Abstract
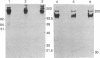
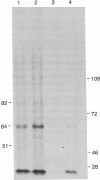
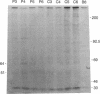
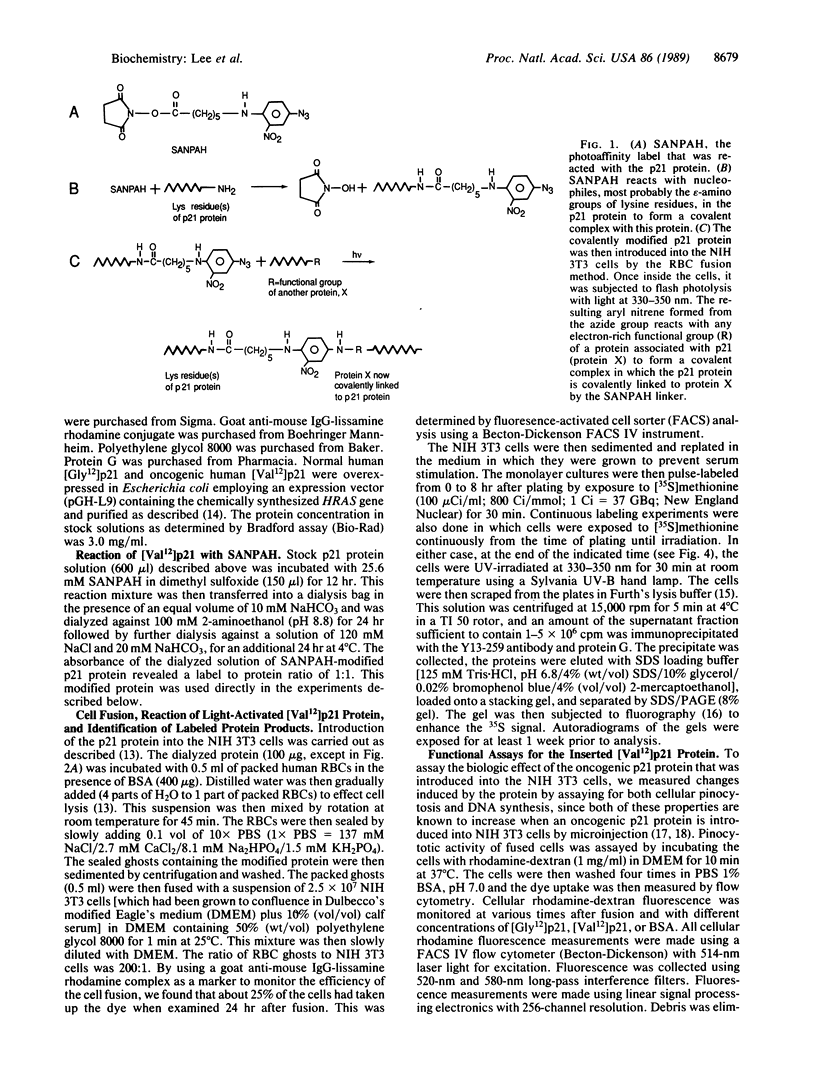
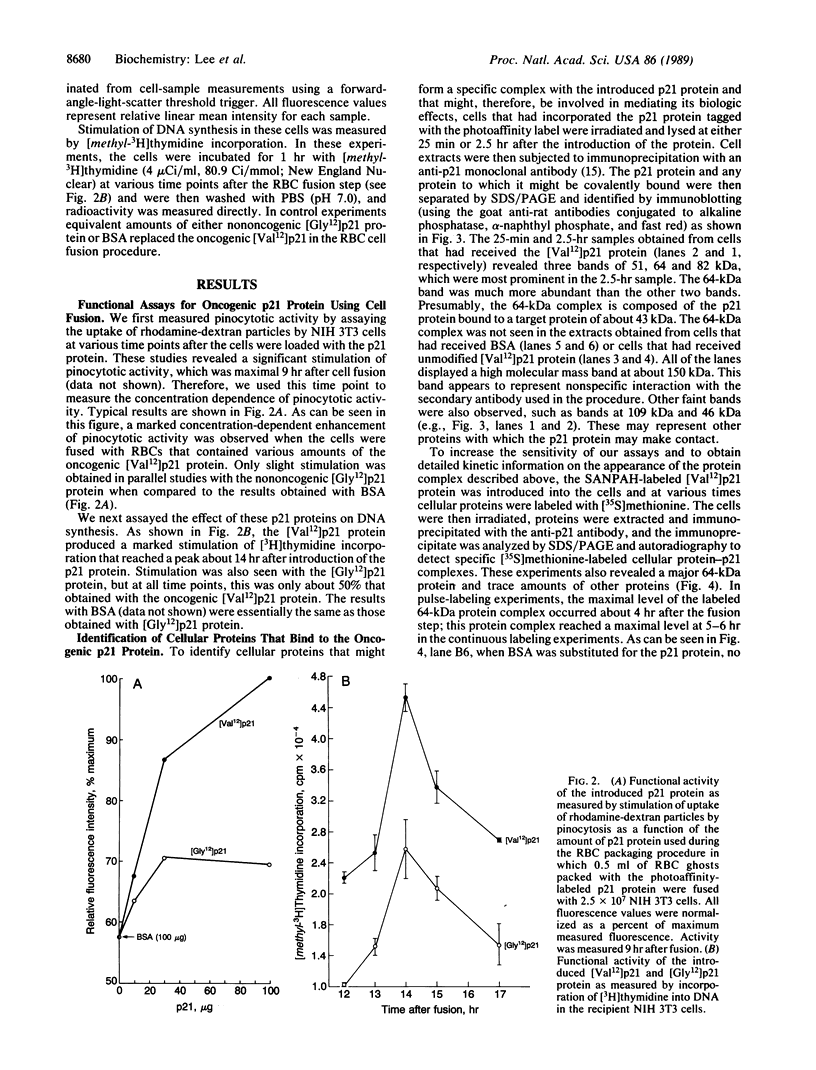
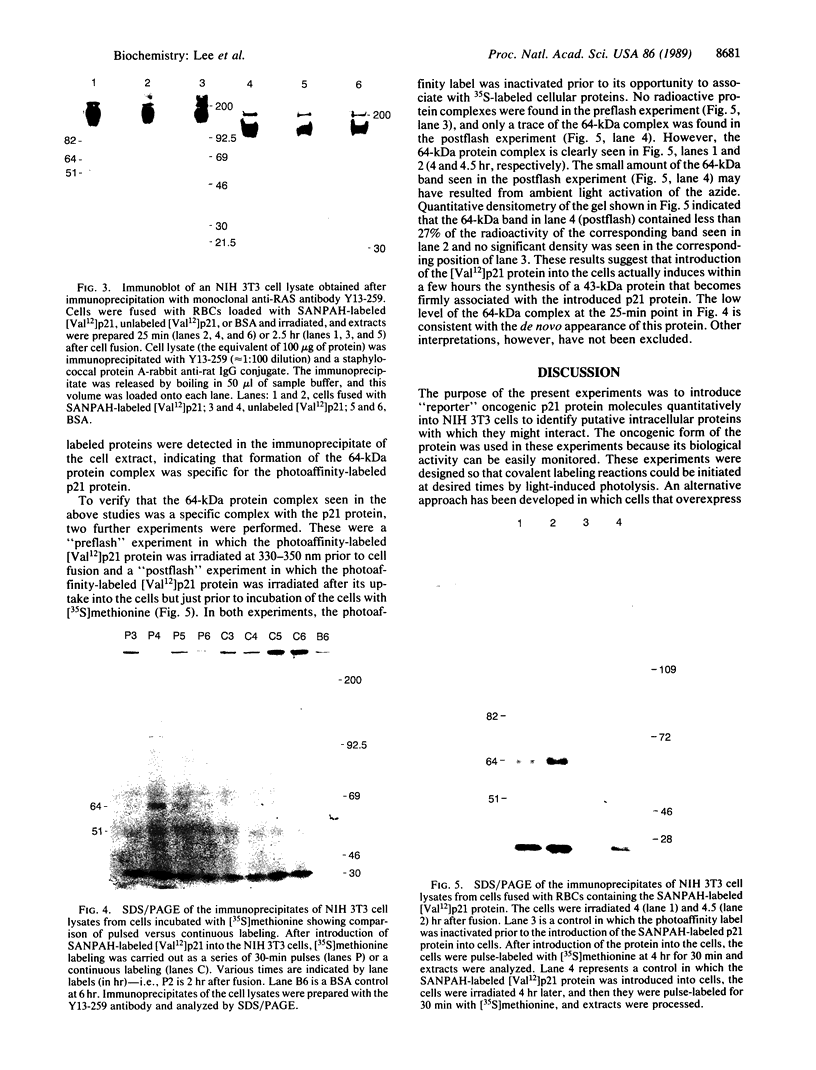
An oncogenic 21-kDa (p21) protein (Harvey RAS protein with Val-12) has been covalently modified with a functional reagent that contains a photoactivatable aromatic azide group. This modified p21 protein has been introduced quantitatively into NIH 3T3 cells using an erythrocyte-mediated fusion technique. The introduced p21 protein was capable of inducing enhanced pinocytosis and DNA synthesis in the recipient cells. To identify the putative intracellular protein(s) that specifically interact with the modified p21 protein, the cells were pulsed with [35S]methionine at selected times after fusion and then UV-irradiated to activate the azide group. The resulting nitrene covalently binds to amino acid residues in adjacent proteins, thus linking the p21 protein to these proteins. The cells were then lysed, and the lysate was immunoprecipitated with the anti-p21 monoclonal antibody Y13-259. The immunoprecipitate was analyzed by SDS/PAGE to identify p21-protein complexes. By using this technique, we found that three protein complexes of 51, 64, and 82 kDa were labeled specifically and reproducibly. The most prominent band is the 64-kDa protein complex that shows a time-dependent rise and fall, peaking within a 5-hr period after introduction of the p21 protein into the cells. These studies provide evidence that in vitro the p21 protein becomes associated with a protein whose mass is about 43 kDa. We suggest that the formation of this complex may play a role in mediating early events involved with cell transformation induced by RAS oncogenes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Weinstein I. B. p21 ras proteins and guanine nucleotides modulate the phosphorylation of 36- and 17-kilodalton mitochondria-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6357–6361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballmer-Hofer K., Schlup V., Burn P., Burger M. M. Isolation of in situ crosslinked ligand-receptor complexes using an anticrosslinker specific antibody. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 1;126(2):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblasts by ras proteins. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.3090687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Aldrich T., Tamanoi F., Taparowsky E., Furth M., Wigler M. Analysis of the transforming potential of the human H-ras gene by random mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4008–4012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Fleming T. P., Warren B. S., Blumberg P. M., Aaronson S. A. Involvement of functional protein kinase C in the mitogenic response to the H-ras oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4146–4149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K., Inoue Y., Nakamori H., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Noguchi S., Nishimura S. Synthesis and expression of a synthetic gene for the activated human c-Ha-ras protein. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;77(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Santos E., Barbacid M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):149–152. doi: 10.1038/300149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronai Z. A., Weinstein I. B. Identification of a UV-induced trans-acting protein that stimulates polyomavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1057–1060. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1057-1060.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N., Bekesi E., Kung H. F., Lowy D. R. Transforming p21 ras protein: flexibility in the major variable region linking the catalytic and membrane-anchoring domains. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2893–2896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J., Riehl R., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a protein associated with p21ras by chemical crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]