Abstract
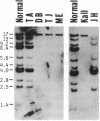
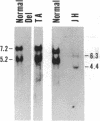
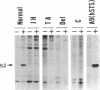
The human steroid sulfatase gene (STS) is located on the distal X chromosome short arm close to the pseudoautosomal region but in a segment of DNA that is unique to the X chromosome. In contrast to most X chromosome-encoded genes, STS expression is not extinguished during the process of X chromosome inactivation. Deficiency of STS (steryl-sulfatase; steryl-sulfate sulfohydrolase, EC 3.1.6.2) activity produces the syndrome of X chromosome-linked ichthyosis, which is one of the most common inborn errors of metabolism in man. Approximately 90% of STS- individuals have large deletions at the STS locus. We and others have found that the end points of such deletions are heterogeneous in their location. One recently ascertained subject was observed to have a 40-kilobase deletion that is entirely intragenic, permitting the cloning and sequencing of the deletion junction. Studies of this patient and of other X chromosome sequences in other subjects permit some insight into the mechanism(s) responsible for generating frequent deletions on the short arm of the X chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballabio A., Carrozzo R., Parenti G., Gil A., Zollo M., Persico M. G., Gillard E., Affara N., Yates J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Molecular heterogeneity of steroid sulfatase deficiency: a multicenter study on 57 unrelated patients, at DNA and protein levels. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Sebastio G., Andria G., Buckle V., Fraser N., Craig I., Rocchi M., Romeo G. Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifas J. M., Morley B. J., Oakey R. E., Kan Y. W., Epstein E. H., Jr Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase: frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9248–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Drumm M. L., Cole J. L., Lockwood W. K., Vande Woude G. F., Iannuzzi M. C. Construction of a general human chromosome jumping library, with application to cystic fibrosis. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2950591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conary J. T., Lorkowski G., Schmidt B., Pohlmann R., Nagel G., Meyer H. E., Krentler C., Cully J., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Genetic heterogeneity of steroid sulfatase deficiency revealed with cDNA for human steroid sulfatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):1010–1017. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A., Gillard E. F., Yates J. R., Mitchell M. J., Aitken D. A., Weir D. M., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. X chromosome deletions detectable by flow cytometry in some patients with steroid sulphatase deficiency (X-linked ichthyosis). Hum Genet. 1988 May;79(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00291709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. J., Magenis R. E., Brown M., Lanman J. T., Jr, Tsai J., O'Lague P., Goodfellow P., Mohandas T., Bergner E. A., Shapiro L. J. Inherited chondrodysplasia punctata due to a deletion of the terminal short arm of an X chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 18;311(16):1010–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410183111603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Blattner P., Harper J. F., Spiro A. J., Alter S., Francke U. Intragenic deletions in 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)/Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) families studied with the dystrophin cDNA: location of breakpoints on HindIII and BglII exon-containing fragment maps, meiotic and mitotic origin of the mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):620–629. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Affara N. A., Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Lambert J., Aitken D. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Deletion of a DNA sequence in eight of nine families with X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulphatase deficiency). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3977–3985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois S., Kastelein J. J., Hayden M. R. Characterization of six partial deletions in the low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene causing familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):60–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Bookstein R., Young L. J., Lin C. J., Rosenfeld M. G., Lee W. H. Molecular mechanism of retinoblastoma gene inactivation in retinoblastoma cell line Y79. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6017–6021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Exon-Alu recombination deletes 5 kilobases from the low density lipoprotein receptor gene, producing a null phenotype in familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3679–3683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levilliers J., Quack B., Weissenbach J., Petit C. Exchange of terminal portions of X- and Y-chromosomal short arms in human XY females. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levilliers J., Quack B., Weissenbach J., Petit C. Exchange of terminal portions of X- and Y-chromosomal short arms in human XY females. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindlöf M., Kiuru A., Käriäinen H., Kalimo H., Lang H., Pihko H., Rapola J., Somer H., Somer M., Savontaus M. L. Gene deletions in X-linked muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):496–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Higgs D. R. Recombination at the human alpha-globin gene cluster: sequence features and topological constraints. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Drosophila has one myosin heavy-chain gene with three developmentally regulated transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J. Steroid sulfatase deficiency and the genetics of the short arm of the human X chromosome. Adv Hum Genet. 1985;14:331-81, 388-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9400-0_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunohara N., Sakuragawa N., Satoyoshi E., Tanae A., Shapiro L. J. A new syndrome of anosmia, ichthyosis, hypogonadism, and various neurological manifestations with deficiency of steroid sulfatase and arylsulfatase C. Ann Neurol. 1986 Feb;19(2):174–181. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vnencak-Jones C. L., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Molecular basis of human growth hormone gene deletions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Gillard E. F., Aitken D. A., Affara N. A., Clayton J. F., Tippett P. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Multipoint linkage analysis of steroid sulfatase (X-linked ichthyosis) and distal Xp markers. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Allen E., Marsh B., Mohandas T., Wang N., Taggart R. T., Shapiro L. J. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Marsh B., Allen E., Tsai S. P., Ellison J., Connolly L., Neiswanger K., Shapiro L. J. The human X-linked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1123–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Marsh B., Mohandas T. K., Shapiro L. J. Isolation of genomic clones homologous to transcribed sequences from human X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):561–571. doi: 10.1007/BF01535221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]