–364. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer R. I., Afifi A. A., Chance J. M. Prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in a retirement community. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Mar;125(3):420–436. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Patterson P. H. Characterization of an inhibitor of neuronal plasminogen activator released by heart cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2664–2673. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02664.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Ng S. Y., Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Evolutionary conservation in the untranslated regions of actin mRNAs: DNA sequence of a human beta-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1687–1696. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard E., Meier R., Halfter W., Rovelli G., Monard D. Detection of glia-derived nexin in the olfactory system of the rat. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt D. E., Cotman C. W., Nieto-Sampedro M., Rowe J. W., Knauer D. J. Identification of a protease inhibitor produced by astrocytes that is structurally and functionally homologous to human protease nexin-I. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 7;415(1):40–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. W., Bergman B. L., Bajpai A., Hersh R. T., Rodriguez H., Jones B. N., Barreda C., Watts S., Baker J. B. Protease nexin. Properties and a modified purification procedure. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7029–7034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., McKinney M., Richelson E. Thrombin binding and stimulation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate formation in neuroblastoma cells. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1986 Jul;12(3):253–262. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney M. C., Fisher R. H., Lewis A. J., Zorzitto M. L., Snow W. G., Reid D. W., Nieuwstraten P. The NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer's disease: a clinicopathologic study of 57 cases. Neurology. 1988 Mar;38(3):359–364. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand W. E., Cunningham D. D. Purification of protease nexin II from human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8508–8514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand W. E., Wagner S. L., Cunningham D. D. Purification of a form of protease nexin 1 that binds heparin with a low affinity. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2176–2181. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S. L., Lau A. L., Cunningham D. D. Binding of protease nexin-1 to the fibroblast surface alters its target proteinase specificity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):611–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S. L., Van Nostrand W. E., Lau A. L., Cunningham D. D. Monoclonal antibodies to protease nexin 1 that differentially block its inhibition of target proteases. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2173–2176. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Kozlowski P. B. Evidence for blood-brain barrier changes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (SDAT). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;396:119–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb26848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurn A. D., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived nexin promotes neurite outgrowth in cultured chick sympathetic neurons. Dev Neurosci. 1988;10(1):17–24. doi: 10.1159/000111951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]