Abstract
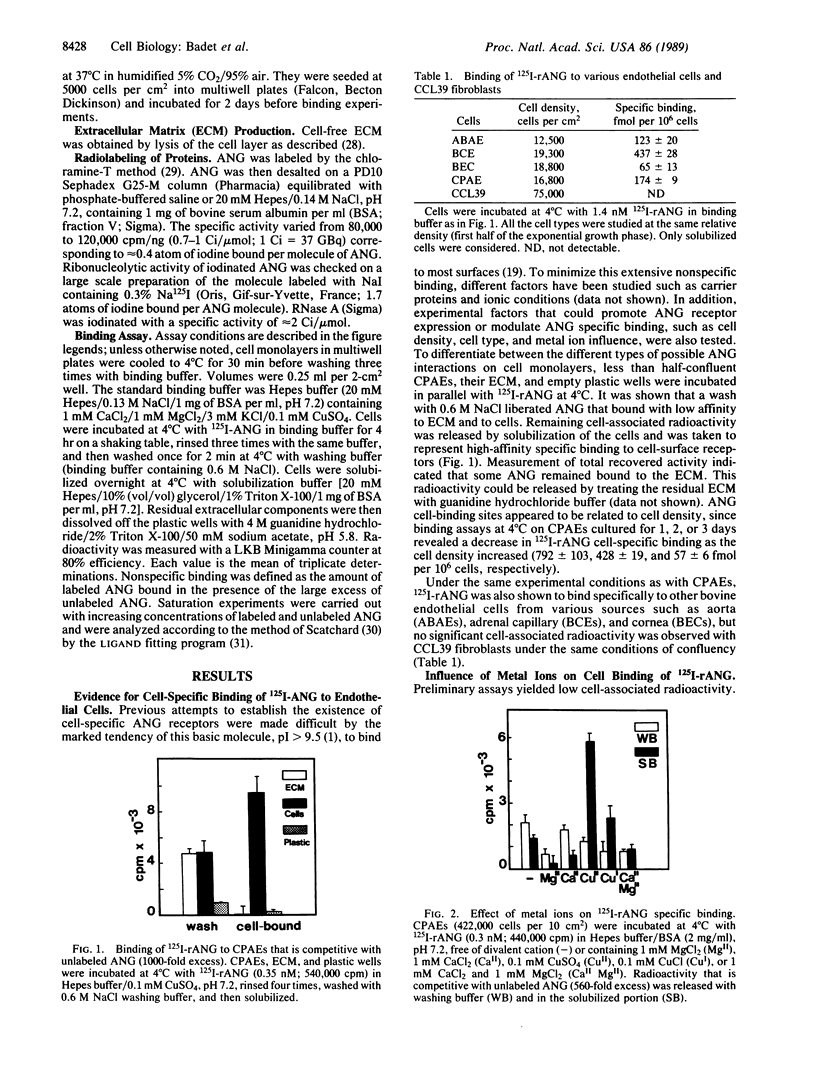
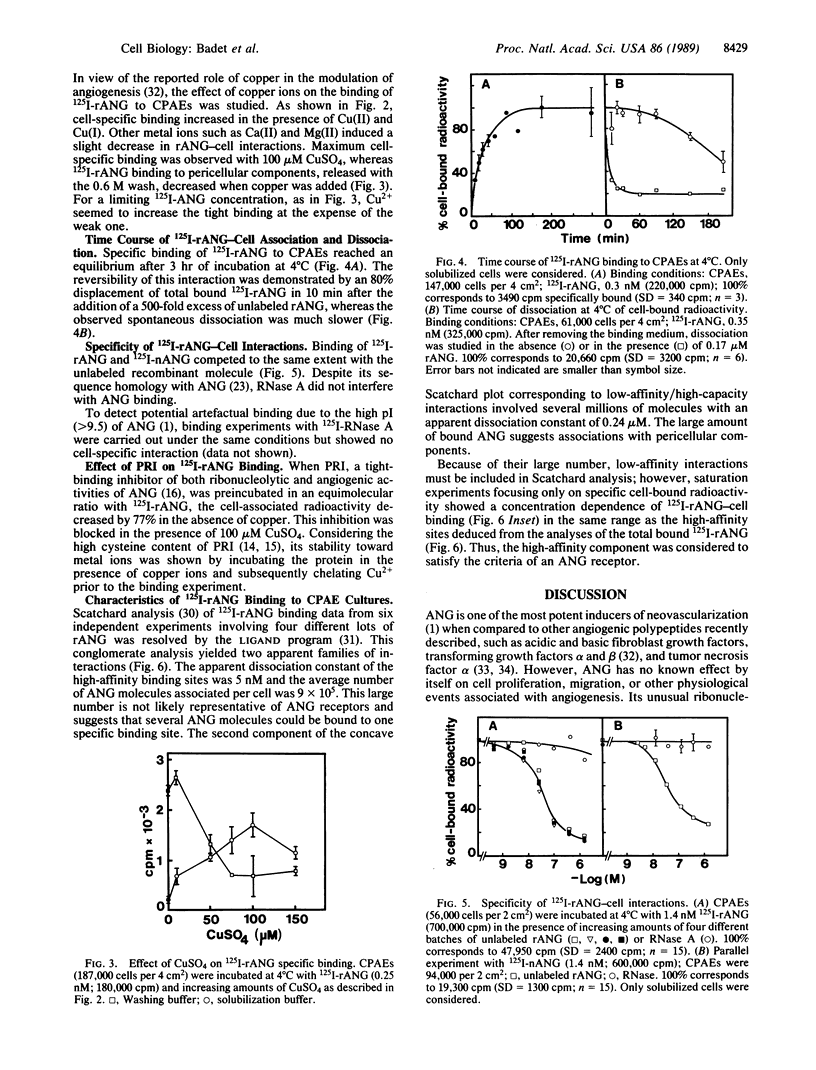
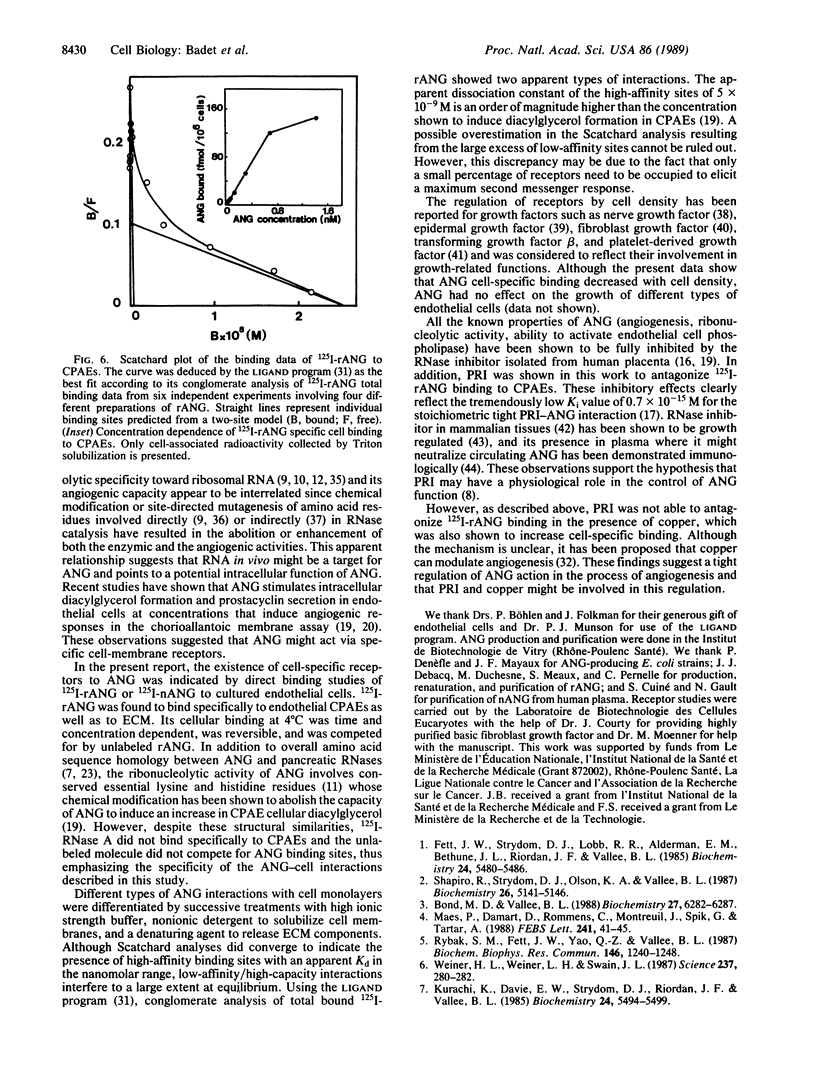
Specific binding of angiogenin (ANG) to calf pulmonary artery endothelial cells was demonstrated. Cellular binding at 4 degrees C of 125I-labeled human recombinant ANG was time and concentration dependent, reversible, and saturable in the presence of increasing amounts of the unlabeled molecules. The interaction was shown to be specific since a large excess of unlabeled ANG reduced labeled ANG binding by 80%, whereas similar doses of RNase A, a structurally related protein, had no effect. Scatchard analyses of binding data revealed two apparent components. High-affinity sites with an apparent dissociation constant of 5 x 10(-9) M were shown to represent cell-specific interactions. The second component, comprising low-affinity/high-capacity sites with an apparent dissociation constant of 0.2 x 10(-6) M, was essentially associated with pericellular components. High-affinity ANG binding sites varied with cell density and were found on other endothelial cells from bovine aorta, cornea, and adrenal cortex capillary but not on Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Divalent copper, a modulator of angiogenesis, was found to induce a severalfold increase in specific cell-bound radioactivity. Placental ribonuclease inhibitor, a tight-binding inhibitor of both ribonucleolytic and angiogenic activities of ANG, abolished 125I-labeled human recombinant ANG binding only in the absence of copper.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bicknell R., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin activates endothelial cell phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5961–5965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin stimulates endothelial cell prostacyclin secretion by activation of phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1573–1577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn P., Wilson G., Moore S. Ribonuclease inhibitor from human placenta. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5904–5910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond M. D., Vallee B. L. Isolation of bovine angiogenin using a placental ribonuclease inhibitor binding assay. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6282–6287. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courty J., Loret C., Chevallier B., Moenner M., Barritault D. Biochemical comparative studies between eye- and brain-derived growth factors. Biochimie. 1987 May;69(5):511–516. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denèfle P., Kovarik S., Guitton J. D., Cartwright T., Mayaux J. F. Chemical synthesis of a gene coding for human angiogenin, its expression in Escherichia coli and conversion of the product into its active form. Gene. 1987;56(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M., Kohtz D. S., Kleinberg D. L. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):286–294. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5480–5486. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fràter-Schröder M., Risau W., Hallmann R., Gautschi P., Böhlen P. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha, a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5277–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Mescher A. L., Birdwell C. R. Stimulation of corneal endothelial cell proliferations in vitro by fibroblast and epidermal growth factors. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Jul;25(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Vallee B. L. Mutagenesis of aspartic acid-116 enhances the ribonucleolytic activity and angiogenic potency of angiogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7139–7143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. F., Jr, Moore F., Bicknell R., Vallee B. L. Modulation of mitogenic stimuli by angiogenin correlates with in vitro phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Armour R., Baldwin J. H., Brown K. D., Yeh Y. C. Density-dependent regulation of growth of BSC-1 cells in cell culture: control of growth by serum factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft N., Shortman K. A suggested control function for the animal tissue ribonuclease-ribonuclease inhibitor system, based on studies of isolated cells and phytohaemagglutinin-transformed lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):164–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90133-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5494–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Fox E. A., Zhou H. M., Strydom D. J., Vallee B. L. Primary structure of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8545–8553. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Tight-binding inhibition of angiogenin and ribonuclease A by placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):225–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Polverini P. J., Shepard H. M., Wiseman D. M., Shively V., Nuseir N. Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):630–632. doi: 10.1038/329630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes P., Damart D., Rommens C., Montreuil J., Spik G., Tartar A. The complete amino acid sequence of bovine milk angiogenin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. The identification and partial characterization of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13860–13868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revoltella R., Bertolini L., Pediconi M. Unmasking of nerve growth factor membrane-specific binding sites in synchronized murine C 1300 neuroblastoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 30;85(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Human angiogenin, an organogenic protein. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jun;57(6):587–590. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Kazakoff P., Ruff E., Kuszynski C., Nebelsick J. Regulatory effects of cell density on the binding of transforming growth factor beta, epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 1;48(15):4266–4271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Gospodarowicz D. Effect of p-nitrophenyl-beta-D-xyloside on proteoglycan synthesis and extracellular matrix formation by bovine corneal endothelial cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3818–3824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak S. M., Fett J. W., Yao Q. Z., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin mRNA in human tumor and normal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1240–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90781-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak S. M., Vallee B. L. Base cleavage specificity of angiogenin with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli 5S RNAs. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2288–2294. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Schneider-Scherzer E., Thurnher M., Auer B., Schweiger M. The primary structure of human ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor (RAI) discloses a novel highly diversified protein superfamily with a common repetitive module. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4151–4156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Fox E. A., Riordan J. F. Role of lysines in human angiogenin: chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1726–1732. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Characteristic ribonucleolytic activity of human angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3527–3532. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Strydom D. J., Olson K. A., Vallee B. L. Isolation of angiogenin from normal human plasma. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5141–5146. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Human placental ribonuclease inhibitor abolishes both angiogenic and ribonucleolytic activities of angiogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2238–2241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Weremowicz S., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Ribonucleolytic activity of angiogenin: essential histidine, lysine, and arginine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8783–8787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D. K., Rybak S. M., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin abolishes cell-free protein synthesis by specific ribonucleolytic inactivation of 40S ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7263–7268. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D. K., Rybak S. M., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin abolishes cell-free protein synthesis by specific ribonucleolytic inactivation of ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8330–8334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J., Fett J. W., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5486–5494. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Weiner L. H., Swain J. L. Tissue distribution and developmental expression of the messenger RNA encoding angiogenin. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):280–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2440105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



