Abstract
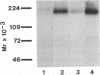
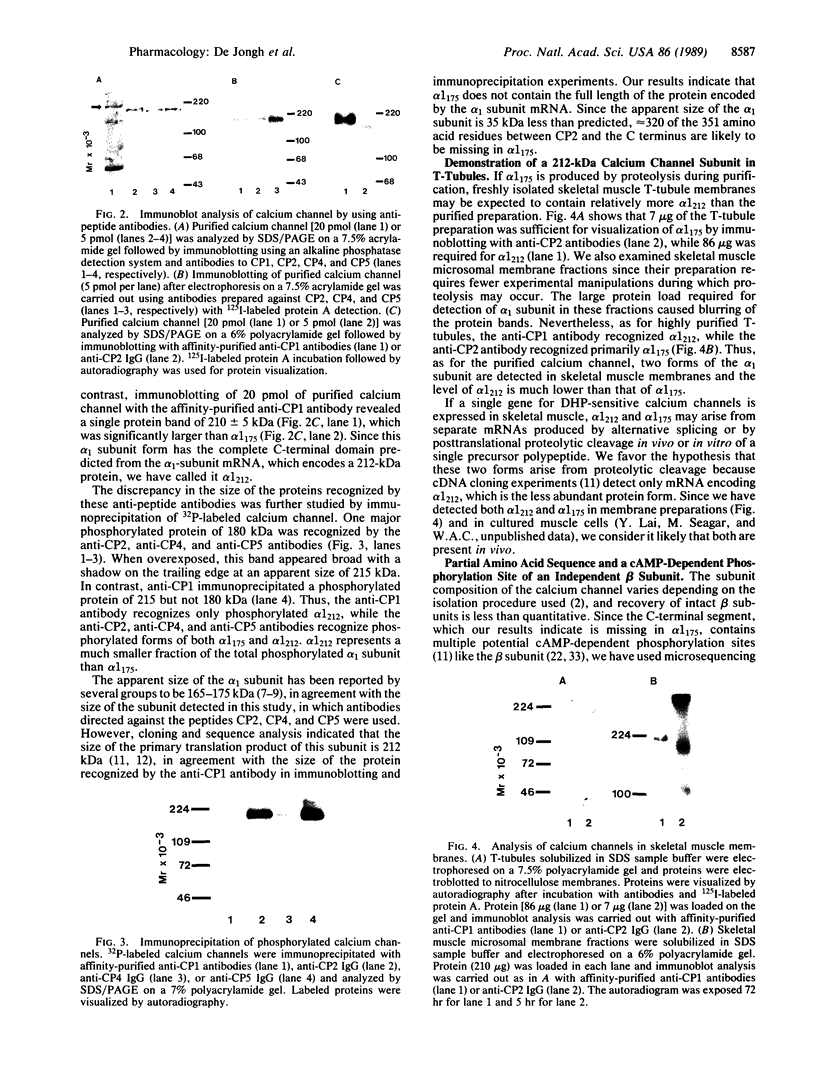
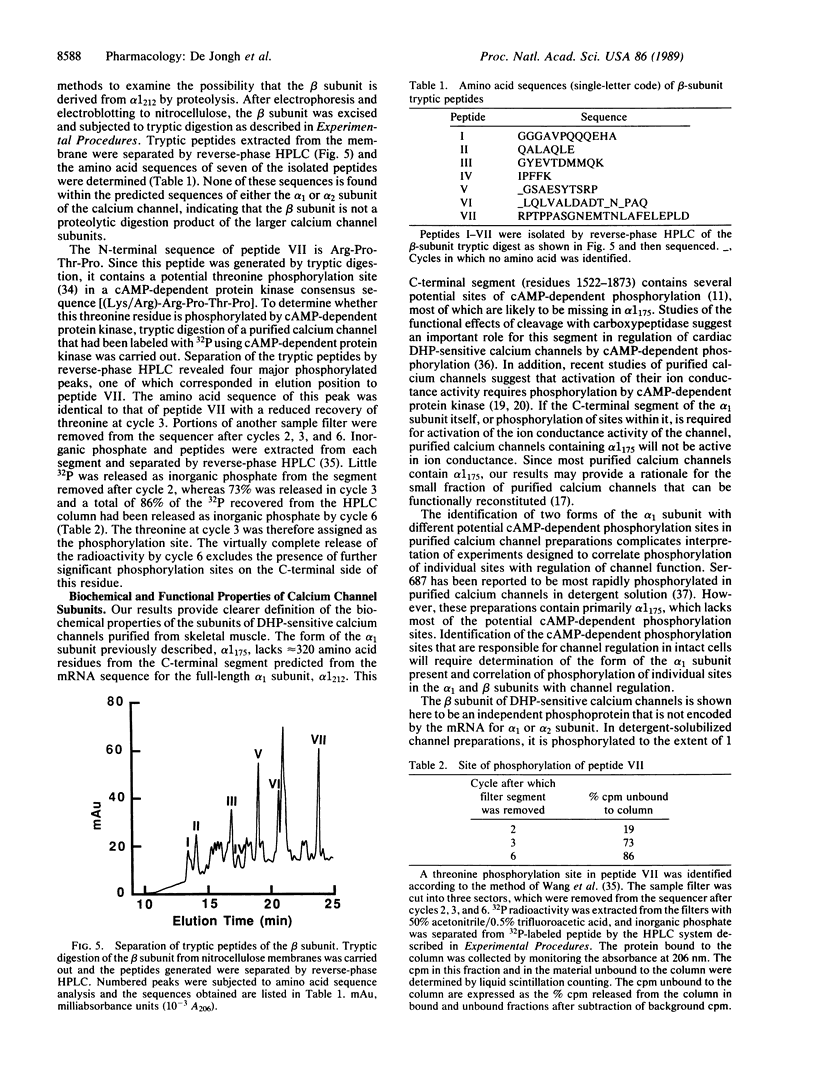
Antibodies prepared against peptides CP2, CP4, and CP5, which occur within the first 1522 amino acid residues of the alpha 1 subunit of dihydropyridine-sensitive skeletal muscle calcium channels, specifically recognized a 175-kDa form of the alpha 1 subunit in immunoblots and immunoprecipitation experiments. In contrast, antibodies prepared against peptide CP1, which represents the C-terminal 18 amino acid residues predicted by cloning and sequence analysis of the alpha 1 subunit, recognized a minor, previously undescribed 212-kDa protein, which is the size predicted for the full length of the alpha 1 subunit from cDNA cloning [Tanabe, T., Takeshima, H., Mikami, A., Flockerzi, V., Takahashi, H., Kangawa, K., Kojima, M., Matsuo, H., Hirose, T. & Numa, S. (1987) Nature (London) 328, 313-318]. Both the 175-kDa and 212-kDa forms were phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and both were present in isolated transverse tubule membranes. The 175-kDa form may arise from posttranslational proteolytic cleavage of the C terminus of the 212-kDa form of the alpha 1 subunit predicted by cDNA cloning and sequence analysis. Partial amino acid sequencing of the 54-kDa beta subunit of the calcium channel indicated this protein was not derived from the proteolytically cleaved C terminus of the alpha 1 subunit. This analysis identified a threonine residue in the sequence (Lys/Arg)-Arg-Pro-Thr-Pro of the beta subunit that was phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Phosphorylation of this residue in the beta subunit may play a role in modulation of calcium channel function. Separate functional roles of the 175-kDa form of the alpha 1 subunit in excitation-contraction coupling and of the 212-kDa form in ion conductance are proposed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barhanin J., Coppola T., Schmid A., Borsotto M., Lazdunski M. The calcium channel antagonists receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle. Reconstitution after purification and subunit characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):525–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor associated with the skeletal muscle voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14255–14263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Seagar M. J., Takahashi M. Molecular properties of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3535–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick C. C., Inui M., Fleischer S. Identification and purification of a transverse tubule coupling protein which binds to the ryanodine receptor of terminal cisternae at the triad junction in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10872–10877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., West L., Flockhart D. A., Lincoln T. M., McCarthy D. Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Reconstitution of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel purified from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3077–3083. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. B., Williams M. E., Ways N. R., Brenner R., Sharp A. H., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P., McKenna E., Koch W. J., Hui A. Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the alpha 1 and alpha 2 subunits of a DHP-sensitive calcium channel. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2458626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. L., Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C. Highly purified sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles are devoid of Ca2+-independent ('basal') ATPase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):552–568. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F., Pelzer D., Cavalié A., Trautwein W. Purified dihydropyridine-binding site from skeletal muscle t-tubules is a functional calcium channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):66–68. doi: 10.1038/323066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Merrick D., Auld V., Dunn R., Goldin A. L., Davidson N., Catterall W. A. Tissue-specific expression of the RI and RII sodium channel subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8682–8686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Trautwein W. Modification of L-type calcium current by intracellularly applied trypsin in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:259–274. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Lazdunski M. Calcium channels: molecular pharmacology, structure and regulation. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(2):81–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01870922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Striessnig J., Glossmann H., Schindler H. Purified skeletal muscle 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor forms phosphorylation-dependent oligomeric calcium channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn H., Nastainczyk W., Röhrkasten A., Schneider T., Hofmann F. Site-specific phosphorylation of the purified receptor for calcium-channel blockers by cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases, protein kinase C, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and casein kinase II. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):535–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung A. T., Imagawa T., Block B., Franzini-Armstrong C., Campbell K. P. Biochemical and ultrastructural characterization of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for a 52,000 Da subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):994–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung A. T., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P. Structural characterization of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for two distinct high molecular weight subunits. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7943–7946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton M. E., Froehner S. C. Monoclonal antibody identifies a 200-kDa subunit of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11904–11907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoki K., Florio V., Catterall W. A. Activation of purified calcium channels by stoichiometric protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6816–6820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callahan C. M., Hosey M. M. Multiple phosphorylation sites in the 165-kilodalton peptide associated with dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6071–6077. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posnett D. N., McGrath H., Tam J. P. A novel method for producing anti-peptide antibodies. Production of site-specific antibodies to the T cell antigen receptor beta-chain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1719–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios E., Brum G. Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):717–720. doi: 10.1038/325717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth P., Röhrkasten A., Biel M., Bosse E., Regulla S., Meyer H. E., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure of the beta subunit of the DHP-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1115–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.2549640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhrkasten A., Meyer H. E., Nastainczyk W., Sieber M., Hofmann F. cAMP-dependent protein kinase rapidly phosphorylates serine- 687 of the skeletal muscle receptor for calcium channel blockers. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15325–15329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., McCleskey E. W., Almers W. Dihydropyridine receptors in muscle are voltage-dependent but most are not functional calcium channels. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):747–751. doi: 10.1038/314747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. H., Campbell K. P. Characterization of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor using subunit-specific polyclonal antibodies. Evidence for a 32,000-Da subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2816–2825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. H., Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P. Identification and characterization of the dihydropyridine-binding subunit of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12309–12315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Seagar M. J., Jones J. F., Reber B. F., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Powell J. A., Numa S. Restoration of excitation-contraction coupling and slow calcium current in dysgenic muscle by dihydropyridine receptor complementary DNA. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):134–139. doi: 10.1038/336134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggle D. J., Janis R. A. Calcium channel ligands. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:347–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaghy P. L., Striessnig J., Miwa K., Knaus H. G., Itagaki K., McKenna E., Glossmann H., Schwartz A. Identification of a novel 1,4-dihydropyridine- and phenylalkylamine-binding polypeptide in calcium channel preparations. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14337–14342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. H., Fiol C. J., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Bell A. W., Hermodson M. A., Roach P. J. Identification of phosphorylation sites in peptides using a gas-phase sequencer. Anal Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;174(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]