Abstract
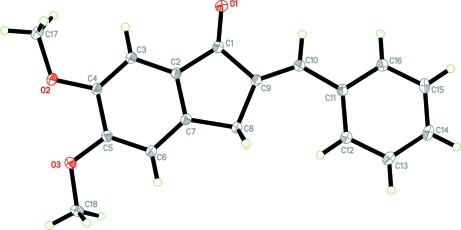
The molecular structure of the title compound, C18H16O3, is roughly planar; the maximum deviation of the indanone ring system is 0.027 (1) Å and it makes a dihedral angle of 2.69 (3)° with the phenyl ring. The torsion angles between the two methoxy groups and the indanone ring are −14.67 (11) and −1.11 (12)°. In the crystal, molecules are connected into a ribbon along the a axis via weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. Weak intermolecular C—H⋯π and π–π [centroid–centroid distance = 3.7086 (6) Å] interactions are also observed.
Related literature
For general background to and the biological activity of chalcone derivatives, see: Boumendjel et al. (2009 ▶); D’Archivio et al. (2008 ▶); Dicarlo et al. (1999 ▶); Echeverria et al. (2009 ▶); Heidenreich et al. (2008 ▶); Katsori & Hadjipavlou-Latina (2009 ▶); Miranda et al. (1999 ▶); Nowakowska (2007 ▶); Shah et al. (2008 ▶); Syed et al. (2008 ▶). For the stability of the temperature controller used in the data collection, see: Cosier & Glazer (1986 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H16O3
M r = 280.31
Monoclinic,

a = 6.0209 (6) Å
b = 14.8550 (14) Å
c = 15.2292 (15) Å
β = 90.603 (2)°
V = 1362.0 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.44 × 0.29 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.960, T max = 0.985
31475 measured reflections
6003 independent reflections
4902 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.130
S = 1.09
6003 reflections
192 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.58 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035695/is2598sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035695/is2598Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of C2–C7 benzene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17A⋯O3i | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.4107 (11) | 152 |
| C18—H18B⋯O2ii | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.5320 (11) | 173 |
| C16—H16A⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.99 | 3.7224 (9) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their thanks to Universiti Sains Malysia (USM) for providing research facilities. HKF thanks USM for the Research University Grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811160 and CSY thanks USM for the award of a USM Fellowship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chalcones have been reported to possess antiinflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer properties (Echeverria et al., 2009; Nowakowska, 2007; Miranda et al., 1999; Shah et al., 2008; Boumendjel et al., 2009; Katsori & Hadjipavlou-Latina, 2009). Chalcones are one of the major classes of natural products with widespread distribution in spices, tea, beer, fruits and vegetables. They have been recently subjects of great interest for their pharmacological activities (Dicarlo et al., 1999). Prostate cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers in men and the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the European Union and United States of America (Heidenreich et al., 2008). Many antitumor drugs have been developed for prostate cancer patients, but their intolerable systemic toxicity often limits their clinical use. Chemoprevention is one of the most promising approaches in prostate cancer research, in which natural or synthetic agents are used to prevent this malignant disease (Heidenreich et al., 2008; Syed et al., 2008; D'Archivio et al., 2008).
The molecular structure of the title compound is essentially coplanar (Fig. 1). The maximum deviation of the indanone group is 0.027 (1) Å and it makes dihedral angle of 2.69 (3)° with the phenyl ring [C11–C16]. The torsion angles of the two methoxy groups are [C17–O2–C4–C5] 165.99 (7) and [C18–O3–C5–C4] 179.19 (7)°.
In the crystal structure, intermolecular C17—H17A···O3 hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules into dimers (Fig. 2). These dimers are interconnected into ribbons propagating along the [100] direction via intermolecular C18—H18B···O2 hydrogen bonds (Fig. 2, Table 1). Weak intermolecular C—H···π (Table 1) and π–π interactions are also observed. [Cg1···Cg2iv of 3.7086 (6) Å; (iv) 1 - x, 1 - y, -z. Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of C2–C7 and C11–C16 benzene ring.]
Experimental
A mixture of 5,6-dimethoxyindan-1-one (0.001 mmol) and benzaldehyde (0.001 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (10 ml) and 30% sodium hydroxide solution (5 ml) was added and stirred for 5 h. After completion of the reaction as evident from TLC, the mixture was poured into crushed ice then neutralized with concentrated HCl. The precipitated solid was filtered, washed with water and recrystallized from ethanol to reveal the title compound as light yellow crystals.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å) and refined using a riding model. A rotating-group model were applied for the methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with atom labels and 50% probability ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of title compound, showing chains along the [100] direction. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C18H16O3 | F(000) = 592 |
| Mr = 280.31 | Dx = 1.367 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 7296 reflections |
| a = 6.0209 (6) Å | θ = 2.7–34.9° |
| b = 14.8550 (14) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 15.2292 (15) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 90.603 (2)° | Yellow, colourless |
| V = 1362.0 (2) Å3 | 0.44 × 0.29 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 6003 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4902 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.048 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 35.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.960, Tmax = 0.985 | k = −23→23 |
| 31475 measured reflections | l = −23→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.130 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0698P)2 + 0.2363P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6003 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 192 parameters | Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.58 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.07043 (10) | 0.71482 (4) | 0.09037 (4) | 0.01685 (13) | |
| O2 | 0.07512 (10) | 0.55593 (4) | 0.41523 (4) | 0.01527 (12) | |
| O3 | 0.42675 (10) | 0.46101 (4) | 0.40716 (4) | 0.01623 (13) | |
| C1 | 0.22764 (13) | 0.66575 (5) | 0.11035 (5) | 0.01189 (13) | |
| C2 | 0.26214 (13) | 0.61731 (5) | 0.19344 (5) | 0.01122 (13) | |
| C3 | 0.12486 (13) | 0.61613 (5) | 0.26768 (5) | 0.01208 (13) | |
| H3A | −0.0055 | 0.6497 | 0.2689 | 0.014* | |
| C4 | 0.18842 (13) | 0.56395 (5) | 0.33862 (5) | 0.01188 (13) | |
| C5 | 0.38768 (13) | 0.51154 (5) | 0.33496 (5) | 0.01213 (13) | |
| C6 | 0.52425 (13) | 0.51522 (5) | 0.26166 (5) | 0.01263 (14) | |
| H6A | 0.6561 | 0.4827 | 0.2602 | 0.015* | |
| C7 | 0.45911 (12) | 0.56873 (5) | 0.19043 (5) | 0.01121 (13) | |
| C8 | 0.57760 (13) | 0.58179 (5) | 0.10412 (5) | 0.01231 (13) | |
| H8A | 0.5966 | 0.5249 | 0.0738 | 0.015* | |
| H8B | 0.7219 | 0.6095 | 0.1131 | 0.015* | |
| C9 | 0.42250 (13) | 0.64368 (5) | 0.05349 (5) | 0.01186 (13) | |
| C10 | 0.43407 (13) | 0.67809 (5) | −0.02828 (5) | 0.01274 (14) | |
| H10A | 0.3154 | 0.7150 | −0.0441 | 0.015* | |
| C11 | 0.60191 (13) | 0.66724 (5) | −0.09638 (5) | 0.01229 (13) | |
| C12 | 0.79718 (14) | 0.61621 (6) | −0.08618 (5) | 0.01469 (14) | |
| H12A | 0.8259 | 0.5868 | −0.0334 | 0.018* | |
| C13 | 0.94801 (14) | 0.60945 (6) | −0.15463 (6) | 0.01690 (15) | |
| H13A | 1.0760 | 0.5751 | −0.1472 | 0.020* | |
| C14 | 0.90917 (15) | 0.65353 (6) | −0.23413 (6) | 0.01682 (15) | |
| H14A | 1.0106 | 0.6487 | −0.2795 | 0.020* | |
| C15 | 0.71743 (15) | 0.70489 (6) | −0.24506 (6) | 0.01576 (15) | |
| H15A | 0.6910 | 0.7349 | −0.2977 | 0.019* | |
| C16 | 0.56526 (14) | 0.71135 (5) | −0.17716 (5) | 0.01416 (14) | |
| H16A | 0.4370 | 0.7454 | −0.1853 | 0.017* | |
| C17 | −0.09525 (14) | 0.62140 (6) | 0.43137 (6) | 0.01619 (15) | |
| H17A | −0.1545 | 0.6122 | 0.4890 | 0.024* | |
| H17B | −0.2118 | 0.6149 | 0.3883 | 0.024* | |
| H17C | −0.0333 | 0.6808 | 0.4276 | 0.024* | |
| C18 | 0.62128 (14) | 0.40534 (6) | 0.40883 (6) | 0.01640 (15) | |
| H18A | 0.6235 | 0.3701 | 0.4617 | 0.025* | |
| H18B | 0.7514 | 0.4426 | 0.4071 | 0.025* | |
| H18C | 0.6192 | 0.3660 | 0.3588 | 0.025* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0151 (3) | 0.0202 (3) | 0.0153 (3) | 0.0057 (2) | 0.0018 (2) | 0.0026 (2) |
| O2 | 0.0144 (3) | 0.0191 (3) | 0.0123 (3) | 0.0035 (2) | 0.0052 (2) | 0.0029 (2) |
| O3 | 0.0157 (3) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.0133 (3) | 0.0048 (2) | 0.0024 (2) | 0.0056 (2) |
| C1 | 0.0121 (3) | 0.0125 (3) | 0.0111 (3) | 0.0000 (2) | 0.0014 (2) | −0.0003 (2) |
| C2 | 0.0117 (3) | 0.0116 (3) | 0.0104 (3) | −0.0001 (2) | 0.0013 (2) | 0.0003 (2) |
| C3 | 0.0116 (3) | 0.0128 (3) | 0.0119 (3) | 0.0004 (2) | 0.0017 (2) | 0.0001 (2) |
| C4 | 0.0109 (3) | 0.0137 (3) | 0.0111 (3) | −0.0003 (2) | 0.0024 (2) | 0.0000 (2) |
| C5 | 0.0122 (3) | 0.0126 (3) | 0.0116 (3) | 0.0001 (2) | 0.0005 (2) | 0.0014 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0116 (3) | 0.0143 (3) | 0.0120 (3) | 0.0013 (2) | 0.0012 (2) | 0.0009 (2) |
| C7 | 0.0112 (3) | 0.0114 (3) | 0.0110 (3) | −0.0005 (2) | 0.0013 (2) | −0.0001 (2) |
| C8 | 0.0118 (3) | 0.0140 (3) | 0.0111 (3) | 0.0013 (2) | 0.0021 (2) | 0.0007 (2) |
| C9 | 0.0118 (3) | 0.0124 (3) | 0.0115 (3) | 0.0005 (2) | 0.0019 (2) | 0.0000 (2) |
| C10 | 0.0134 (3) | 0.0130 (3) | 0.0118 (3) | 0.0010 (2) | 0.0015 (2) | 0.0003 (2) |
| C11 | 0.0136 (3) | 0.0120 (3) | 0.0113 (3) | −0.0004 (2) | 0.0015 (2) | 0.0002 (2) |
| C12 | 0.0143 (3) | 0.0165 (3) | 0.0133 (3) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0019 (3) | 0.0014 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0148 (3) | 0.0193 (4) | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0038 (3) | −0.0005 (3) |
| C14 | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0185 (4) | 0.0146 (3) | −0.0029 (3) | 0.0057 (3) | −0.0015 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0186 (4) | 0.0164 (3) | 0.0123 (3) | −0.0030 (3) | 0.0024 (3) | 0.0015 (3) |
| C16 | 0.0154 (3) | 0.0145 (3) | 0.0126 (3) | 0.0003 (2) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0013 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0141 (3) | 0.0189 (4) | 0.0156 (3) | 0.0024 (3) | 0.0043 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C18 | 0.0153 (3) | 0.0169 (3) | 0.0171 (4) | 0.0032 (3) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0032 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.2303 (10) | C10—C11 | 1.4645 (11) |
| O2—C4 | 1.3628 (10) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C17 | 1.4366 (10) | C11—C12 | 1.4061 (11) |
| O3—C5 | 1.3499 (10) | C11—C16 | 1.4092 (11) |
| O3—C18 | 1.4338 (10) | C12—C13 | 1.3933 (12) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4687 (11) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C9 | 1.5017 (11) | C13—C14 | 1.3941 (12) |
| C2—C7 | 1.3894 (11) | C13—H13A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.4076 (11) | C14—C15 | 1.3923 (13) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3805 (11) | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.3920 (12) |
| C4—C5 | 1.4318 (11) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3945 (11) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3977 (11) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.5146 (11) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.5154 (11) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.3487 (11) | ||
| C4—O2—C17 | 116.88 (6) | C9—C10—H10A | 114.5 |
| C5—O3—C18 | 118.07 (7) | C11—C10—H10A | 114.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 127.21 (7) | C12—C11—C16 | 118.04 (7) |
| O1—C1—C9 | 126.20 (7) | C12—C11—C10 | 124.30 (7) |
| C2—C1—C9 | 106.59 (6) | C16—C11—C10 | 117.65 (7) |
| C7—C2—C3 | 121.92 (7) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.47 (8) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 109.82 (7) | C13—C12—H12A | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 128.26 (7) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.8 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.38 (7) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.74 (8) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.8 | C12—C13—H13A | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.8 | C14—C13—H13A | 119.6 |
| O2—C4—C3 | 125.58 (7) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.50 (8) |
| O2—C4—C5 | 114.40 (7) | C15—C14—H14A | 120.2 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.02 (7) | C13—C14—H14A | 120.2 |
| O3—C5—C6 | 125.08 (7) | C16—C15—C14 | 120.02 (8) |
| O3—C5—C4 | 114.17 (7) | C16—C15—H15A | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.75 (7) | C14—C15—H15A | 120.0 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.72 (7) | C15—C16—C11 | 121.21 (8) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 120.6 | C15—C16—H16A | 119.4 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 120.6 | C11—C16—H16A | 119.4 |
| C2—C7—C6 | 120.16 (7) | O2—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C2—C7—C8 | 111.85 (7) | O2—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 127.99 (7) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 103.06 (6) | O2—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 111.2 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 111.2 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 111.2 | O3—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8B | 111.2 | O3—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.1 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C1 | 119.86 (7) | O3—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 131.47 (7) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C1—C9—C8 | 108.67 (6) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 130.91 (7) | ||
| O1—C1—C2—C7 | 179.73 (8) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.24 (11) |
| C9—C1—C2—C7 | −0.12 (8) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −178.92 (7) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.09 (13) | C2—C7—C8—C9 | −1.30 (8) |
| C9—C1—C2—C3 | −179.76 (7) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.91 (8) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.86 (11) | O1—C1—C9—C10 | −0.86 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.74 (7) | C2—C1—C9—C10 | 179.00 (7) |
| C17—O2—C4—C3 | −14.67 (11) | O1—C1—C9—C8 | 179.44 (8) |
| C17—O2—C4—C5 | 165.99 (7) | C2—C1—C9—C8 | −0.71 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—O2 | 179.62 (7) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.48 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.07 (11) | C7—C8—C9—C1 | 1.18 (8) |
| C18—O3—C5—C6 | −1.11 (12) | C1—C9—C10—C11 | −179.66 (8) |
| C18—O3—C5—C4 | 179.19 (7) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.03 (15) |
| O2—C4—C5—O3 | 1.72 (10) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.40 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—O3 | −177.66 (7) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | 178.97 (8) |
| O2—C4—C5—C6 | −178.00 (7) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.44 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.62 (12) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 179.93 (8) |
| O3—C5—C6—C7 | 178.15 (7) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.46 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −2.16 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.04 (13) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 1.31 (11) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.54 (13) |
| C1—C2—C7—C6 | −178.36 (7) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.55 (12) |
| C3—C2—C7—C8 | −179.41 (7) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.06 (12) |
| C1—C2—C7—C8 | 0.92 (9) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.60 (7) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 is the centroid of C2–C7 benzene ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17A···O3i | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.4107 (11) | 152 |
| C18—H18B···O2ii | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.5320 (11) | 173 |
| C16—H16A···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.99 | 3.7224 (9) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IS2598).
References
- Boumendjel, A., Ronot, X. & Boutonnat, J. (2009). Curr. Drug Targets, 10, 363–371. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107.
- D’Archivio, M., Santangelo, C., Scazzocchio, B., Vari, R., Filesi, C., Masella, R. & Giovannini, C. (2008). Int. J. Mol. Sci.9, 213–228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dicarlo, G., Mascolo, N., Izzo, A. A. & Capasso, F. (1999). Life Sci.65, 337–353. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Echeverria, C., Santibanez, J. S., Donoso-Tauda, O., Escobar, C. A. & Ramirez-Tagle, R. (2009). Int. J. Mol. Sci.10, 221–231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, A., Aus, G., Bolla, M., Joniau, S., Matveev, V. B., Schmid, H. P. & Zattoni, F. (2008). Eur. Urol.53, 68–80. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Katsori, A. M. & Hadjipavlou-Latina, D. (2009). Curr. Med. Chem.16, 1062–1081. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C. L., Stevens, J. F., Helmrich, A., Henderson, M. C., Rodriguez, R. J., Yang, Y. H., Deinzer, M. L., Barnes, D. W. & Buhler, D. R. (1999). Food Chem. Toxicol.37, 271–285. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nowakowska, Z. (2007). Eur. J. Med. Chem.42, 125–137. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shah, A., Khan, A. M., Qureshi, R., Ansari, F. L., Nazar, M. F. & Shah, S. S. (2008). Int. J. Mol. Sci.9, 1424–1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Syed, D. N., Suh, Y., Afag, F. & Mukhtar, H. (2008). Cancer Lett.265, 167–176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035695/is2598sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035695/is2598Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report