Abstract
The characteristic wavelength at which a visual pigment absorbs light is regulated by interactions between protein (opsin) and retinylidene Schiff base chromophore. By using site-directed mutagenesis, charged amino acids in bovine rhodopsin transmembrane helix C were systematically replaced. Substitution of glutamic acid-134 or arginine-135 did not affect spectral properties. However, substitution of glutamic acid-122 by glutamine or by aspartic acid formed pigments that were blue-shifted in light absorption (lambda max = 480 nm and 475 nm, respectively). While the substitution of glutamic acid-113 by aspartic acid gave a slightly red-shifted pigment (lambda max = 505 nm), replacement by glutamine formed a pigment that was strikingly blue-shifted in light absorption (lambda max = 380 nm). The 380-nm species existed in a pH-dependent equilibrium with a 490-nm species such that at acidic pH all of the pigment was converted to lambda max = 490 nm. We conclude that glutamic acid-113 serves as the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in rhodopsin. We believe that this opsin-chromophore interaction is an example of a general mechanism of color regulation in the visual pigments.
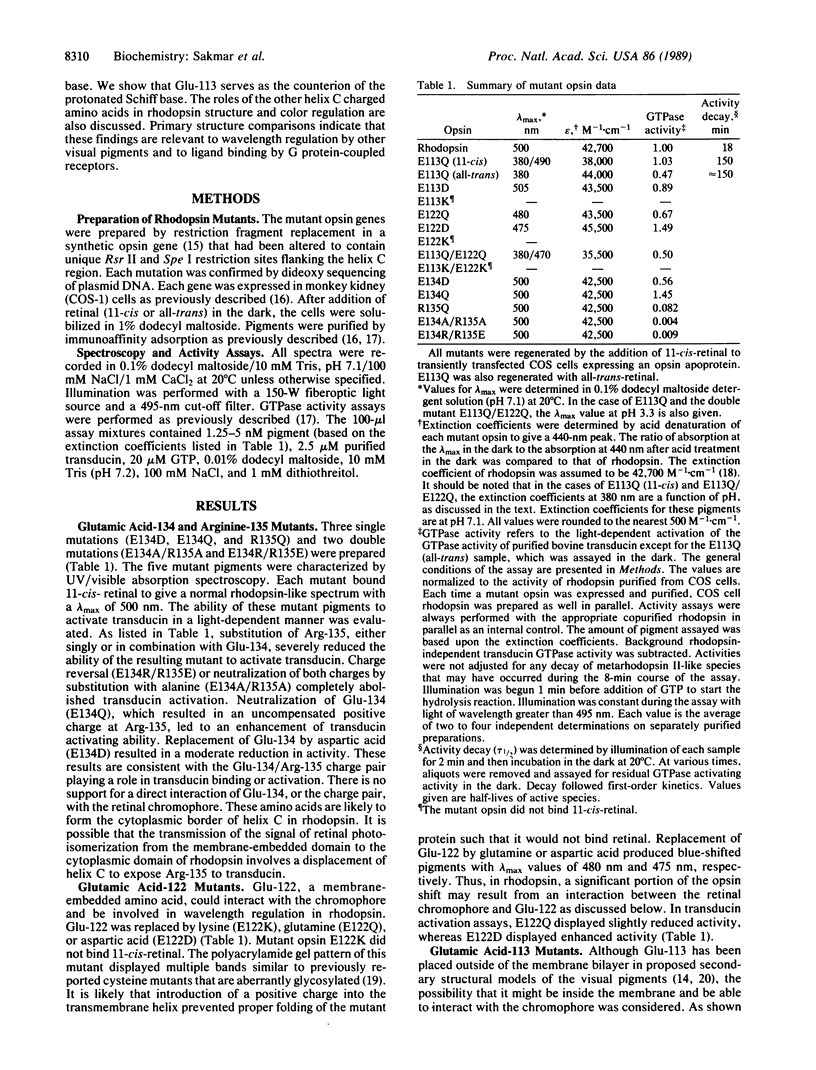
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birge R. R., Murray L. P., Pierce B. M., Akita H., Balogh-Nair V., Findsen L. A., Nakanishi K. Two-photon spectroscopy of locked-11-cis-rhodopsin: evidence for a protonated Schiff base in a neutral protein binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4117–4121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz P. E., Mohler J. H., Navangul H. V. Anion-induced wavelength regulation of absorption maxima of Schiff bases of retinal. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):848–855. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M. Trigger and amplification mechanisms in visual phototransduction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:331–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Zuker C. S., Rubin G. M. An opsin gene expressed in only one photoreceptor cell type of the Drosophila eye. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):705–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Oprian D. D., Khorana H. G. A single amino acid substitution in rhodopsin (lysine 248----leucine) prevents activation of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2119–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryxell K. J., Meyerowitz E. M. An opsin gene that is expressed only in the R7 photoreceptor cell of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):443–451. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A., McDowell J. H., Curtis D. R., Wang J. K., Juszczak E., Fong S. L., Rao J. K., Argos P. The structure of bovine rhodopsin. Biophys Struct Mech. 1983;9(4):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00535659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. A., Stark W. S., Walker J. A. Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):415–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Hubbell W. L. Preparation and properties of phospholipid bilayers containing rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROPF A., HUBBARD R. The mechanism of bleaching rhodopsin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Nov 12;74(2):266–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb39550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakitani H., Kakitani T., Rodman H., Honig B. On the mechanism of wavelength regulation in visual pigments. Photochem Photobiol. 1985 Apr;41(4):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1985.tb03514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kito Y., Suzuki T., Azuma M., Sekoguti Y. Absorption spectrum of rhodopsin denatured with acid. Nature. 1968 Jun 8;218(5145):955–957. doi: 10.1038/218955a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longstaff C., Calhoon R. D., Rando R. R. Deprotonation of the Schiff base of rhodopsin is obligate in the activation of the G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow G. R., Barry B. A., Mathies R. A. Why are blue visual pigments blue? A resonance Raman microprobe study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1515–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollevanger L. C., Kentgens A. P., Pardoen J. A., Courtin J. M., Veeman W. S., Lugtenburg J., de Grip W. J. High-resolution solid-state 13C-NMR study of carbons C-5 and C-12 of the chromophore of bovine rhodopsin. Evidence for a 6-S-cis conformation with negative-charge perturbation near C-12. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Tousa J. E., Baehr W., Martin R. L., Hirsh J., Pak W. L., Applebury M. L. The Drosophila ninaE gene encodes an opsin. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Molday R. S., Kaufman R. J., Khorana H. G. Expression of a synthetic bovine rhodopsin gene in monkey kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8874–8878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Zolotarev A. S., Artamonov I. D., Bespalov I. A., Dergachev A. E., Tsuda M. Octopus rhodopsin. Amino acid sequence deduced from cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADDING C. M., WALD G. The stability of rhodopsin and opsin; effects of pH and aging. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Jul 20;39(6):923–933. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.6.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Rands E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A. Conserved aspartic acid residues 79 and 113 of the beta-adrenergic receptor have different roles in receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10267–10271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G. The molecular basis of visual excitation. Nature. 1968 Aug 24;219(5156):800–807. doi: 10.1038/219800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


