Abstract
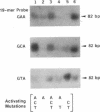
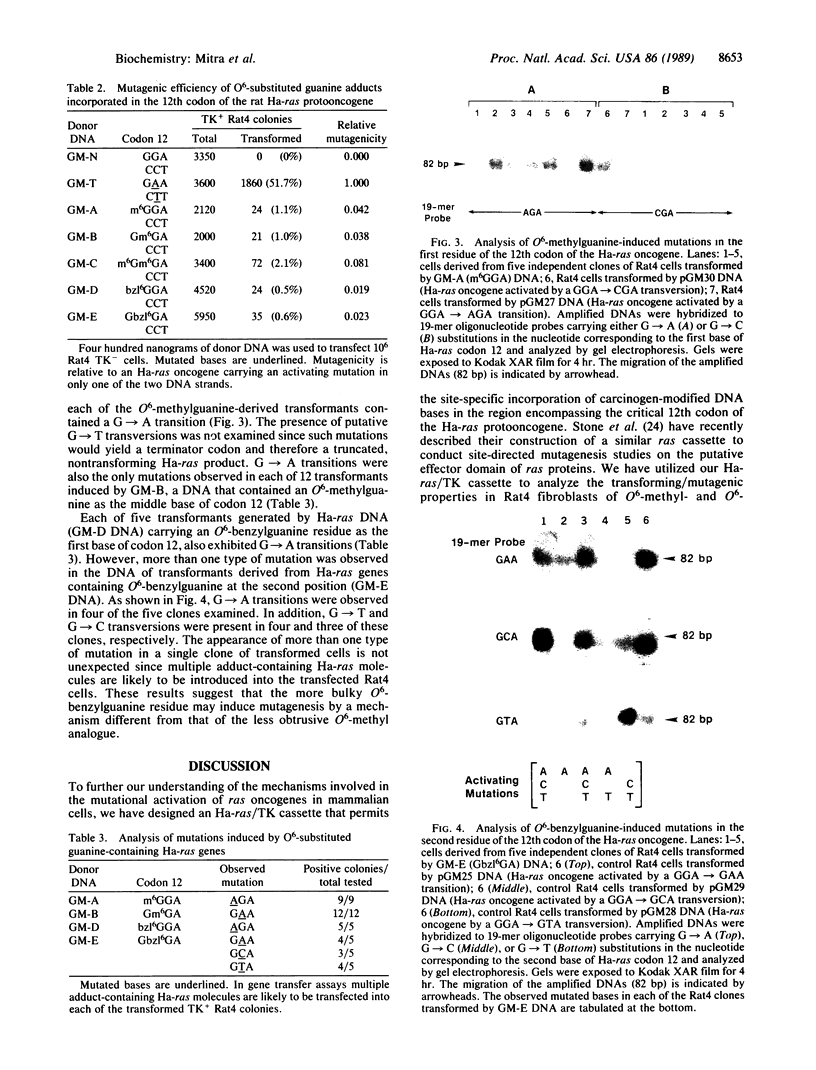
We have designed an Ha-ras/thymidine kinase (TK) cassette that permits the incorporation of chemically synthesized adducts within specific domains of the rat Ha-ras protooncogene. This cassette has been used to evaluate the mutagenicity of O6-substituted guanine residues, including O6-methylguanine and O6-benzylguanine, incorporated within the 12th codon of this locus. Mutations were monitored by the ability of these modified Ha-ras DNAs to transform Rat4 TK-cells. Our results indicate that both types of O6-substituted guanines are substantially mutagenic, although the methyl substituent induced a 2-fold higher percentage of transformed Rat4 TK+ colonies than its bulkier benzyl analogue. Interestingly, the mutagenicity of both O6-substituted guanines was found to be independent of their relative position within codon 12, therefore suggesting that the specific activation of Ha-ras oncogenes by GGA----GAA mutations in tumors induced by methylating carcinogens might be due to differences in the accessibility of these guanine residues to the carcinogen rather than to a differential rate of repair. Molecular analysis of the mutations induced by these O6-substituted guanines indicated that O6-methylguanine exclusively induced G----A transitions. In contrast, O6-benzylguanine produced G----C and G----T transversions in addition to G----A transitions. These results suggest that O6-methylguanine and its bulkier analogue O6-benzylguanine may induce mutagenesis by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balmain A., Brown K. Oncogene activation in chemical carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:147–182. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu A. K., Essigmann J. M. Site-specifically modified oligodeoxynucleotides as probes for the structural and biological effects of DNA-damaging agents. Chem Res Toxicol. 1988 Jan-Feb;1(1):1–18. doi: 10.1021/tx00001a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. A., Gordon A. J., Glickman B. W. Influence of neighbouring base sequence on N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90668-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. A., Gordon A. J., Glickman B. W. Mutational specificity of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Sep;9(9):1607–1610. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.9.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M. E., Oplinger M., Pegg A. E. Sequence specificity of guanine alkylation and repair. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Nov;9(11):2139–2143. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.11.2139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druckrey H., Preussmann R., Ivankovic S., Schmähl D. Organotrope carcinogene Wirkungen bei 65 verschiedenen N-Nitroso-Verbindungen an BD-Ratten. Z Krebsforsch. 1967;69(2):103–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Aldrich T., Tamanoi F., Taparowsky E., Furth M., Wigler M. Analysis of the transforming potential of the human H-ras gene by random mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4008–4012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullino P. M., Pettigrew H. M., Grantham F. H. N-nitrosomethylurea as mammary gland carcinogen in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Feb;54(2):401–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Barbacid M. Oncogene detection at the single cell level. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):647–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauly G. T., Powers M., Pei G. K., Moschel R. C. Synthesis and properties of H-ras DNA sequences containing O6-substituted 2'-deoxyguanosine residues at the first, second, or both positions of codon 12. Chem Res Toxicol. 1988 Nov-Dec;1(6):391–397. doi: 10.1021/tx00006a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. Methylation of the O6 position of guanine in DNA is the most likely initiating event in carcinogenesis by methylating agents. Cancer Invest. 1984;2(3):223–231. doi: 10.3109/07357908409104376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds S. H., Stowers S. J., Patterson R. M., Maronpot R. R., Aaronson S. A., Anderson M. W. Activated oncogenes in B6C3F1 mouse liver tumors: implications for risk assessment. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1309–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.3629242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Kuśmierek J. T. Chemical mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:655–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Vass W. C., Willumsen B. M., Lowy D. R. p21-ras effector domain mutants constructed by "cassette" mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3565–3569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar S., Notario V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Induction of mammary carcinomas in rats by nitroso-methylurea involves malignant activation of H-ras-1 locus by single point mutations. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):658–661. doi: 10.1038/306658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topal M. D. DNA repair, oncogenes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1988 May;9(5):691–696. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.5.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topal M. D., Eadie J. S., Conrad M. O6-methylguanine mutation and repair is nonuniform. Selection for DNA most interactive with O6-methylguanine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9879–9885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman R. W., Stowers S. J., Miller E. C., Anderson M. W., Miller J. A. Activating mutations of the c-Ha-ras protooncogene in chemically induced hepatomas of the male B6C3 F1 mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5825–5829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbl H., Sukumar S., Arthur A. V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Direct mutagenesis of Ha-ras-1 oncogenes by N-nitroso-N-methylurea during initiation of mammary carcinogenesis in rats. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):382–385. doi: 10.1038/315382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]