Abstract
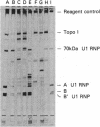
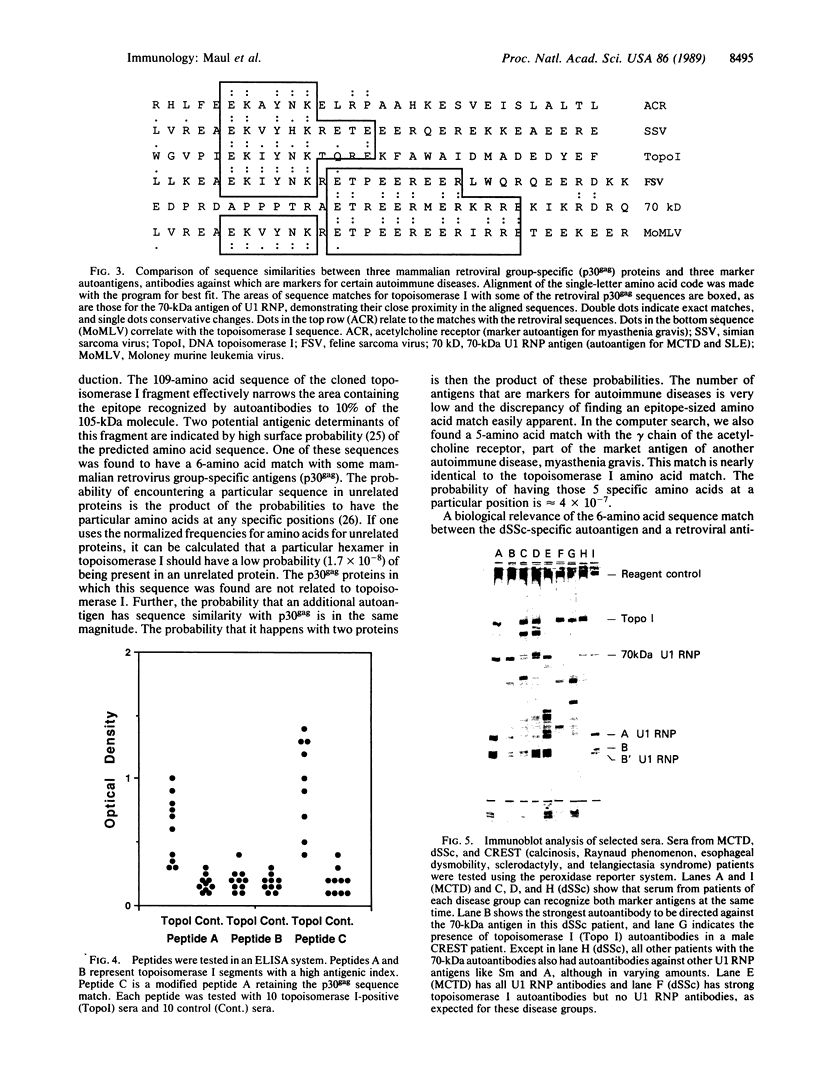
The possibility that viruses play a role in the etiology of various autoimmune diseases has been proposed. One approach to the search for these agents involves identifying potential crossreactive epitopes in viruses that infect cells of the immune system or of the target tissues. Antibodies to DNA topoisomerase I are the marker autoantibodies for diffuse systemic sclerosis. The major epitope of the antigen was therefore sought through cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for human topoisomerase I and eventually by the synthesis of the smallest possible peptide recognized by sera from patients with the diffuse form of systemic sclerosis. The antigenic 11-amino acid sequence contains 6 sequential amino acids that are identical to a sequence present in the group-specific antigen (p30gag) of some mammalian retroviruses. This sequence is separated by only 1 amino acid from the retroviral epitope sequence that crossreacts with autoantibodies against the marker antigen for mixed connective-tissue disease and systemic lupus erythematosus, the 70-kDa polypeptide of U1 ribonucleoprotein particles. These findings suggest that a retroviral agent may be involved in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis and other connective tissue diseases and that antibodies to intracellular antigens are not involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease but may be useful as footprints for tracking the potential etiological agent of autoimmune disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bikel I., Roberts T. M., Bladon M. T., Green R., Amann E., Livingston D. M. Purification of biologically active simian virus 40 small tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):906–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arpa P., Machlin P. S., Ratrie H., 3rd, Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W., Earnshaw W. C. cDNA cloning of human DNA topoisomerase I: catalytic activity of a 67.7-kDa carboxyl-terminal fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2543–2547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Orcutt B. C. Methods for identifying proteins by using partial sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A. S., Achten M., Tan E. M. Identification of a nuclear protein (Scl-70) as a unique target of human antinuclear antibodies in scleroderma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10514–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J., Prosser P. R., Holborow E. J., Jaquet H. Autoimmune reactions and virus-like particles in germ-free NZB mice. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):755–757. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng W. K., Pandit S. D., Sternglanz R. Mapping of the active site tyrosine of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13373–13376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French B. T., Maul H. M., Maul G. G. Screening cDNA expression libraries with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies using an amplified biotin-avidin-peroxidase technique. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Amino acid homology between the encephalitogenic site of myelin basic protein and virus: mechanism for autoimmunity. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1043–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.2414848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B., Wroblewska Z., Frankel M. E., Koprowski H. Molecular mimicry in virus infection: crossreaction of measles virus phosphoprotein or of herpes simplex virus protein with human intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisher K., Cunningham M. W. Myosin: a link between streptococci and heart. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2578225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit H., Spouge J. L., Cornette J. L., Cease K. B., Delisi C., Berzofsky J. A. Prediction of immunodominant helper T cell antigenic sites from the primary sequence. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2213–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., French B. T., van Venrooij W. J., Jimenez S. A. Topoisomerase I identified by scleroderma 70 antisera: enrichment of topoisomerase I at the centromere in mouse mitotic cells before anaphase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5145–5149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucheton M., Graafland H., Fanton H., Ursule L., Ferrier P., Larsen C. J. Presence of circulating antibodies against gag-gene MuLV proteins in patients with autoimmune connective tissue disorders. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):468–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shero J. H., Bordwell B., Rothfield N. F., Earnshaw W. C. High titers of autoantibodies to topoisomerase I (Scl-70) in sera from scleroderma patients. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.3003910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrash C., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., Sternglanz R. Cloning, characterization, and sequence of the yeast DNA topoisomerase I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4374–4378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Morino K., Uzawa S., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. Cloning and sequencing of Schizosaccharomyces pombe DNA topoisomerase I gene, and effect of gene disruption. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9727–9739. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):395–403. doi: 10.1038/317395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]