Abstract
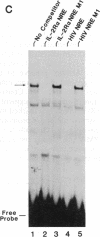
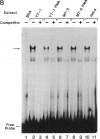
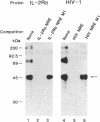
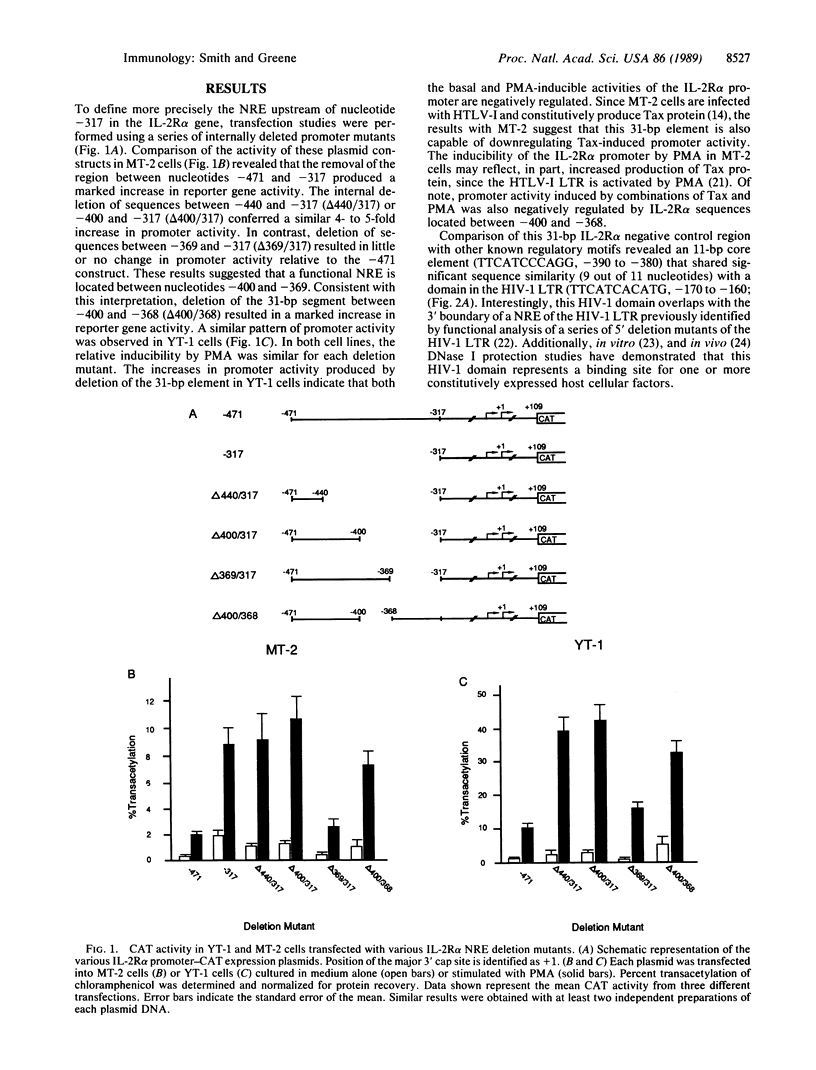
We have investigated the biochemical basis for negative regulation of interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain (IL-2R alpha) gene expression. Transient transfection studies employing internally deleted forms of the IL-2R alpha promoter localized a negative regulatory element (NRE) between nucleotides -400 and -368 relative to the major distal transcription start (cap) site. This 31-base-pair (bp) element is involved in the attenuation of both basal and inducible IL-2R alpha promoter activity. Comparison of this IL-2R alpha NRE with other known regulatory motifs revealed an 11-bp core element (TTCATCCCAGG) that was strikingly similar to a protein-binding domain within the long terminal repeat of the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1). This viral domain has been previously implicated in the negative control of HIV-1 gene expression. In vitro protein-DNA binding studies demonstrated that the same constitutively expressed approximately 50-kDa protein (SP-50) specifically bound to both the IL-2R alpha and HIV-1 NRE core elements. Mutation of the 11-bp IL-2R alpha NRE core element, which disrupted protein binding, significantly augmented basal as well as Tax protein- or phorbol ester-induced IL-2R alpha promoter activity in vivo, suggesting that SP-50 functions as a transcriptional silencer.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Feinberg M. B., Wolf J. B., Holbrook N. J., Wong-Staal F., Leonard W. J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Noguchi P. D., Cunningham R. E., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression: effects of phorbol diester, phospholipase C, and reexposure to lectin or antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3054–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukovich M., Wano Y., Le thi Bich Thuy, Katz P., Cullen B. R., Kehrl J. H., Greene W. C. A second human interleukin-2 binding protein that may be a component of high-affinity interleukin-2 receptors. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):518–522. doi: 10.1038/327518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R., Maguire J. E., Singer D. S. Identification of negative and positive regulatory elements associated with a class I major histocompatibility complex gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):695–703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Wu F. K., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Interactions of cellular proteins involved in the transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3761–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M. Growth of human T lymphocytes: an analysis of interleukin 2 and its cellular receptor. Prog Hematol. 1986;14:283–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Tsudo M., Minamoto S., Kono T., Doi T., Miyata T., Miyasaka M., Taniguchi T. Interleukin-2 receptor beta chain gene: generation of three receptor forms by cloned human alpha and beta chain cDNA's. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):551–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2785715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the trans-activation-responsive region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):673–679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.673-679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Luethy J. D., Kin J. Transient expression of foreign genes in lymphoid cells is enhanced by phorbol ester. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2610–2613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Taniguchi T., Tsuru S., Yoshida M. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor gene expression by p40x encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2883–2888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Greene W. C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor alpha subunit (Tac or CD25 antigen) gene expression: binding of inducible nuclear proteins to discrete promoter sequences correlates with transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4468–4472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Stenzel M., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Effects of long terminal repeat mutations on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4115–4119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4115-4119.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Gorka C., Baltimore D. T-cell-specific expression of interleukin 2: evidence for a negative regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Rusk C. M., Yodoi J., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 binding molecule distinct from the Tac protein: analysis of its role in formation of high-affinity receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Hatakeyama M., Kashima N., Fuse A., Hamuro J., Nishi-Takaoka C., Yamada G. Molecular analysis of the interleukin-2 system. Immunol Rev. 1986 Aug;92:121–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Wang H. M., Kato K., Smith K. A. Interleukin 2 high-affinity receptor expression requires two distinct binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):223–238. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Demonstration of a non-Tac peptide that binds interleukin 2: a potential participant in a multichain interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9694–9698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wano Y., Feinberg M., Hosking J. B., Bogerd H., Greene W. C. Stable expression of the tax gene of type I human T-cell leukemia virus in human T cells activates specific cellular genes involved in growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9733–9737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]