Abstract
In the title compound, C25H18Cl2N2O, the cyclohexene ring has a sofa conformation. All the substituents in the cyclohexene ring, except the cyano group (which is axial) occupy equatorial positions. The crystal structure is stabilized through N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a chain extending along the b axis and through C—H⋯N and C—H⋯Cl interactions. It is remarkable that only one of the amino H atoms is involved in hydrogen bonding.
Related literature
For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Rodriguez & Dulcere (1993 ▶).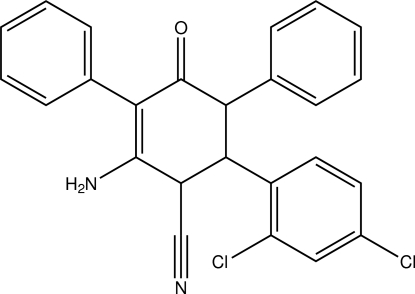
Experimental
Crystal data
C25H18Cl2N2O
M r = 433.31
Monoclinic,
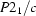
a = 10.8650 (9) Å
b = 14.0010 (3) Å
c = 14.3021 (6) Å
β = 94.697 (10)°
V = 2168.3 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.32 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.21 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
18613 measured reflections
3269 independent reflections
2457 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.041
θmax = 23.7°
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.127
S = 1.07
3269 reflections
271 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL/PC (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL/PC; molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL/PC.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035567/bt5346sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035567/bt5346Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2B⋯O1i | 0.86 | 1.91 | 2.759 (3) | 171 |
| C33—H33⋯N11ii | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.402 (4) | 131 |
| C52—H52⋯Cl2iii | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.897 (3) | 174 |
| C54—H54⋯N11iv | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.541 (4) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 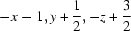 ; (ii)
; (ii) 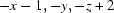 ; (iii)
; (iii) 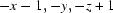 ; (iv)
; (iv) 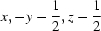 .
.
Acknowledgments
SAB sincerely thank the Vice Chancellor and Management of Kalasalingam University, Anand Nagar, Krishnan Koil, for their support and encouragement. SA thanks the Vice Chancellor of Anna University of Technology, Tirunelveli, for his support and encouragement.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Alkenes undergo co-halogenation reactions to afford bifunctional compounds which serve as potential synthons towards the synthesis of various heterocyclic compounds (Rodriguez & Dulcere, 1993). The regio/stereoselectivity of such addition reactions is governed by various factors, one being structural features of the alkene. We were interested in investigating some of the structure features in the title compound, which may alter the regio/stereoselectivity in addition reactions.
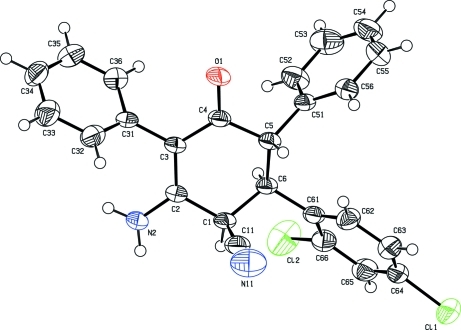
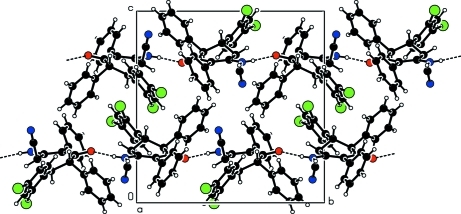
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The cyclohexene ring is in a sofa conformation. Two phenyl rings are oriented with a dihedral angle of 54.8 (1)° to each other. Further, the dichlorophenyl rings are making dihedral angles of 66.7 (1)° and 84.3 (1)° with the phenyl rings of C31/C36 and C51/C56 respectively. The crystal structure is stabilized by intermolecular C—H···N, C—H···Cl and classical N—H···O hydrgeon bonds (Tab. 1). The packing diagram of the title compound is shown in Fig. 2.
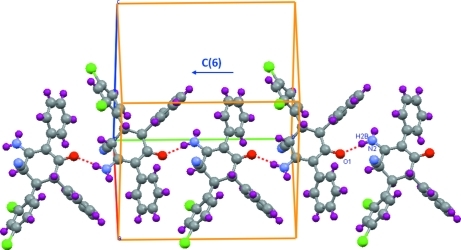
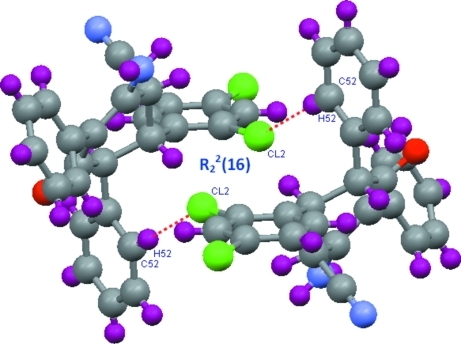
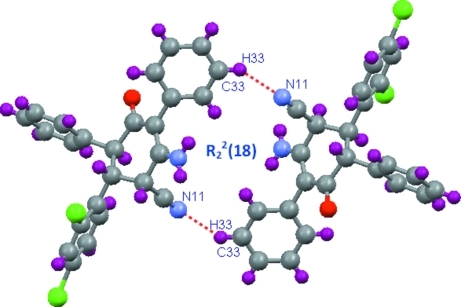
A chain C(6) motif extending along the b axis of the unit cell is observed through classical N—H···O hydrogen bond (Fig.3). Centrosymmetric ring R22(16) motif is formed around the crystallographic inversion centre through C—H···Cl bond (Fig. 4). Further, another ring R22(18) motif is observed around crystallographic inversion centre through a C—H···N bond (Fig. 5). These ring motifs are connected along c axis of the unit cell through another C—H···N bond [C54—H54···N11(x, -y - 1/2, z - 1/2)].
Experimental
A mixture of 1,3-diphenylacetone 5 (1 mmol), 2-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methylene]malononitrile (1 mmol), and sodium ethoxide (2 mmol) was ground well in a mortar and pestle at ambient temperature for about 15–30 sec. Then water (50–70 ml) was added to the mixture and the product was filtered and washed with water, dried in vacuo and subjected to flash chromatographic purification employing flash silica gel (230–400 mesh) with petroleum ether-ethyl acetate mixture as eluent. The products were further recrystallized from ethanol-ethyl acetate mixture (1:2 v/v).
Refinement
All the H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq (parent atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The title molecule with the atom numbering scheme. The displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title structure viewed down the a axis. (Cl is shown in green, N in blue, O in red, C in black and H as circle)
Fig. 3.
Chain C(6) motif formed through N—H···O hydrogen bonds. H-bond are drawn as dashed lines. (Cl is shown in green, N in blue, O in red, C in black and H in pink)
Fig. 4.
Ring R22(16) motif formed through C—H···Cl hydrogen bonds. H-bonds are drawn as dashed lines. (Cl is shown in green, N in blue, O in red, C in black and H in pink)
Fig. 5.
Ring R22(18) motif formed through C—H···N hydrogen bonds. H-bonds are drawn as dashed lines. (Cl is shown in green, N in blue, O in red, C in black and H in pink)
Crystal data
| C25H18Cl2N2O | F(000) = 896 |
| Mr = 433.31 | Dx = 1.327 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4312 reflections |
| a = 10.8650 (9) Å | θ = 2.1–20.1° |
| b = 14.0010 (3) Å | µ = 0.32 mm−1 |
| c = 14.3021 (6) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 94.697 (10)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 2168.3 (2) Å3 | 0.21 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2457 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.041 |
| graphite | θmax = 23.7°, θmin = 1.9° |
| ω scans | h = −12→12 |
| 18613 measured reflections | k = −15→15 |
| 3269 independent reflections | l = −11→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.127 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0688P)2 + 0.6095P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3269 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 271 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F^2^ against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F^2^, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F^2^. The threshold expression of F^2^ > σ(F^2^) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F^2^ are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | −0.4045 (2) | 0.02803 (16) | 0.72770 (17) | 0.0330 (6) | |
| H1 | −0.4171 | 0.0873 | 0.6918 | 0.040* | |
| C11 | −0.3249 (3) | 0.04896 (18) | 0.8132 (2) | 0.0431 (7) | |
| N11 | −0.2610 (3) | 0.0631 (2) | 0.8783 (2) | 0.0732 (8) | |
| C2 | −0.5291 (2) | −0.00720 (16) | 0.75371 (18) | 0.0368 (6) | |
| N2 | −0.6097 (2) | 0.06106 (15) | 0.76626 (19) | 0.0593 (7) | |
| H2A | −0.6820 | 0.0468 | 0.7825 | 0.071* | |
| H2B | −0.5901 | 0.1198 | 0.7582 | 0.071* | |
| C3 | −0.5514 (2) | −0.10311 (16) | 0.76488 (18) | 0.0339 (6) | |
| C31 | −0.6736 (2) | −0.13559 (16) | 0.79292 (18) | 0.0349 (6) | |
| C32 | −0.7174 (3) | −0.1068 (2) | 0.8762 (2) | 0.0499 (7) | |
| H32 | −0.6686 | −0.0681 | 0.9170 | 0.060* | |
| C33 | −0.8332 (3) | −0.1348 (2) | 0.9000 (2) | 0.0570 (8) | |
| H33 | −0.8622 | −0.1139 | 0.9559 | 0.068* | |
| C34 | −0.9040 (3) | −0.1925 (2) | 0.8420 (2) | 0.0529 (8) | |
| H34 | −0.9823 | −0.2105 | 0.8573 | 0.064* | |
| C35 | −0.8600 (3) | −0.2245 (2) | 0.7603 (2) | 0.0553 (8) | |
| H35 | −0.9075 | −0.2658 | 0.7214 | 0.066* | |
| C36 | −0.7462 (2) | −0.19578 (18) | 0.7358 (2) | 0.0450 (7) | |
| H36 | −0.7179 | −0.2173 | 0.6800 | 0.054* | |
| C4 | −0.4589 (2) | −0.17242 (16) | 0.74985 (17) | 0.0341 (6) | |
| O1 | −0.47452 (17) | −0.25760 (11) | 0.76898 (14) | 0.0518 (5) | |
| C5 | −0.3365 (2) | −0.14431 (15) | 0.71259 (17) | 0.0317 (6) | |
| H5 | −0.2750 | −0.1411 | 0.7665 | 0.038* | |
| C51 | −0.2942 (2) | −0.22077 (16) | 0.64729 (17) | 0.0326 (6) | |
| C52 | −0.3644 (3) | −0.2437 (2) | 0.56597 (19) | 0.0503 (7) | |
| H52 | −0.4376 | −0.2109 | 0.5501 | 0.060* | |
| C53 | −0.3271 (3) | −0.3151 (2) | 0.5073 (2) | 0.0637 (9) | |
| H53 | −0.3759 | −0.3305 | 0.4529 | 0.076* | |
| C54 | −0.2196 (3) | −0.3629 (2) | 0.5289 (2) | 0.0623 (9) | |
| H54 | −0.1945 | −0.4104 | 0.4891 | 0.075* | |
| C55 | −0.1493 (3) | −0.3410 (2) | 0.6084 (2) | 0.0587 (8) | |
| H55 | −0.0756 | −0.3735 | 0.6233 | 0.070* | |
| C56 | −0.1864 (2) | −0.27073 (18) | 0.6676 (2) | 0.0442 (7) | |
| H56 | −0.1376 | −0.2569 | 0.7224 | 0.053* | |
| C6 | −0.3415 (2) | −0.04533 (15) | 0.66641 (16) | 0.0304 (6) | |
| H6 | −0.3942 | −0.0514 | 0.6078 | 0.037* | |
| C61 | −0.2188 (2) | −0.00592 (16) | 0.64069 (17) | 0.0331 (6) | |
| C62 | −0.1086 (2) | −0.02628 (18) | 0.69160 (19) | 0.0421 (7) | |
| H62 | −0.1091 | −0.0689 | 0.7414 | 0.051* | |
| C63 | 0.0019 (3) | 0.01363 (19) | 0.6720 (2) | 0.0495 (7) | |
| H63 | 0.0744 | −0.0020 | 0.7078 | 0.059* | |
| C64 | 0.0039 (2) | 0.07653 (18) | 0.5992 (2) | 0.0447 (7) | |
| C65 | −0.1028 (3) | 0.09852 (19) | 0.54492 (19) | 0.0482 (7) | |
| H65 | −0.1012 | 0.1407 | 0.4948 | 0.058* | |
| C66 | −0.2121 (2) | 0.05682 (18) | 0.56630 (18) | 0.0408 (6) | |
| Cl1 | 0.14075 (7) | 0.13127 (6) | 0.57487 (7) | 0.0697 (3) | |
| Cl2 | −0.34352 (8) | 0.08729 (7) | 0.49620 (6) | 0.0767 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0406 (14) | 0.0178 (12) | 0.0411 (15) | −0.0015 (10) | 0.0056 (12) | 0.0034 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0529 (17) | 0.0276 (14) | 0.0496 (19) | −0.0052 (12) | 0.0085 (15) | −0.0023 (13) |
| N11 | 0.091 (2) | 0.0676 (19) | 0.0584 (18) | −0.0100 (16) | −0.0111 (17) | −0.0102 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0385 (14) | 0.0216 (13) | 0.0509 (16) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0069 (12) | −0.0025 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0484 (14) | 0.0201 (11) | 0.113 (2) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0288 (14) | 0.0001 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0390 (14) | 0.0188 (12) | 0.0445 (15) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0072 (11) | −0.0015 (10) |
| C31 | 0.0398 (14) | 0.0173 (12) | 0.0481 (16) | −0.0011 (10) | 0.0057 (12) | 0.0014 (11) |
| C32 | 0.0500 (17) | 0.0442 (16) | 0.0569 (19) | −0.0121 (13) | 0.0128 (14) | −0.0087 (14) |
| C33 | 0.0554 (18) | 0.059 (2) | 0.059 (2) | −0.0105 (16) | 0.0200 (15) | −0.0041 (16) |
| C34 | 0.0399 (15) | 0.0469 (17) | 0.073 (2) | −0.0075 (13) | 0.0103 (15) | 0.0120 (15) |
| C35 | 0.0475 (17) | 0.0484 (18) | 0.069 (2) | −0.0146 (14) | 0.0020 (16) | −0.0070 (15) |
| C36 | 0.0460 (16) | 0.0388 (15) | 0.0505 (17) | −0.0032 (13) | 0.0063 (13) | −0.0033 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0414 (14) | 0.0208 (13) | 0.0401 (15) | −0.0012 (11) | 0.0043 (11) | −0.0006 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0584 (12) | 0.0189 (10) | 0.0814 (14) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0072 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0370 (13) | 0.0220 (12) | 0.0352 (14) | 0.0006 (10) | −0.0015 (11) | 0.0004 (10) |
| C51 | 0.0376 (14) | 0.0218 (12) | 0.0388 (15) | −0.0035 (10) | 0.0065 (12) | 0.0008 (10) |
| C52 | 0.0589 (17) | 0.0416 (16) | 0.0487 (18) | 0.0059 (14) | −0.0059 (14) | −0.0082 (14) |
| C53 | 0.091 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.0431 (18) | −0.0098 (19) | 0.0013 (17) | −0.0123 (15) |
| C54 | 0.083 (2) | 0.0398 (17) | 0.068 (2) | −0.0021 (17) | 0.0296 (19) | −0.0153 (16) |
| C55 | 0.0547 (18) | 0.0407 (17) | 0.083 (2) | 0.0088 (14) | 0.0164 (17) | −0.0076 (16) |
| C56 | 0.0407 (15) | 0.0344 (15) | 0.0573 (18) | 0.0007 (12) | 0.0024 (13) | −0.0041 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0348 (13) | 0.0208 (12) | 0.0354 (14) | −0.0018 (10) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0017 (10) |
| C61 | 0.0396 (14) | 0.0224 (12) | 0.0376 (15) | −0.0010 (10) | 0.0054 (11) | −0.0021 (11) |
| C62 | 0.0411 (15) | 0.0352 (14) | 0.0498 (17) | −0.0036 (12) | 0.0021 (13) | 0.0074 (12) |
| C63 | 0.0398 (15) | 0.0422 (16) | 0.066 (2) | −0.0031 (13) | 0.0035 (14) | −0.0018 (15) |
| C64 | 0.0464 (17) | 0.0334 (15) | 0.0574 (18) | −0.0070 (12) | 0.0222 (14) | −0.0106 (13) |
| C65 | 0.063 (2) | 0.0375 (15) | 0.0464 (17) | −0.0061 (14) | 0.0205 (15) | 0.0027 (13) |
| C66 | 0.0467 (15) | 0.0349 (14) | 0.0405 (15) | −0.0003 (12) | 0.0026 (12) | 0.0035 (12) |
| Cl1 | 0.0587 (5) | 0.0600 (5) | 0.0957 (7) | −0.0188 (4) | 0.0390 (4) | −0.0138 (4) |
| Cl2 | 0.0674 (6) | 0.0881 (7) | 0.0720 (6) | −0.0043 (5) | −0.0109 (4) | 0.0438 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C11 | 1.469 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.516 (3) | C51—C56 | 1.375 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.546 (3) | C51—C52 | 1.375 (4) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9800 | C52—C53 | 1.388 (4) |
| C11—N11 | 1.132 (3) | C52—H52 | 0.9300 |
| C2—N2 | 1.319 (3) | C53—C54 | 1.358 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.376 (3) | C53—H53 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C54—C55 | 1.353 (5) |
| N2—H2B | 0.8600 | C54—H54 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.426 (3) | C55—C56 | 1.380 (4) |
| C3—C31 | 1.489 (3) | C55—H55 | 0.9300 |
| C31—C36 | 1.376 (3) | C56—H56 | 0.9300 |
| C31—C32 | 1.379 (4) | C6—C61 | 1.516 (3) |
| C32—C33 | 1.387 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9800 |
| C32—H32 | 0.9300 | C61—C62 | 1.379 (3) |
| C33—C34 | 1.353 (4) | C61—C66 | 1.386 (3) |
| C33—H33 | 0.9300 | C62—C63 | 1.374 (4) |
| C34—C35 | 1.373 (4) | C62—H62 | 0.9300 |
| C34—H34 | 0.9300 | C63—C64 | 1.365 (4) |
| C35—C36 | 1.371 (4) | C63—H63 | 0.9300 |
| C35—H35 | 0.9300 | C64—C65 | 1.376 (4) |
| C36—H36 | 0.9300 | C64—Cl1 | 1.734 (3) |
| C4—O1 | 1.238 (3) | C65—C66 | 1.380 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.524 (3) | C65—H65 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C51 | 1.517 (3) | C66—Cl2 | 1.730 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.534 (3) | ||
| C11—C1—C2 | 109.7 (2) | C56—C51—C52 | 117.7 (2) |
| C11—C1—C6 | 110.3 (2) | C56—C51—C5 | 121.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 111.65 (18) | C52—C51—C5 | 120.7 (2) |
| C11—C1—H1 | 108.4 | C51—C52—C53 | 120.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 108.4 | C51—C52—H52 | 119.7 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 108.4 | C53—C52—H52 | 119.7 |
| N11—C11—C1 | 177.9 (3) | C54—C53—C52 | 120.4 (3) |
| N2—C2—C3 | 124.5 (2) | C54—C53—H53 | 119.8 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 114.5 (2) | C52—C53—H53 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.0 (2) | C55—C54—C53 | 119.7 (3) |
| C2—N2—H2A | 120.0 | C55—C54—H54 | 120.1 |
| C2—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C53—C54—H54 | 120.1 |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C54—C55—C56 | 120.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.9 (2) | C54—C55—H55 | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—C31 | 119.9 (2) | C56—C55—H55 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C31 | 119.2 (2) | C51—C56—C55 | 121.4 (3) |
| C36—C31—C32 | 118.0 (2) | C51—C56—H56 | 119.3 |
| C36—C31—C3 | 120.5 (2) | C55—C56—H56 | 119.3 |
| C32—C31—C3 | 121.5 (2) | C61—C6—C5 | 115.67 (19) |
| C31—C32—C33 | 121.0 (3) | C61—C6—C1 | 109.56 (18) |
| C31—C32—H32 | 119.5 | C5—C6—C1 | 110.94 (18) |
| C33—C32—H32 | 119.5 | C61—C6—H6 | 106.7 |
| C34—C33—C32 | 120.0 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 106.7 |
| C34—C33—H33 | 120.0 | C1—C6—H6 | 106.7 |
| C32—C33—H33 | 120.0 | C62—C61—C66 | 116.0 (2) |
| C33—C34—C35 | 119.8 (3) | C62—C61—C6 | 122.6 (2) |
| C33—C34—H34 | 120.1 | C66—C61—C6 | 121.3 (2) |
| C35—C34—H34 | 120.1 | C63—C62—C61 | 122.9 (3) |
| C36—C35—C34 | 120.4 (3) | C63—C62—H62 | 118.5 |
| C36—C35—H35 | 119.8 | C61—C62—H62 | 118.5 |
| C34—C35—H35 | 119.8 | C64—C63—C62 | 119.1 (3) |
| C35—C36—C31 | 120.9 (3) | C64—C63—H63 | 120.4 |
| C35—C36—H36 | 119.6 | C62—C63—H63 | 120.4 |
| C31—C36—H36 | 119.6 | C63—C64—C65 | 120.6 (2) |
| O1—C4—C3 | 120.7 (2) | C63—C64—Cl1 | 120.4 (2) |
| O1—C4—C5 | 117.7 (2) | C65—C64—Cl1 | 119.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.5 (2) | C64—C65—C66 | 118.7 (3) |
| C51—C5—C4 | 110.51 (19) | C64—C65—H65 | 120.6 |
| C51—C5—C6 | 111.97 (19) | C66—C65—H65 | 120.6 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 112.53 (19) | C65—C66—C61 | 122.6 (2) |
| C51—C5—H5 | 107.2 | C65—C66—Cl2 | 116.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 107.2 | C61—C66—Cl2 | 120.5 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 107.2 | ||
| C2—C1—C11—N11 | 121 (8) | C56—C51—C52—C53 | 0.3 (4) |
| C6—C1—C11—N11 | −2(8) | C5—C51—C52—C53 | −178.5 (2) |
| C11—C1—C2—N2 | 87.0 (3) | C51—C52—C53—C54 | −0.8 (5) |
| C6—C1—C2—N2 | −150.4 (2) | C52—C53—C54—C55 | 0.5 (5) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | −91.5 (3) | C53—C54—C55—C56 | 0.1 (5) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 31.1 (3) | C52—C51—C56—C55 | 0.4 (4) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | 180.0 (3) | C5—C51—C56—C55 | 179.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.7 (4) | C54—C55—C56—C51 | −0.6 (4) |
| N2—C2—C3—C31 | 0.0 (4) | C51—C5—C6—C61 | −63.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C31 | 178.4 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C61 | 171.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C31—C36 | 120.0 (3) | C51—C5—C6—C1 | 170.83 (19) |
| C4—C3—C31—C36 | −59.9 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 45.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C31—C32 | −60.1 (4) | C11—C1—C6—C61 | −58.9 (2) |
| C4—C3—C31—C32 | 120.0 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C61 | 178.81 (19) |
| C36—C31—C32—C33 | −2.4 (4) | C11—C1—C6—C5 | 70.0 (2) |
| C3—C31—C32—C33 | 177.7 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −52.3 (3) |
| C31—C32—C33—C34 | 1.2 (5) | C5—C6—C61—C62 | −31.7 (3) |
| C32—C33—C34—C35 | 1.1 (5) | C1—C6—C61—C62 | 94.5 (3) |
| C33—C34—C35—C36 | −2.1 (5) | C5—C6—C61—C66 | 151.3 (2) |
| C34—C35—C36—C31 | 0.8 (4) | C1—C6—C61—C66 | −82.4 (3) |
| C32—C31—C36—C35 | 1.4 (4) | C66—C61—C62—C63 | 1.0 (4) |
| C3—C31—C36—C35 | −178.7 (2) | C6—C61—C62—C63 | −176.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | 172.7 (2) | C61—C62—C63—C64 | 0.2 (4) |
| C31—C3—C4—O1 | −7.4 (4) | C62—C63—C64—C65 | −1.3 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −5.6 (4) | C62—C63—C64—Cl1 | 177.9 (2) |
| C31—C3—C4—C5 | 174.4 (2) | C63—C64—C65—C66 | 1.0 (4) |
| O1—C4—C5—C51 | 38.1 (3) | Cl1—C64—C65—C66 | −178.2 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C51 | −143.6 (2) | C64—C65—C66—C61 | 0.4 (4) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | 164.1 (2) | C64—C65—C66—Cl2 | 179.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −17.7 (3) | C62—C61—C66—C65 | −1.4 (4) |
| C4—C5—C51—C56 | −117.1 (3) | C6—C61—C66—C65 | 175.8 (2) |
| C6—C5—C51—C56 | 116.6 (2) | C62—C61—C66—Cl2 | 179.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C51—C52 | 61.7 (3) | C6—C61—C66—Cl2 | −3.5 (3) |
| C6—C5—C51—C52 | −64.6 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2B···O1i | 0.86 | 1.91 | 2.759 (3) | 171 |
| C33—H33···N11ii | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.402 (4) | 131 |
| C52—H52···Cl2iii | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.897 (3) | 174 |
| C54—H54···N11iv | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.541 (4) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x−1, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x−1, −y, −z+2; (iii) −x−1, −y, −z+1; (iv) x, −y−1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5346).
References
- Bruker (2001). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Rodriguez, J. & Dulcere, J.-P. (1993). Synthesis, pp. 1176–1205.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035567/bt5346sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810035567/bt5346Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report