Abstract
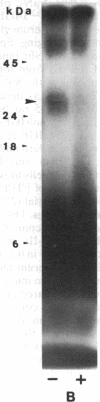
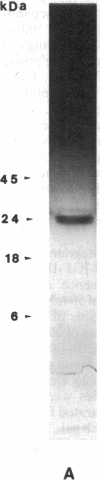
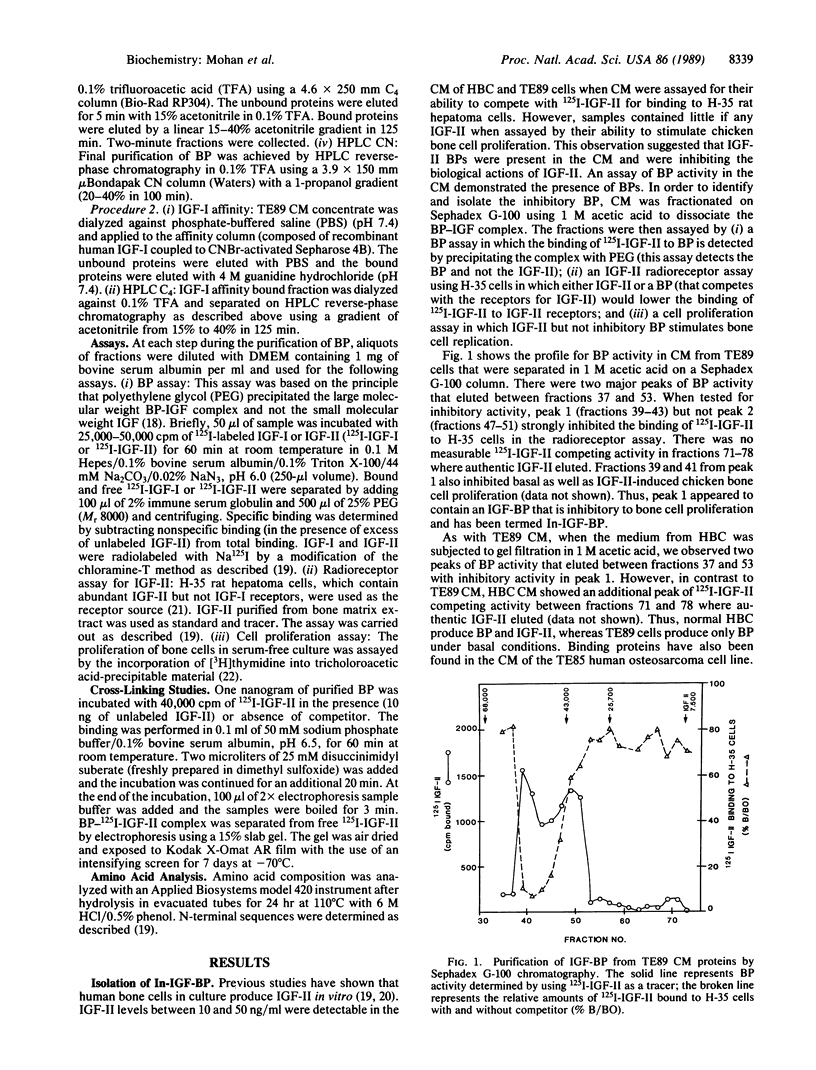
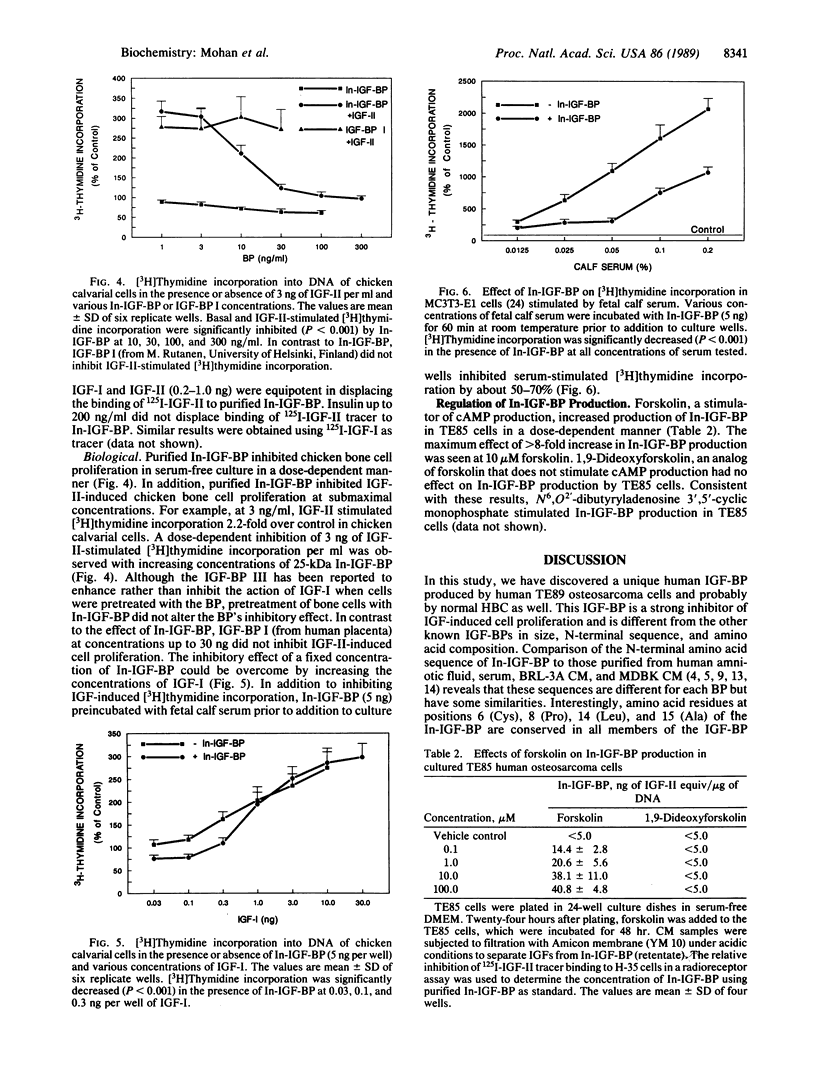
Inhibitory insulin-like growth factor binding protein (In-IGF-BP) has been purified to homogeneity from medium conditioned by TE89 human osteosarcoma cells by two different methods using Sephadex G-100 gel filtration, FPLC Mono Q ion-exchange, HPLC C4 reverse-phase, HPLC CN reverse-phase, and affinity chromatographies. In-IGF-BP thus purified appeared to be homogeneous and unique by the following criteria. (i) N-terminal sequence analysis yielded a unique sequence (Asp-Glu-Ala-Ile-His-Cys-Pro-Pro-Glu-Ser-Glu-Ala-Lys-Leu-Ala). (ii) Amino acid composition of In-IGF-BP revealed marked differences with the amino acid compositions of other known BPs. (iii) In-IGF-BP exhibited a single band with a molecular mass of 25 kDa under reducing conditions on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. IGF-I and IGF-II but not insulin displaced the binding of 125I-labeled IGF-I or 125I-labeled IGF-II binding to In-IGF-BP. In-IGF-BP inhibited basal, IGF-stimulated bone cell proliferation and serum-stimulated bone cell proliferation. Forskolin increased synthesis of In-IGF-BP in TE85 human osteosarcoma cells in a dose-dependent manner. Based on these findings, we conclude that In-IGF-BP is a protein that has a unique sequence and significant biological actions on bone cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C. The insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;91(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. C., Keyte J. W. N-terminal amino acid sequence of human pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha 1-globulin, an endometrial insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein--evidence for two small molecular weight IGF binding proteins. Endocrinology. 1988 Aug;123(2):1202–1204. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-2-1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. T., Stetler G. L., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Busby W. H., Clemmons D. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a human insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A., Groffen C., Kortleve D. J., Geurts van Kessel A., Drop S. L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IBP-1). EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2417–2423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Chiariotti L., Orlowski C. C., Mehlman T., Burgess W. H., Ackerman E. J., Bruni C. B., Rechler M. M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA clone encoding a fetal rat binding protein for insulin-like growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5148–5154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Liu F., Powell D., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins from cultured human fibroblasts. Characterization and hormonal regulation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):852–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI113968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Ward A. P., Goldberg A. C., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Characterization of somatomedin binding in human serum by ultracentrifugation and gel filtration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):916–921. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Leon D. D., Wilson D. M., Bakker B., Lamsom G., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins from human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):567–574. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mellow J. S., Baxter R. C. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein both inhibits and potentiates IGF-I-stimulated DNA synthesis in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):199–204. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80824-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Aalto-Setälä K., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A., Kontula K. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein/placental protein 12 and tissue-specific expression of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinen R., Kalkkinen N., Huhtala M. L., Seppälä M., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Placental protein 12 is a decidual protein that binds somatomedin and has an identical N-terminal amino acid sequence with somatomedin-binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1375–1378. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkhart S., Mohan S., Linkhart T. A., Kumegawa M., Baylink D. J. Human skeletal growth factor stimulates collagen synthesis and inhibits proliferation in a clonal osteoblast cell line (MC3T3-E1). J Cell Physiol. 1986 Aug;128(2):307–312. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGF-BPs) produced by human skin fibroblasts: immunological relationship to other human IGF-BPs. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):1907–1915. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-1907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein secretion by muscle cells: effect of cellular differentiation and proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Dec;137(3):505–512. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Jennings J. C., Linkhart T. A., Baylink D. J. Isolation and purification of a low-molecular-weight skeletal growth factor from human bones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 19;884(2):234–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Jennings J. C., Linkhart T. A., Baylink D. J. Primary structure of human skeletal growth factor: homology with human insulin-like growth factor-II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 14;966(1):44–55. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., MacDonald R. G., Brackett J. L., Mole J. E., Anderson J. K., Czech M. P. Purification and amino-terminal sequence of an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein secreted by rat liver BRL-3A cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11180–11188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocrant I., Pham H., Oh Y., Rosenfeld R. G. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins of cultured rat astroglial and neuronal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1316–1322. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. The biological and structural characterization of specific serum binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors. J Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;118(1):7–18. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1180007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Enberg G., Jörnvall H., Hall K. Isolation and characterization of a somatomedin-binding protein from mid-term human amniotic fluid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Isaksson M., Jörnvall H., Hall K. The somatomedin-binding protein isolated from a human hepatoma cell line is identical to the human amniotic fluid somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritvos O., Ranta T., Jalkanen J., Suikkari A. M., Voutilainen R., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human decidua inhibits the binding and biological action of IGF-I in cultured choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2150–2157. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suikkari A. M., Jalkanen J., Koistinen R., Bützow R., Ritvos O., Ranta T., Seppälä M. Human granulosa cells synthesize low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):1088–1090. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo L., Mottershead D. G., Ballard F. J., Wallace J. C. The bovine insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein purified from conditioned medium requires the N-terminal tripeptide in IGF-1 for binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90580-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wergedal J. E., Mohan S., Taylor A. K., Baylink D. J. Skeletal growth factor is produced by human osteoblast-like cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 28;889(2):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Cachianes G., Henzel W. J., Winslow G. A., Spencer S. A., Hellmiss R., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Cloning and expression of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1176–1185. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]