Abstract
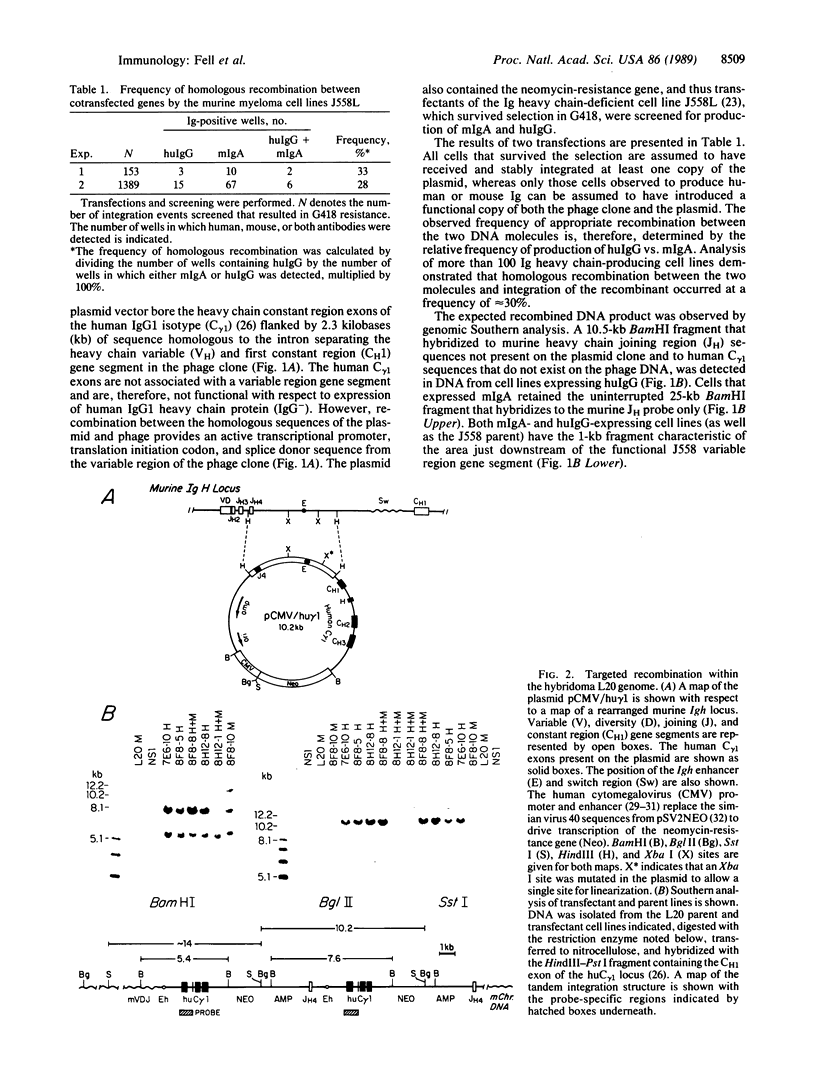
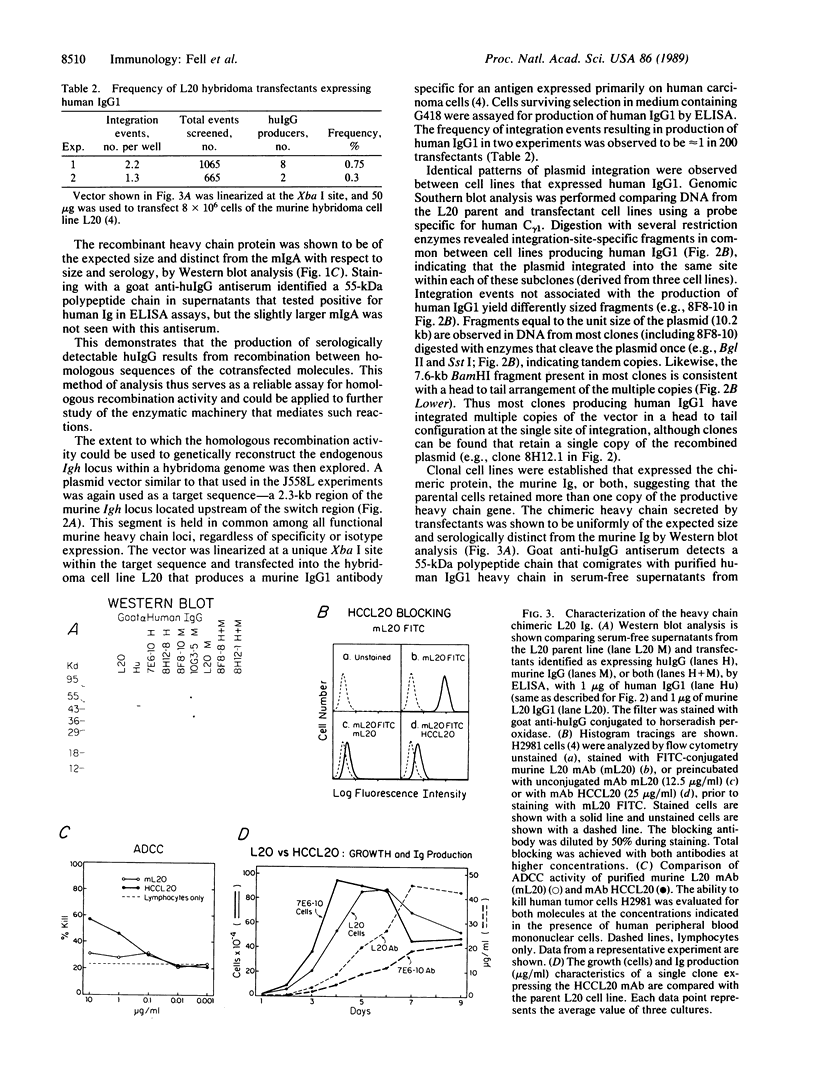
We demonstrate that murine myeloma cells can efficiently mediate homologous recombination. The murine myeloma cell line J558L was shown to appropriately recombine two transfected DNA molecules in approximately 30% of cells that received and integrated intact copies of both molecules. This activity was then exploited to direct major reconstructions of an endogenous locus within a hybridoma cell line. Production of antigen-specific chimeric heavy chain was achieved by targeting the human IgG1 heavy chain constant region (C gamma 1) exons to the genomic heavy chain locus of a hybridoma cell line secreting antibody specific for a human tumor-associated antigen. The frequency of productive genomic recombinations was approximately 1 in 200 transfectants, with accumulation of the chimeric protein reaching greater than 20 micrograms/ml in culture supernatants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. D., Shulman M. J. Homologous recombination between transferred and chromosomal immunoglobulin kappa genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4041–4047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode C., Runge M. S., Branscomb E. E., Newell J. B., Matsueda G. R., Haber E. Antibody-directed fibrinolysis. An antibody specific for both fibrin and tissue plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulianne G. L., Hozumi N., Shulman M. J. Production of functional chimaeric mouse/human antibody. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):643–646. doi: 10.1038/312643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Gregg R. G., Maeda N., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W., Thompson S., Smithies O. Targetted correction of a mutant HPRT gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):576–578. doi: 10.1038/330576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. W., Berson B. J., Hood L. E. The nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin C gamma1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4071–4079. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foecking M. K., Hofstetter H. Powerful and versatile enhancer-promoter unit for mammalian expression vectors. Gene. 1986;45(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Thomas K., Capecchi M. R. Nonreciprocal exchanges of information between DNA duplexes coinjected into mammalian cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway P. J., Oram J. D., Downing R. G., Patel K. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: BamHI, EcoRI and PstI restriction endonuclease cleavage maps. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström I., Horn D., Linsley P., Brown J. P., Brankovan V., Hellström K. E. Monoclonal mouse antibodies raised against human lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):3917–3923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin M., Berg P. Homologous integration in mammalian cells without target gene selection. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1353–1363. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. T., Dear P. H., Foote J., Neuberger M. S., Winter G. Replacing the complementarity-determining regions in a human antibody with those from a mouse. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):522–525. doi: 10.1038/321522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Recombination in mouse L cells between DNA introduced into cells and homologous chromosomal sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1391–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Robinson R. R., Hellström K. E., Murray E. D., Jr, Chang C. P., Hellström I. Chimeric mouse-human IgG1 antibody that can mediate lysis of cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3439–3443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Robinson R. R., Murray E. D., Jr, Ledbetter J. A., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Production of a mouse-human chimeric monoclonal antibody to CD20 with potent Fc-dependent biologic activity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3521–3526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L., Johnson M. J., Herzenberg L. A., Oi V. T. Chimeric human antibody molecules: mouse antigen-binding domains with human constant region domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Williams G. T., Fox R. O. Recombinant antibodies possessing novel effector functions. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):604–608. doi: 10.1038/312604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell N., Richards J. E., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. J genes for heavy chain immunoglobulins of mouse. Science. 1980 Sep 5;209(4461):1128–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.6250219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Yokoyama M., Araki K., Ueda R., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Recombinant human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody specific for common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):999–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahagan B. G., Dorai H., Saltzgaber-Muller J., Toneguzzo F., Guindon C. A., Lilly S. P., McDonald K. W., Morrissey D. V., Stone B. A., Davis G. L. A genetically engineered murine/human chimeric antibody retains specificity for human tumor-associated antigen. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):1066–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon J., Gefter M. L., Manser T., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Ptashne M. Expression of a VHC kappa chimaeric protein in mouse myeloma cells. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):364–367. doi: 10.1038/309364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L. K., Curtis P., Rakowicz-Szulczynska E., Ghrayeb J., Chang N., Morrison S. L., Koprowski H. Chimeric antibody with human constant regions and mouse variable regions directed against carcinoma-associated antigen 17-1A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda S., Naito T., Hama K., Noma T., Honjo T. Construction of chimaeric processed immunoglobulin genes containing mouse variable and human constant region sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):452–454. doi: 10.1038/314452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]