Abstract
In the title compound, C15H12ClF3N4O2, the dihydropyrimidine ring exhibits an envelope conformation. The dihedral angle between the mean planes of the dihydropyrimidine and phenyl rings is 83.94 (6)°. The OCH2CH3 group is disordered over two sites with occupancies of 0.155 (3) and 0.845 (3). The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the anticancer activity, inhibition of the MDM2-p53 protein–protein interaction and the antituberculosis and dehydrogenase inhibitory activity of [1,2,4]triazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives, see: Zhang et al. (2007 ▶); Allen et al. (2009 ▶); Pereyaslavskaya et al. (2008 ▶); Gujjar et al. (2009 ▶). For the bioactivity of trifluoromethylated molecules, see: Kirk, (2006 ▶). For the preparation of trifluoromethylated [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives, see Pryadeina et al. (2004 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).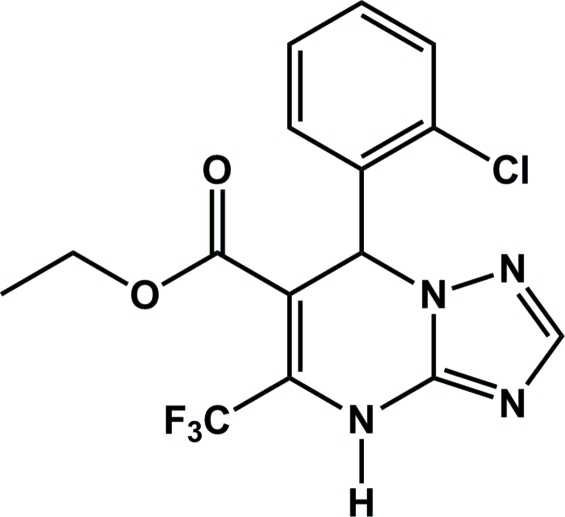
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H12ClF3N4O2
M r = 372.74
Monoclinic,

a = 9.8927 (12) Å
b = 6.8055 (6) Å
c = 24.403 (3) Å
β = 99.237 (9)°
V = 1621.6 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 113 K
0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear;Rigaku/MSC, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.930, T max = 0.945
14364 measured reflections
3835 independent reflections
3058 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.043
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.121
S = 1.08
3835 reflections
242 parameters
6 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810037712/hg2715sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810037712/hg2715Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯N4i | 0.90 (2) | 1.96 (2) | 2.843 (2) | 166.3 (19) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Special Fund for the President’s Project (Project 2009 KJZ20) of Xuzhou Medical College.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives are known because of their wide range of biological activities. For example, some of the trizaolopyrimidines can be used as anticancer agents (Zhang et al., 2007), inhibitor of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction (Allen et al., 2009), antituberculosis agents (Pereyaslavskaya et al., 2008) and dehydrogenase inhibitors (Gujjar et al., 2009). Therefore, the preparation or structural modification of these nitrogen-containing heterocyclic scaffolds is of considerable interest for both organic and medicinal chemistry. The introduction of a trifluoromethyl group into organic molecules often changes their physical, chemical, and physiological properties (Kirk, 2006). During the synthesis of trifluoromethylated 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives, the title compound (I) was isolated and its structure was determined by X-ray analysis. The results are presented here.
In the title molecule (Fig. 1), the 1,2,4-triazole ring adopts a planar conformation. Cremer & Pople puckering analysis (Cremer &Pople, 1975) can not be performed, for its weighted average absolute torsion angle is 0.7°, less than 5.0°. The dihydropyrimidine ring system is in an envelope conformation, for Cremer & Pople puckering analysis shows θ(2) and φ(2) are 0.094 (2)Å and 346.4 (10)°, respectively. Its puckering amplitude (Q) is 0.099 (2)Å. Besides, the distance between atom C2 and the mean N2/C1/N1/C4/C3 plane (r.m.s. deviation 0.016 Å) is 0.136 (2) Å, which also confirms the conformation of the dihydropyrimidine ring. The dihedral angle between the aforementioned weighted plane and phenyl ring is 83.94 (6)°, which shows the two units are nearly perpendicular.
The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular N—H···N hydrogen bonds (Table 1, Fig.2).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized according the procedure reported by Pryadeina et al. (2004). A mixture of 0.01 mol of ethyl 4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxobutanoate, 0.01 mol of 2-chlorobenzaldehyde and 0.01 mol of 1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine in 20 mL of ethanol containing a catalytic amount of hydrochloric acid was heated for 12 h under reflux. Then the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was added to a solution of p-toluenesulfonic acid, 0.05 g, in 100 mL of benzene, and the mixture was heated for 8 h with simultaneous removal of water as azeotrope with benzene. The solution was filtered while hot, the filtrate was evaporated, and the precipitate was recrystallized from ethanol. Cooling the ethanol solution slowly gave single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction.
Refinement
The H atoms bound to N atoms were located in a difference map and were refined freely [refined N–H length, 0.90 (2)Å]. All other H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C–H = 0.95, 0.98, 0.99 or 1.00 Å, and included in the final cycles of refinement using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(parent atom). The OCH2CH3 group is disordered over two sites with occupancies of 0.155 (3) and 0.845 (3). The atom pairs of C12 and C12', C13 and C13', and O2 and O2' are constrained to have the same anisotropic displacement parameters. The bond lengths of ethyl group of C12–C13 and C12'–C13' is restrained to 1.54Å with esd of 0.01Å. The distance between O2 and C12, O2' and C12' is restrained to 1.42Å with esd of 0.01Å. The atoms of O2 and O2' are restrained to be at the distance of 1.38Å from the atom of C11 with esd of 0.01Å.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme. The minor part of the disordered moieties were omitted for clarity.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram of the title compound. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The minor part of the disordered moieties were omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C15H12ClF3N4O2 | F(000) = 760 |
| Mr = 372.74 | Dx = 1.527 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71070 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 3832 reflections |
| a = 9.8927 (12) Å | θ = 2.4–27.9° |
| b = 6.8055 (6) Å | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| c = 24.403 (3) Å | T = 113 K |
| β = 99.237 (9)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1621.6 (3) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn diffractometer | 3835 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 3058 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| confocal | Rint = 0.043 |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 2.4° |
| ω scans | h = −13→13 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan CrystalClear | k = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.930, Tmax = 0.945 | l = −32→32 |
| 14364 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.121 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.08 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0596P)2 + 0.2191P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3835 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 242 parameters | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 6 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | −0.02142 (6) | 1.41310 (7) | 0.14247 (2) | 0.04311 (18) | |
| F1 | 0.35904 (10) | 0.54406 (16) | 0.01321 (5) | 0.0375 (3) | |
| F2 | 0.44949 (11) | 0.82808 (16) | 0.01419 (5) | 0.0334 (3) | |
| F3 | 0.47647 (11) | 0.65227 (16) | 0.08811 (5) | 0.0329 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.33660 (14) | 1.2697 (2) | 0.11875 (6) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.14288 (14) | 0.6813 (2) | 0.03869 (6) | 0.0211 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.00227 (14) | 0.9257 (2) | 0.06666 (6) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| N3 | −0.13449 (15) | 0.9673 (2) | 0.06434 (6) | 0.0261 (3) | |
| N4 | −0.10446 (14) | 0.6764 (2) | 0.02200 (6) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.01658 (17) | 0.7543 (2) | 0.04212 (7) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.11062 (17) | 1.0474 (2) | 0.09691 (7) | 0.0205 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.1003 | 1.1842 | 0.0819 | 0.025* | |
| C3 | 0.24727 (17) | 0.9649 (2) | 0.08603 (7) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.25580 (16) | 0.7931 (2) | 0.05905 (7) | 0.0199 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.09913 (17) | 1.0529 (2) | 0.15815 (7) | 0.0217 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.04123 (19) | 1.2105 (3) | 0.18215 (8) | 0.0274 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.0304 (2) | 1.2109 (3) | 0.23816 (8) | 0.0356 (5) | |
| H7 | −0.0083 | 1.3206 | 0.2541 | 0.043* | |
| C8 | 0.0765 (2) | 1.0501 (3) | 0.27056 (8) | 0.0381 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.0690 | 1.0490 | 0.3089 | 0.046* | |
| C9 | 0.1329 (2) | 0.8925 (3) | 0.24762 (8) | 0.0355 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.1644 | 0.7823 | 0.2700 | 0.043* | |
| C10 | 0.14409 (19) | 0.8941 (3) | 0.19169 (8) | 0.0284 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.1833 | 0.7842 | 0.1761 | 0.034* | |
| C11 | 0.36016 (18) | 1.1040 (3) | 0.10611 (7) | 0.0249 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.48511 (16) | 1.0381 (3) | 0.10610 (10) | 0.0390 (6) | 0.845 (3) |
| C12 | 0.5990 (2) | 1.1697 (4) | 0.12467 (11) | 0.0315 (6) | 0.845 (3) |
| H12A | 0.5678 | 1.3077 | 0.1199 | 0.038* | 0.845 (3) |
| H12B | 0.6721 | 1.1489 | 0.1019 | 0.038* | 0.845 (3) |
| C13 | 0.6540 (3) | 1.1316 (5) | 0.18435 (12) | 0.0518 (8) | 0.845 (3) |
| H13A | 0.5832 | 1.1607 | 0.2070 | 0.078* | 0.845 (3) |
| H13B | 0.7338 | 1.2157 | 0.1960 | 0.078* | 0.845 (3) |
| H13C | 0.6812 | 0.9934 | 0.1892 | 0.078* | 0.845 (3) |
| O2' | 0.4728 (9) | 0.9900 (15) | 0.1298 (5) | 0.0390 (6) | 0.155 (3) |
| C12' | 0.5996 (11) | 1.0954 (19) | 0.1454 (7) | 0.0315 (6) | 0.155 (3) |
| H12C | 0.5860 | 1.2056 | 0.1704 | 0.038* | 0.155 (3) |
| H12D | 0.6309 | 1.1499 | 0.1120 | 0.038* | 0.155 (3) |
| C13' | 0.7072 (14) | 0.952 (2) | 0.1752 (7) | 0.0518 (8) | 0.155 (3) |
| H13D | 0.6847 | 0.9190 | 0.2117 | 0.078* | 0.155 (3) |
| H13E | 0.7979 | 1.0133 | 0.1796 | 0.078* | 0.155 (3) |
| H13F | 0.7076 | 0.8317 | 0.1530 | 0.078* | 0.155 (3) |
| C14 | 0.38686 (17) | 0.7050 (2) | 0.04419 (7) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| C15 | −0.19178 (18) | 0.8142 (3) | 0.03716 (7) | 0.0255 (4) | |
| H15 | −0.2884 | 0.8001 | 0.0285 | 0.031* | |
| H1 | 0.146 (2) | 0.567 (3) | 0.0203 (9) | 0.039 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0546 (4) | 0.0261 (3) | 0.0533 (4) | 0.0094 (2) | 0.0228 (3) | 0.0025 (2) |
| F1 | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0361 (6) | 0.0564 (8) | −0.0049 (5) | 0.0118 (5) | −0.0233 (5) |
| F2 | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0366 (6) | 0.0418 (7) | −0.0032 (4) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0102 (5) |
| F3 | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0370 (6) | 0.0359 (6) | 0.0063 (5) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0070 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0310 (8) | 0.0290 (7) | 0.0506 (9) | −0.0071 (6) | 0.0063 (6) | −0.0098 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0259 (8) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0039 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0150 (7) | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0231 (7) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0043 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0317 (8) | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0046 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0172 (7) | 0.0261 (8) | 0.0245 (8) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0028 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0175 (8) | 0.0224 (8) | 0.0191 (8) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0208 (8) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0027 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0186 (8) | 0.0250 (8) | 0.0207 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0235 (8) | 0.0194 (8) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0177 (8) | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0205 (8) | −0.0036 (7) | 0.0027 (7) | −0.0028 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0251 (9) | 0.0283 (9) | 0.0295 (10) | −0.0030 (7) | 0.0069 (7) | −0.0045 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0440 (12) | 0.0329 (11) | −0.0062 (9) | 0.0134 (8) | −0.0141 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0311 (11) | 0.0631 (14) | 0.0207 (9) | −0.0098 (10) | 0.0057 (8) | −0.0034 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0525 (12) | 0.0260 (10) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0043 (8) | 0.0104 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0249 (9) | 0.0341 (10) | 0.0263 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0046 (7) | 0.0019 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0215 (9) | 0.0318 (10) | 0.0217 (9) | −0.0031 (7) | 0.0051 (7) | −0.0037 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0652 (16) | −0.0059 (7) | 0.0001 (8) | −0.0180 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0184 (10) | 0.0282 (14) | 0.0467 (16) | −0.0069 (9) | 0.0016 (10) | −0.0065 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0329 (15) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0506 (17) | −0.0184 (13) | 0.0010 (12) | −0.0013 (15) |
| O2' | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0652 (16) | −0.0059 (7) | 0.0001 (8) | −0.0180 (10) |
| C12' | 0.0184 (10) | 0.0282 (14) | 0.0467 (16) | −0.0069 (9) | 0.0016 (10) | −0.0065 (11) |
| C13' | 0.0329 (15) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0506 (17) | −0.0184 (13) | 0.0010 (12) | −0.0013 (15) |
| C14 | 0.0197 (8) | 0.0227 (8) | 0.0258 (9) | −0.0040 (6) | 0.0059 (7) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0313 (9) | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0020 (7) | −0.0029 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C6 | 1.7407 (19) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| F1—C14 | 1.3339 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.369 (3) |
| F2—C14 | 1.3293 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| F3—C14 | 1.326 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.387 (3) |
| O1—C11 | 1.202 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.359 (2) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C4 | 1.377 (2) | C11—O2 | 1.315 (2) |
| N1—H1 | 0.90 (2) | C11—O2' | 1.404 (8) |
| N2—C1 | 1.329 (2) | O2—C12 | 1.453 (3) |
| N2—N3 | 1.3744 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.493 (4) |
| N2—C2 | 1.458 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| N3—C15 | 1.314 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| N4—C1 | 1.329 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| N4—C15 | 1.366 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C5 | 1.517 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.526 (2) | O2'—C12' | 1.442 (9) |
| C2—H2 | 1.0000 | C12'—C13' | 1.539 (9) |
| C3—C4 | 1.351 (2) | C12'—H12C | 0.9900 |
| C3—C11 | 1.486 (2) | C12'—H12D | 0.9900 |
| C4—C14 | 1.524 (2) | C13'—H13D | 0.9800 |
| C5—C10 | 1.385 (2) | C13'—H13E | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.389 (2) | C13'—H13F | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.388 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.384 (3) | ||
| C1—N1—C4 | 118.45 (14) | C5—C10—C9 | 121.27 (18) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 116.7 (14) | C5—C10—H10 | 119.4 |
| C4—N1—H1 | 124.6 (14) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.4 |
| C1—N2—N3 | 109.72 (13) | O1—C11—O2 | 122.77 (17) |
| C1—N2—C2 | 127.16 (14) | O1—C11—O2' | 125.9 (5) |
| N3—N2—C2 | 122.86 (13) | O2—C11—O2' | 29.2 (5) |
| C15—N3—N2 | 101.51 (14) | O1—C11—C3 | 121.07 (16) |
| C1—N4—C15 | 101.41 (14) | O2—C11—C3 | 116.05 (16) |
| N4—C1—N2 | 111.19 (15) | O2'—C11—C3 | 106.8 (4) |
| N4—C1—N1 | 127.88 (15) | C11—O2—C12 | 118.11 (18) |
| N2—C1—N1 | 120.91 (15) | O2—C12—C13 | 109.9 (2) |
| N2—C2—C5 | 110.32 (13) | O2—C12—H12A | 109.7 |
| N2—C2—C3 | 107.61 (13) | C13—C12—H12A | 109.7 |
| C5—C2—C3 | 112.88 (14) | O2—C12—H12B | 109.7 |
| N2—C2—H2 | 108.6 | C13—C12—H12B | 109.7 |
| C5—C2—H2 | 108.6 | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.2 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 108.6 | C11—O2'—C12' | 115.7 (8) |
| C4—C3—C11 | 127.56 (16) | O2'—C12'—C13' | 108.4 (10) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.99 (15) | O2'—C12'—H12C | 110.0 |
| C11—C3—C2 | 110.36 (14) | C13'—C12'—H12C | 110.0 |
| C3—C4—N1 | 122.93 (16) | O2'—C12'—H12D | 110.0 |
| C3—C4—C14 | 125.36 (15) | C13'—C12'—H12D | 110.0 |
| N1—C4—C14 | 111.62 (14) | H12C—C12'—H12D | 108.4 |
| C10—C5—C6 | 117.92 (16) | C12'—C13'—H13D | 109.5 |
| C10—C5—C2 | 119.70 (15) | C12'—C13'—H13E | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C2 | 122.36 (15) | H13D—C13'—H13E | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.26 (18) | C12'—C13'—H13F | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—Cl1 | 117.98 (15) | H13D—C13'—H13F | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—Cl1 | 120.75 (14) | H13E—C13'—H13F | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.36 (18) | F3—C14—F2 | 107.78 (13) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.3 | F3—C14—F1 | 106.64 (14) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 | F2—C14—F1 | 106.11 (14) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.29 (18) | F3—C14—C4 | 113.45 (14) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.9 | F2—C14—C4 | 111.87 (14) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 | F1—C14—C4 | 110.60 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 119.89 (19) | N3—C15—N4 | 116.16 (15) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 | N3—C15—H15 | 121.9 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 | N4—C15—H15 | 121.9 |
| C1—N2—N3—C15 | −0.87 (18) | C2—C5—C6—Cl1 | −0.2 (2) |
| C2—N2—N3—C15 | −175.36 (15) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.9 (3) |
| C15—N4—C1—N2 | −0.70 (18) | Cl1—C6—C7—C8 | 178.59 (15) |
| C15—N4—C1—N1 | −179.05 (17) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.3 (3) |
| N3—N2—C1—N4 | 1.04 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.1 (3) |
| C2—N2—C1—N4 | 175.24 (15) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −0.5 (3) |
| N3—N2—C1—N1 | 179.53 (15) | C2—C5—C10—C9 | −178.84 (16) |
| C2—N2—C1—N1 | −6.3 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C5 | 0.0 (3) |
| C4—N1—C1—N4 | 175.37 (16) | C4—C3—C11—O1 | 163.90 (19) |
| C4—N1—C1—N2 | −2.8 (2) | C2—C3—C11—O1 | −12.7 (2) |
| C1—N2—C2—C5 | −112.47 (18) | C4—C3—C11—O2 | −12.5 (3) |
| N3—N2—C2—C5 | 61.02 (19) | C2—C3—C11—O2 | 170.95 (18) |
| C1—N2—C2—C3 | 11.1 (2) | C4—C3—C11—O2' | −42.3 (6) |
| N3—N2—C2—C3 | −175.44 (14) | C2—C3—C11—O2' | 141.1 (6) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | −8.1 (2) | O1—C11—O2—C12 | 2.9 (3) |
| C5—C2—C3—C4 | 113.82 (18) | O2'—C11—O2—C12 | −103.3 (10) |
| N2—C2—C3—C11 | 168.67 (13) | C3—C11—O2—C12 | 179.19 (18) |
| C5—C2—C3—C11 | −69.36 (18) | C11—O2—C12—C13 | 96.5 (3) |
| C11—C3—C4—N1 | −175.26 (16) | O1—C11—O2'—C12' | −35.7 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | 1.0 (3) | O2—C11—O2'—C12' | 58.5 (11) |
| C11—C3—C4—C14 | 0.8 (3) | C3—C11—O2'—C12' | 172.2 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—C14 | 177.07 (15) | C11—O2'—C12'—C13' | 174.9 (12) |
| C1—N1—C4—C3 | 5.2 (2) | C3—C4—C14—F3 | 66.0 (2) |
| C1—N1—C4—C14 | −171.36 (14) | N1—C4—C14—F3 | −117.51 (15) |
| N2—C2—C5—C10 | 77.54 (19) | C3—C4—C14—F2 | −56.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—C5—C10 | −42.9 (2) | N1—C4—C14—F2 | 120.30 (15) |
| N2—C2—C5—C6 | −100.70 (18) | C3—C4—C14—F1 | −174.22 (16) |
| C3—C2—C5—C6 | 138.88 (17) | N1—C4—C14—F1 | 2.25 (19) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.9 (3) | N2—N3—C15—N4 | 0.5 (2) |
| C2—C5—C6—C7 | 179.21 (16) | C1—N4—C15—N3 | 0.1 (2) |
| C10—C5—C6—Cl1 | −178.49 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···N4i | 0.90 (2) | 1.96 (2) | 2.843 (2) | 166.3 (19) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG2715).
References
- Allen, J. G., Bourbeau, M. P., Wohlhieter, G. E., Bartberger, M. D., Michelsen, K., Hungate, R., Gadwood, R. C., Gaston, R. D., Evans, B., Mann, L. W., Matison, M. E., Schneider, S., Huang, X., Yu, D. Y., Andrews, P. S., Reichelt, A., Long, A. M., Yakowec, P., Yang, E. Y., Lee, T. A. & Oliner, J. D. (2009). J. Med. Chem.52, 7044–7053. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc.97, 1354–1358.
- Gujjar, R., Marwaha, A., El Mazouni, F., White, J., White, K. L., Creason, S., Shackleford, D. M., Baldwin, J., Charman, W. N., Buckner, F. S., Charman, S., Rathod, P. K. & Phillips, M. A. (2009). J. Med. Chem.52, 1864–1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kirk, K. L. (2006). J. Fluorine Chem.127,1013–1029.
- Pereyaslavskaya, E. S., Potemkin, V. A., Bartashevich, E. V., Grishina, M. A., Rusinov, G. L., Fedorova, O. V., Zhidovinova, M. S. & Ovchinnikova, I. G. (2008). Pharm. Chem. J.42, 622–625.
- Pryadeina, M. V., Burgart, Ya. V., Saloutin, V. I., Kodess, M. I., Ulomskii, E. N. & Rusinov, V. L. (2004). Russ. J. Org. Chem.40, 902–907.
- Rigaku/MSC (2002). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC Inc., The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N., Ayral-Kaloustian, S., Nguyen, T., Afragola, J., Hernandez, R., Lucas, J., Gibbons, J. & Beyer, C. (2007). J. Med. Chem.50, 319–327. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810037712/hg2715sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810037712/hg2715Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




