Abstract
In the title compound, C13H11Cl2NO2S, the methyl-substituted aromatic ring is disordered over two positions [occupancy ratio 0.705 (5):0.295 (5)]. The dihedral angles between the two aromatic rings are 74.9 (1) and 71.0 (3)° in the two disorder components. The crystal structure features centrosymmetric dimers linked by pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the preparation of the title compound, see: Savitha & Gowda (2006 ▶). For our studies of the effect of substituents on the structures of N-(aryl)arylsulfonamides, see: Gowda et al. (2008 ▶, 2010a ▶,b
▶); For related structures, see: Gelbrich et al. (2007 ▶); Perlovich et al. (2006 ▶).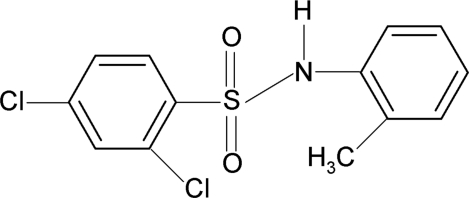
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H11Cl2NO2S
M r = 316.19
Monoclinic,
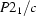
a = 8.106 (1) Å
b = 14.854 (2) Å
c = 11.772 (1) Å
β = 97.34 (1)°
V = 1405.8 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 5.52 mm−1
T = 299 K
0.35 × 0.25 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.248, T max = 0.339
5256 measured reflections
2501 independent reflections
2205 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
3 standard reflections every 120 min intensity decay: 1.0%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.098
S = 1.04
2501 reflections
240 parameters
8 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3
Data collection: CAD-4-PC (Enraf–Nonius, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4-PC; data reduction: REDU4 (Stoe & Cie, 1987 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035166/bt5340sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035166/bt5340Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O2i | 0.84 (2) | 2.13 (2) | 2.936 (2) | 159 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
As part of a study of the substituent effects on the structures of N-(aryl)arylsulfonamides (Gowda et al., 2008; Gowda et al. 2010a,b), the structure of 2,4-dichloro-N-(2-methylphenyl)-benzenesulfonamide (I) has been determined (Fig. 1). The methylsubstituted anilino ring is disordered. The conformations of the N—C bonds in the C—SO2—NH—C segment have gauche torsions with respect to the S═O bonds in one of the disordered components.
The molecule is twisted at the S atom with the C1—SO2—NH—C7 torsion angles of -85.1 (3)° and -47.2 (5)° in the major and minor components, respectively, compared to the values of 55.1 (3)° (molecule 1) and -48.3 (3)° (molecule 2) in 2,4-dichloro-N-(phenyl)-benzenesulfonamide (II) (Gowda et al., 2010b), -60.2 (2)° in 2,4-dichloro-N- (3-methylphenyl)benzenesulfonamide (III)(Gowda et al., 2010a) and 72.0 (2)° in N-(2-methylphenyl)-benzenesulfonamide (IV) (Gowda et al., 2008).
The sulfonyl benzene and the aniline benzene rings in (I) are tilted relative to each other by 74.9 (1)° and 71.0 (3)° in the two components, compared to the values of 80.5 (2)° in molecule 1 and 64.9 (1)° in molecule 2 of (II), 68.6 (1)° in (III) and 61.5 (1)° in (IV).
The other bond parameters in (I) are similar to those observed in (II), (III), (IV) and other aryl sulfonamides (Perlovich et al., 2006; Gelbrich et al., 2007).
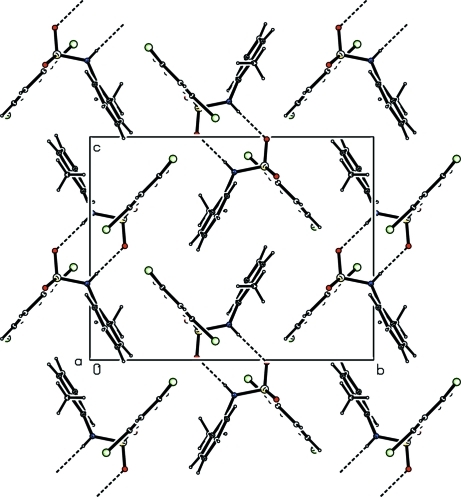
In the crystal structure, the pairs of intermolecular N–H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules through inversion-related dimers into infinite chains running parallel to the c-axis. Part of the crystal structure is shown in Fig. 2.
Experimental
The solution of 1,3-dichlorobenzene (10 ml) in chloroform (40 ml) was treated dropwise with chlorosulfonic acid (25 ml) at 0 ° C. After the initial evolution of hydrogen chloride subsided, the reaction mixture was brought to room temperature and poured into crushed ice in a beaker. The chloroform layer was separated, washed with cold water and allowed to evaporate slowly. The residual 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonylchloride was treated with o-toluidine in the stoichiometric ratio and boiled for ten minutes. The reaction mixture was then cooled to room temperature and added to ice cold water (100 ml). The resultant solid 2,4-dichloro-N-(2-methylphenyl)benzenesulfonamide was filtered under suction and washed thoroughly with cold water. It was then recrystallized to constant melting point from dilute ethanol. The purity of the compound was checked and characterized by recording its infrared and NMR spectra (Savitha & Gowda, 2006).
Prism like colourless single crystals used in X-ray diffraction studies were grown in ethanolic solution by slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
The H atom of the NH group was located in a difference map and its coordinates were refined with the N—H distance restrained to 0.86 (2) %A. The other H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å. All H atoms were refined with isotropic displacement parameters set to 1.2 times of the Ueq of the parent atom.
Atoms C7–C12 of the phenyl ring and C13 of the methyl group are disordered and were refined using a split model. The corresponding site-occupation factors were refined so that their sum was unity [0.705 (5) and 0.295 (5)]. The corresponding bond distances in the disordered groups were restrained to be equal.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of (I), showing the atom labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. Only the major occupied component is shown.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing of (I) with hydrogen bonding shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C13H11Cl2NO2S | F(000) = 648 |
| Mr = 316.19 | Dx = 1.494 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54180 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 8.106 (1) Å | θ = 4.6–16.5° |
| b = 14.854 (2) Å | µ = 5.52 mm−1 |
| c = 11.772 (1) Å | T = 299 K |
| β = 97.34 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1405.8 (3) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.25 × 0.25 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | 2205 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.033 |
| graphite | θmax = 67.0°, θmin = 4.8° |
| ω/2θ scans | h = 0→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (North et al., 1968) | k = −17→17 |
| Tmin = 0.248, Tmax = 0.339 | l = −14→13 |
| 5256 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 120 min |
| 2501 independent reflections | intensity decay: 1.0% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0521P)2 + 0.4627P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.005 |
| 2501 reflections | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 240 parameters | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 8 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0021 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.1368 (2) | 0.33703 (12) | 0.20574 (15) | 0.0386 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.2961 (3) | 0.36013 (12) | 0.18389 (16) | 0.0404 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.4340 (3) | 0.31932 (15) | 0.24250 (19) | 0.0502 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.5403 | 0.3342 | 0.2269 | 0.060* | |
| C4 | 0.4113 (3) | 0.25585 (15) | 0.3250 (2) | 0.0533 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.2555 (3) | 0.23232 (14) | 0.34875 (19) | 0.0520 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.2430 | 0.1899 | 0.4051 | 0.062* | |
| C6 | 0.1183 (3) | 0.27211 (13) | 0.28857 (17) | 0.0450 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.0124 | 0.2556 | 0.3032 | 0.054* | |
| C7A | −0.1071 (5) | 0.5236 (2) | 0.2565 (3) | 0.0446 (8) | 0.705 (5) |
| C8A | 0.0002 (5) | 0.5685 (2) | 0.3379 (4) | 0.0532 (9) | 0.705 (5) |
| C9A | −0.072 (2) | 0.6089 (7) | 0.4284 (7) | 0.071 (3) | 0.705 (5) |
| H9A | −0.0061 | 0.6448 | 0.4807 | 0.085* | 0.705 (5) |
| C10A | −0.2337 (8) | 0.5970 (3) | 0.4412 (4) | 0.0903 (16) | 0.705 (5) |
| H10A | −0.2750 | 0.6187 | 0.5061 | 0.108* | 0.705 (5) |
| C11A | −0.3369 (8) | 0.5525 (4) | 0.3577 (6) | 0.0851 (17) | 0.705 (5) |
| H11A | −0.4495 | 0.5469 | 0.3644 | 0.102* | 0.705 (5) |
| C12A | −0.2749 (7) | 0.5167 (3) | 0.2651 (5) | 0.0608 (12) | 0.705 (5) |
| H12A | −0.3455 | 0.4877 | 0.2081 | 0.073* | 0.705 (5) |
| C13A | 0.1816 (13) | 0.5795 (9) | 0.3311 (9) | 0.074 (3) | 0.705 (5) |
| H13A | 0.1967 | 0.6110 | 0.2619 | 0.088* | 0.705 (5) |
| H13B | 0.2331 | 0.5214 | 0.3309 | 0.088* | 0.705 (5) |
| H13C | 0.2316 | 0.6134 | 0.3960 | 0.088* | 0.705 (5) |
| N1 | −0.0460 (2) | 0.49066 (12) | 0.15829 (14) | 0.0462 (4) | |
| H1N | 0.003 (3) | 0.5230 (16) | 0.1141 (19) | 0.055* | |
| O1 | −0.1805 (2) | 0.34262 (12) | 0.17683 (16) | 0.0629 (4) | |
| O2 | −0.0363 (2) | 0.37672 (10) | 0.01067 (12) | 0.0560 (4) | |
| Cl1 | 0.32844 (7) | 0.44230 (4) | 0.08450 (4) | 0.05248 (18) | |
| Cl2 | 0.58543 (10) | 0.20713 (6) | 0.40131 (8) | 0.0887 (3) | |
| S1 | −0.04615 (6) | 0.38428 (3) | 0.13094 (4) | 0.04322 (17) | |
| C7B | −0.0109 (13) | 0.5386 (5) | 0.2733 (7) | 0.043 (2) | 0.295 (5) |
| C8B | −0.1310 (11) | 0.5537 (5) | 0.3435 (6) | 0.055 (2) | 0.295 (5) |
| C9B | −0.080 (4) | 0.5925 (14) | 0.4520 (14) | 0.052 (4) | 0.295 (5) |
| H9B | −0.1519 | 0.5919 | 0.5073 | 0.062* | 0.295 (5) |
| C10B | 0.0727 (13) | 0.6305 (6) | 0.4773 (8) | 0.068 (3) | 0.295 (5) |
| H10B | 0.0964 | 0.6653 | 0.5429 | 0.082* | 0.295 (5) |
| C11B | 0.1903 (13) | 0.6177 (7) | 0.4071 (10) | 0.074 (3) | 0.295 (5) |
| H11B | 0.2974 | 0.6398 | 0.4274 | 0.088* | 0.295 (5) |
| C12B | 0.151 (3) | 0.5715 (16) | 0.3043 (19) | 0.054 (4) | 0.295 (5) |
| H12B | 0.2317 | 0.5624 | 0.2561 | 0.064* | 0.295 (5) |
| C13B | −0.3078 (15) | 0.5262 (10) | 0.3116 (11) | 0.067 (4) | 0.295 (5) |
| H13D | −0.3132 | 0.4623 | 0.2989 | 0.081* | 0.295 (5) |
| H13E | −0.3532 | 0.5569 | 0.2429 | 0.081* | 0.295 (5) |
| H13F | −0.3709 | 0.5415 | 0.3725 | 0.081* | 0.295 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0406 (10) | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0390 (9) | −0.0031 (8) | 0.0029 (7) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0429 (11) | 0.0354 (9) | 0.0432 (10) | −0.0030 (8) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0395 (11) | 0.0490 (12) | 0.0620 (13) | −0.0002 (9) | 0.0059 (9) | −0.0007 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0516 (13) | 0.0457 (11) | 0.0600 (12) | 0.0073 (10) | −0.0036 (10) | 0.0029 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0623 (14) | 0.0420 (10) | 0.0511 (11) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0077 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0460 (11) | 0.0422 (10) | 0.0474 (11) | −0.0066 (9) | 0.0082 (8) | 0.0013 (8) |
| C7A | 0.050 (2) | 0.0363 (16) | 0.0468 (19) | 0.0050 (15) | 0.0028 (16) | 0.0013 (13) |
| C8A | 0.060 (3) | 0.0448 (18) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0001 (16) | 0.0025 (18) | 0.0001 (16) |
| C9A | 0.111 (5) | 0.051 (5) | 0.050 (4) | −0.003 (3) | 0.012 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C10A | 0.110 (4) | 0.084 (3) | 0.085 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.020 (2) |
| C11A | 0.071 (3) | 0.084 (4) | 0.109 (5) | 0.005 (3) | 0.047 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| C12A | 0.056 (3) | 0.053 (2) | 0.074 (4) | 0.0074 (18) | 0.013 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C13A | 0.059 (4) | 0.080 (5) | 0.077 (7) | −0.011 (3) | −0.006 (4) | −0.019 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0526 (11) | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0424 (9) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0069 (7) | 0.0035 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0595 (9) | 0.0888 (12) | −0.0069 (7) | 0.0073 (8) | 0.0146 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0650 (11) | 0.0557 (9) | 0.0431 (8) | −0.0070 (7) | −0.0094 (7) | −0.0048 (6) |
| Cl1 | 0.0507 (3) | 0.0533 (3) | 0.0544 (3) | −0.0078 (2) | 0.0107 (2) | 0.0094 (2) |
| Cl2 | 0.0639 (4) | 0.0861 (5) | 0.1097 (6) | 0.0179 (4) | −0.0134 (4) | 0.0310 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0373 (3) | 0.0435 (3) | 0.0472 (3) | −0.00531 (19) | −0.00115 (19) | 0.00201 (19) |
| C7B | 0.062 (7) | 0.032 (4) | 0.033 (4) | 0.002 (4) | −0.001 (4) | −0.008 (3) |
| C8B | 0.068 (6) | 0.045 (4) | 0.054 (5) | 0.007 (4) | 0.017 (4) | −0.002 (3) |
| C9B | 0.091 (10) | 0.035 (7) | 0.033 (6) | 0.004 (6) | 0.022 (6) | 0.007 (5) |
| C10B | 0.093 (7) | 0.053 (5) | 0.057 (5) | 0.004 (5) | 0.004 (5) | −0.020 (4) |
| C11B | 0.064 (6) | 0.075 (6) | 0.076 (6) | −0.003 (5) | −0.014 (5) | −0.030 (5) |
| C12B | 0.065 (11) | 0.046 (6) | 0.047 (7) | −0.006 (6) | −0.004 (7) | −0.014 (5) |
| C13B | 0.048 (8) | 0.088 (10) | 0.069 (10) | −0.002 (6) | 0.021 (6) | −0.021 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.391 (3) | C12A—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.393 (3) | C13A—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C1—S1 | 1.770 (2) | C13A—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (3) | C13A—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C2—Cl1 | 1.7337 (19) | N1—C7B | 1.524 (9) |
| C3—C4 | 1.382 (3) | N1—S1 | 1.6125 (18) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | N1—H1N | 0.844 (17) |
| C4—C5 | 1.373 (3) | O1—S1 | 1.4183 (17) |
| C4—Cl2 | 1.732 (2) | O2—S1 | 1.4326 (15) |
| C5—C6 | 1.373 (3) | C7B—C8B | 1.374 (11) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C7B—C12B | 1.402 (17) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C8B—C9B | 1.415 (16) |
| C7A—C12A | 1.381 (7) | C8B—C13B | 1.492 (13) |
| C7A—C8A | 1.381 (5) | C9B—C10B | 1.36 (3) |
| C7A—N1 | 1.403 (4) | C9B—H9B | 0.9300 |
| C8A—C9A | 1.413 (11) | C10B—C11B | 1.352 (15) |
| C8A—C13A | 1.492 (11) | C10B—H10B | 0.9300 |
| C9A—C10A | 1.350 (15) | C11B—C12B | 1.393 (16) |
| C9A—H9A | 0.9300 | C11B—H11B | 0.9300 |
| C10A—C11A | 1.375 (8) | C12B—H12B | 0.9300 |
| C10A—H10A | 0.9300 | C13B—H13D | 0.9600 |
| C11A—C12A | 1.366 (7) | C13B—H13E | 0.9600 |
| C11A—H11A | 0.9300 | C13B—H13F | 0.9600 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.02 (18) | C8A—C13A—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 123.26 (14) | H13A—C13A—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—S1 | 117.69 (15) | H13B—C13A—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.80 (19) | C7A—N1—C7B | 31.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 117.70 (16) | C7A—N1—S1 | 121.00 (19) |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 121.49 (15) | C7B—N1—S1 | 129.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.6 (2) | C7A—N1—H1N | 123.6 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C7B—N1—H1N | 103.4 (17) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.7 | S1—N1—H1N | 115.0 (17) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.7 (2) | O1—S1—O2 | 118.99 (10) |
| C5—C4—Cl2 | 119.84 (18) | O1—S1—N1 | 109.42 (11) |
| C3—C4—Cl2 | 118.43 (18) | O2—S1—N1 | 105.99 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.4 (2) | O1—S1—C1 | 105.83 (10) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.3 | O2—S1—C1 | 108.16 (10) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.3 | N1—S1—C1 | 108.06 (9) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.5 (2) | C8B—C7B—C12B | 119.8 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 | C8B—C7B—N1 | 123.0 (9) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.8 | C12B—C7B—N1 | 117.1 (11) |
| C12A—C7A—C8A | 121.6 (4) | C7B—C8B—C9B | 117.4 (14) |
| C12A—C7A—N1 | 119.3 (4) | C7B—C8B—C13B | 122.4 (9) |
| C8A—C7A—N1 | 118.9 (4) | C9B—C8B—C13B | 120.1 (14) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A | 116.3 (7) | C10B—C9B—C8B | 121.5 (16) |
| C7A—C8A—C13A | 123.6 (5) | C10B—C9B—H9B | 119.2 |
| C9A—C8A—C13A | 120.0 (7) | C8B—C9B—H9B | 119.2 |
| C10A—C9A—C8A | 122.0 (8) | C11B—C10B—C9B | 120.1 (10) |
| C10A—C9A—H9A | 119.0 | C11B—C10B—H10B | 120.0 |
| C8A—C9A—H9A | 119.0 | C9B—C10B—H10B | 120.0 |
| C9A—C10A—C11A | 119.6 (5) | C10B—C11B—C12B | 119.9 (13) |
| C9A—C10A—H10A | 120.2 | C10B—C11B—H11B | 120.1 |
| C11A—C10A—H10A | 120.2 | C12B—C11B—H11B | 120.1 |
| C12A—C11A—C10A | 120.4 (6) | C11B—C12B—C7B | 120.1 (18) |
| C12A—C11A—H11A | 119.8 | C11B—C12B—H12B | 120.0 |
| C10A—C11A—H11A | 119.8 | C7B—C12B—H12B | 120.0 |
| C11A—C12A—C7A | 119.7 (6) | C8B—C13B—H13D | 109.5 |
| C11A—C12A—H12A | 120.1 | C8B—C13B—H13E | 109.5 |
| C7A—C12A—H12A | 120.1 | H13D—C13B—H13E | 109.5 |
| C8A—C13A—H13A | 109.5 | C8B—C13B—H13F | 109.5 |
| C8A—C13A—H13B | 109.5 | H13D—C13B—H13F | 109.5 |
| H13A—C13A—H13B | 109.5 | H13E—C13B—H13F | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.4 (3) | C7A—N1—S1—O1 | 29.7 (3) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.13 (16) | C7B—N1—S1—O1 | 67.6 (5) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl1 | −178.41 (15) | C7A—N1—S1—O2 | 159.2 (2) |
| S1—C1—C2—Cl1 | 3.1 (2) | C7B—N1—S1—O2 | −162.9 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.0 (3) | C7A—N1—S1—C1 | −85.1 (2) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C4 | 177.79 (16) | C7B—N1—S1—C1 | −47.2 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.5 (3) | C2—C1—S1—O1 | 179.13 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—Cl2 | −178.15 (17) | C6—C1—S1—O1 | 0.62 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.6 (3) | C2—C1—S1—O2 | 50.59 (18) |
| Cl2—C4—C5—C6 | 179.28 (17) | C6—C1—S1—O2 | −127.93 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.3 (3) | C2—C1—S1—N1 | −63.73 (18) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.8 (3) | C6—C1—S1—N1 | 117.75 (16) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.39 (16) | C7A—N1—C7B—C8B | 1.1 (5) |
| C12A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −1.7 (7) | S1—N1—C7B—C8B | −86.0 (8) |
| N1—C7A—C8A—C9A | 173.1 (5) | C7A—N1—C7B—C12B | −176.0 (15) |
| C12A—C7A—C8A—C13A | −178.6 (8) | S1—N1—C7B—C12B | 96.9 (13) |
| N1—C7A—C8A—C13A | −3.8 (8) | C12B—C7B—C8B—C9B | −7.9 (19) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—C10A | 6.4 (11) | N1—C7B—C8B—C9B | 175.0 (12) |
| C13A—C8A—C9A—C10A | −176.6 (9) | C12B—C7B—C8B—C13B | 175.7 (15) |
| C8A—C9A—C10A—C11A | −7.2 (13) | N1—C7B—C8B—C13B | −1.4 (12) |
| C9A—C10A—C11A—C12A | 3.2 (11) | C7B—C8B—C9B—C10B | 14 (3) |
| C10A—C11A—C12A—C7A | 1.3 (9) | C13B—C8B—C9B—C10B | −170.0 (16) |
| C8A—C7A—C12A—C11A | −2.0 (7) | C8B—C9B—C10B—C11B | −12 (3) |
| N1—C7A—C12A—C11A | −176.8 (5) | C9B—C10B—C11B—C12B | 5(2) |
| C12A—C7A—N1—C7B | 177.2 (8) | C10B—C11B—C12B—C7B | 0(3) |
| C8A—C7A—N1—C7B | 2.3 (5) | C8B—C7B—C12B—C11B | 1(2) |
| C12A—C7A—N1—S1 | −67.5 (4) | N1—C7B—C12B—C11B | 178.6 (13) |
| C8A—C7A—N1—S1 | 117.6 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O2i | 0.84 (2) | 2.13 (2) | 2.936 (2) | 159 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5340).
References
- Enraf–Nonius (1996). CAD-4-PC Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Gelbrich, T., Hursthouse, M. B. & Threlfall, T. L. (2007). Acta Cryst. B63, 621–632. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S., Babitha, K. S. & Fuess, H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S., Nirmala, P. G. & Fuess, H. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, o1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S., Nirmala, P. G. & Fuess, H. (2010b). Private communication (refcode CCDC 740692). CCDC, Union Road, Cambridge, England.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Perlovich, G. L., Tkachev, V. V., Schaper, K.-J. & Raevsky, O. A. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o780–o782.
- Savitha, M. B. & Gowda, B. T. (2006). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 60, 600–606.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (1987). REDU4Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035166/bt5340sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035166/bt5340Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report