Abstract
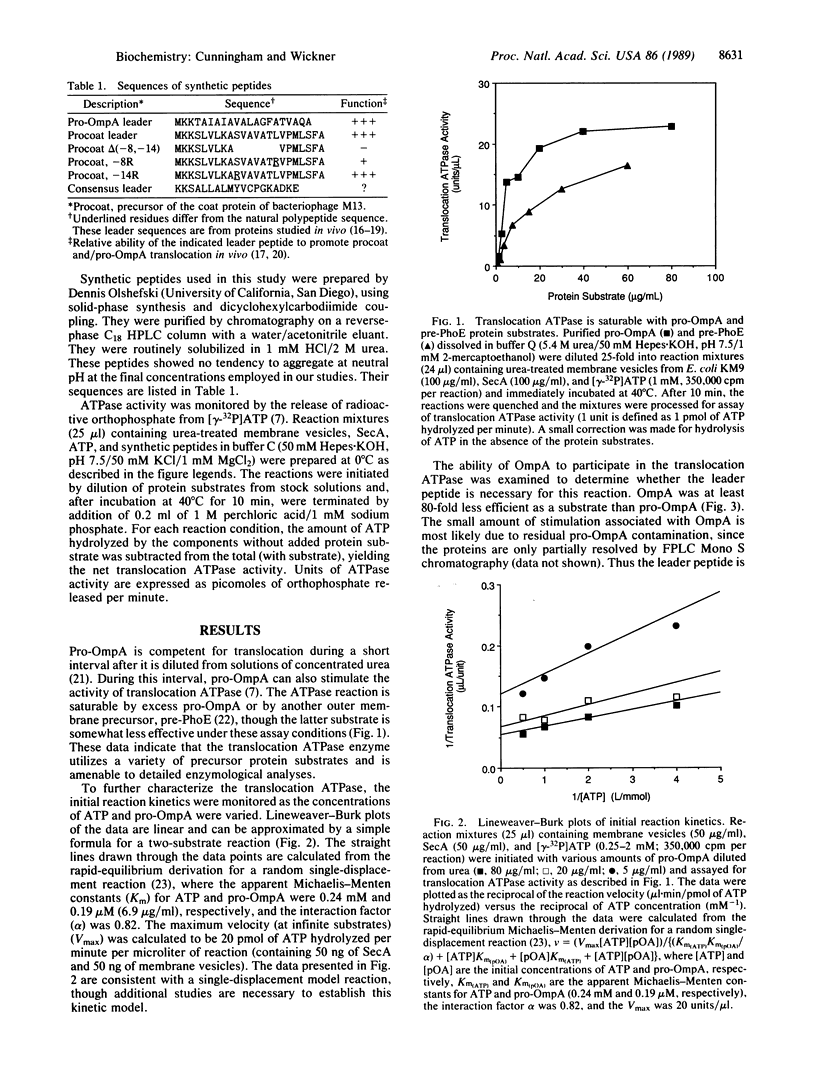
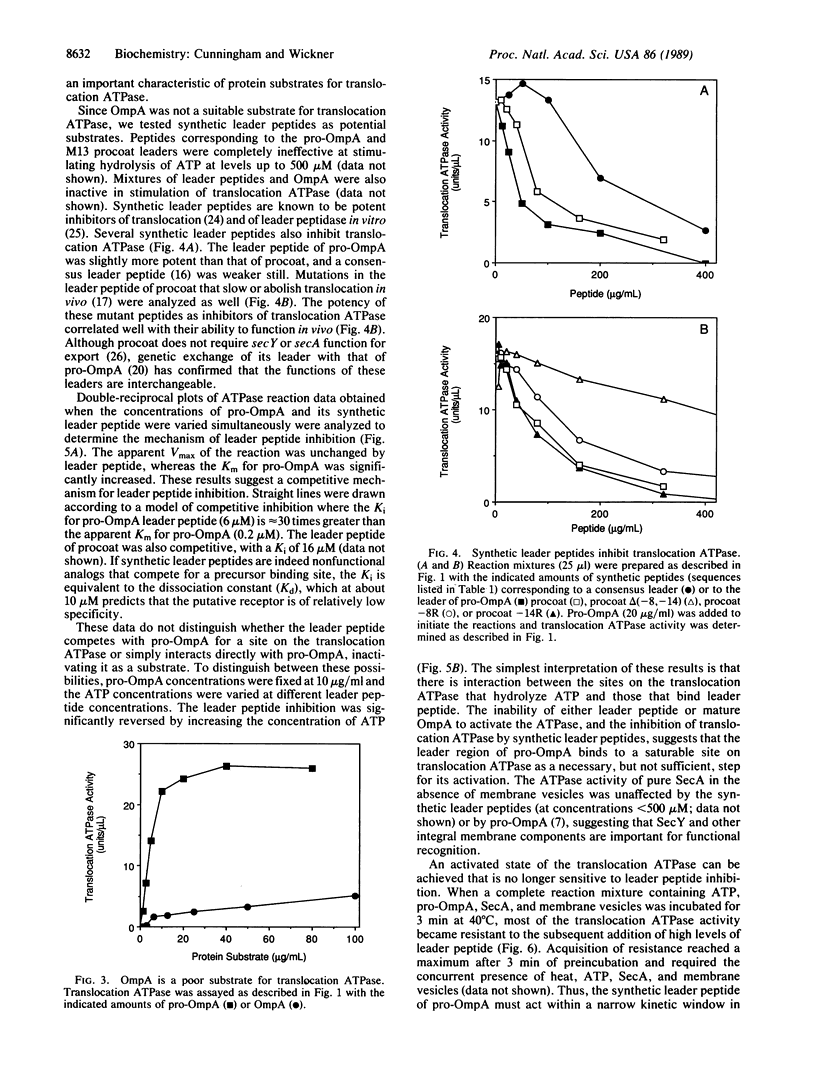
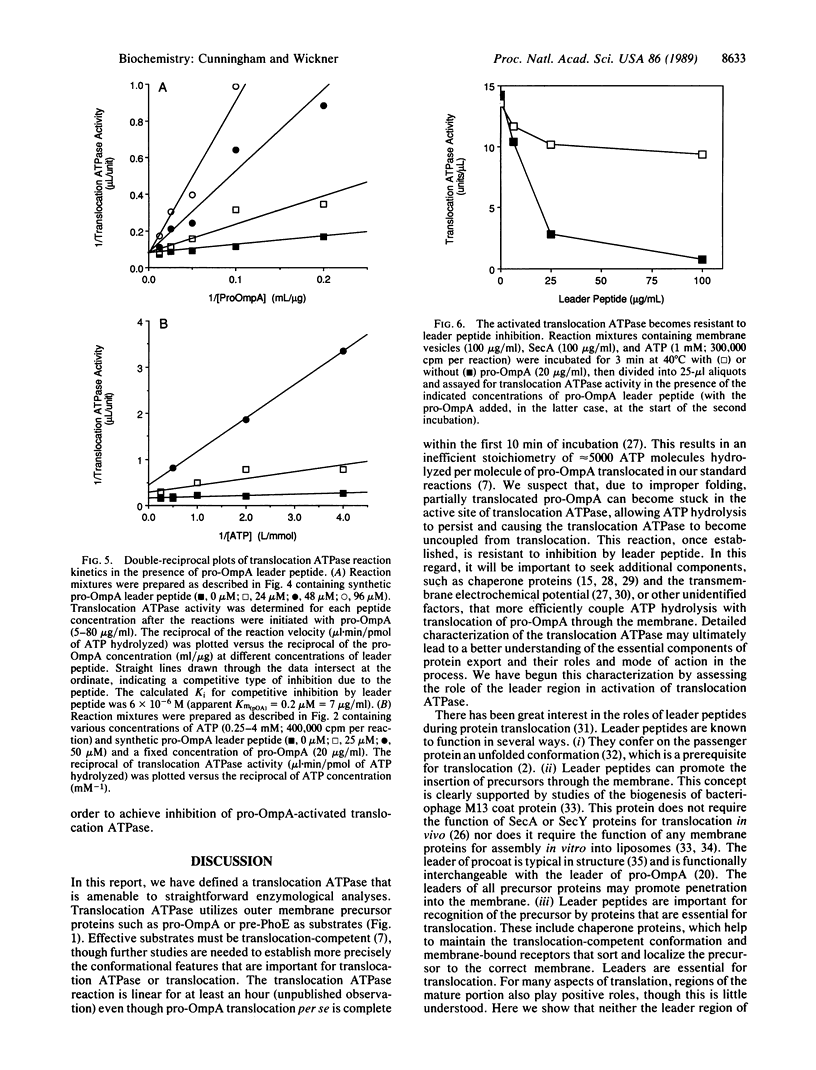
The ATP-hydrolytic activity of SecA protein is stimulated up to 100-fold by the translocation-competent precursor to outer membrane protein A (pro-OmpA) in conjunction with inner-membrane vesicles bearing active SecY [Lill, R., Cunningham, K., Brundage, L., Ito, K., Oliver, D. & Wickner, W. (1989) EMBO J. 8, 961-966]. This reaction is saturable, with Michaelis-Menten kinetics for an enzyme with two substrates, ATP and pro-OmpA, and is defined as translocation ATPase. Another precursor protein, pre-PhoE, is also a substrate for this translocation ATPase. Neither OmpA nor its synthetic leader peptide are effective substrates for translocation ATPase, suggesting that both domains of the complete precursor are necessary for the reaction. The leader peptide is a potent inhibitor and apparently competes with pro-OmpA for necessary binding sites on translocation ATPase. After a brief preincubation, the activity of translocation ATPase becomes resistant to inhibition by leader peptide, suggesting that the leader peptide is recognized at an early step in the protein translocation pathway. Our enzymological studies show that translocation ATPase recognizes and functionally binds the leader region of precursor proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacallao R., Crooke E., Shiba K., Wickner W., Ito K. The secY protein can act post-translationally to promote bacterial protein export. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12907–12910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Silhavy T. J. PrlA is important for the translocation of exported proteins across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkareva E. S., Lissin N. M., Girshovich A. S. Transient association of newly synthesized unfolded proteins with the heat-shock GroEL protein. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):254–257. doi: 10.1038/336254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Chen L., Tai P. C., Oliver D. B. SecA protein is required for secretory protein translocation into E. coli membrane vesicles. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C., Briggs M. S., Gierasch L. M. Protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles is inhibited by functional synthetic signal peptides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1427–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Schmidmayr W., Krämer C., Chen-Schmeisser U., Henning U. Primary structure of major outer membrane protein II (ompA protein) of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4592–4596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier D. N., Bankaitis V. A., Weiss J. B., Bassford P. J., Jr The antifolding activity of SecB promotes the export of the E. coli maltose-binding protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Brundage L., Rice M., Wickner W. ProOmpA spontaneously folds in a membrane assembly competent state which trigger factor stabilizes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1831–1835. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Guthrie B., Lecker S., Lill R., Wickner W. ProOmpA is stabilized for membrane translocation by either purified E. coli trigger factor or canine signal recognition particle. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1003–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90115-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Wickner W. Trigger factor: a soluble protein that folds pro-OmpA into a membrane-assembly-competent form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Lill R., Crooke E., Rice M., Moore K., Wickner W., Oliver D. SecA protein, a peripheral protein of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane, is essential for the functional binding and translocation of proOmpA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):955–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vrije T., Tommassen J., De Kruijff B. Optimal posttranslational translocation of the precursor of PhoE protein across Escherichia coli membrane vesicles requires both ATP and the protonmotive force. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 12;900(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schatz G. Protein unfolding and the energetics of protein translocation across biological membranes. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90458-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fandl J. P., Tai P. C. Biochemical evidence for the secY24 defect in Escherichia coli protein translocation and its suppression by soluble cytoplasmic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7448–7452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Novel secA alleles improve export of maltose-binding protein synthesized with a defective signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):402–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.402-409.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L., Movva N. R., Wickner W. Both ATP and the electrochemical potential are required for optimal assembly of pro-OmpA into Escherichia coli inner membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4219–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L., Wickner W. M13 procoat inserts into liposomes in the absence of other membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13281–13285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Kreil G., Wickner W. Both hydrophobic domains of M13 procoat are required to initiate membrane insertion. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3681–3685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04699.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Kreil G., Wickner W. Recombinant forms of M13 procoat with an OmpA leader sequence or a large carboxy-terminal extension retain their independence of secY function. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):501–505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I. Preprotein conformation: the year's major theme in translocation studies. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Dec;13(12):471–474. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Konigsberg W. Reinvestigation of a region of the fd bacteriophage coat protein sequence. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 25;88(3):598–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S., Liu G., Topping T. B., Cover W. H., Randall L. L. Modulation of folding pathways of exported proteins by the leader sequence. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1033–1035. doi: 10.1126/science.3278378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Unity in function in the absence of consensus in sequence: role of leader peptides in export. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1156–1159. doi: 10.1126/science.2646712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Kaderbhai M. A., Austen B. M. Identification of signal sequence binding proteins integrated into the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):767–777. doi: 10.1042/bj2420767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Schatz G. Protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1307–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. Mechanisms of membrane assembly: general lessons from the study of M13 coat protein and Escherichia coli leader peptidase. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1081–1086. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Moore K., Dibb N., Geissert D., Rice M. Inhibition of purified Escherichia coli leader peptidase by the leader (signal) peptide of bacteriophage M13 procoat. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3821–3822. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3821-3822.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. Secretion and membrane assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Jul;14(7):280–283. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Rice M., Wickner W. Effects of two sec genes on protein assembly into the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1836–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Proton motive force-dependent and -independent protein translocation revealed by an efficient in vitro assay system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1723–1728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



