Abstract
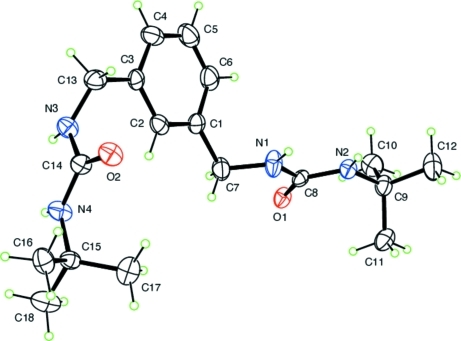
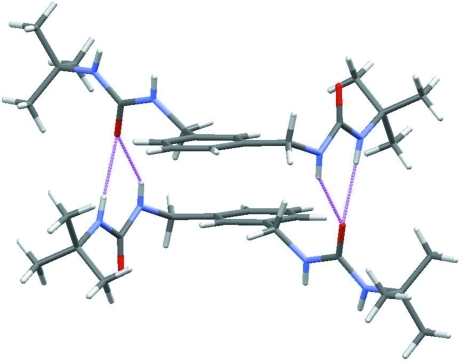
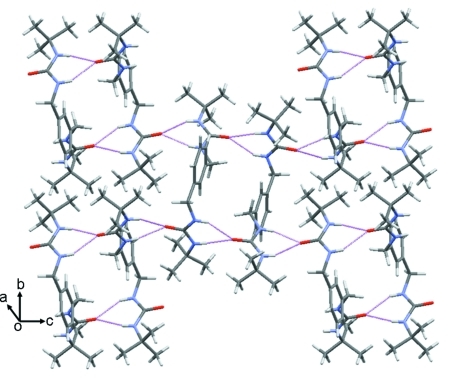
The title compound, C18H30N4O2, contains two tert-butyl urea groups, each connected to a benzene ring though a methylene group. One of the groups occupies a position almost normal to the aromatic plane with a C—N—C—C torsion angle of −94.4 (4)°, while the other is considerably twisted from the ring with a C—N—C—C torsion angle of −136.1 (4)°. In the crystal, pairs of molecules are connected to each other, forming centrosymmetric dimers in which two NH groups of one molecule act as hydrogen-bond donors to one carbonyl O atom of the other molecule. The dimers are linked into sheets parallel to (100) by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving the remaining N—H and C=O groups.
Related literature
For general background to urea-based compounds, see: Brooks et al. (2008 ▶); Carr et al. (1998 ▶); Chauhan et al. (2008 ▶); Gomez et al. (2005 ▶); Hiscock et al. (2009 ▶); Hossain (2008 ▶); Kyne et al. (2001 ▶); Lorenzo et al. (2009 ▶); Pérez-Casas & Yatsimirsky (2008 ▶); Tejeda et al. (2000 ▶); Ghosh et al. (2007 ▶). For related structures, see: Jose et al. (2007 ▶); Lo & Ng (2008 ▶).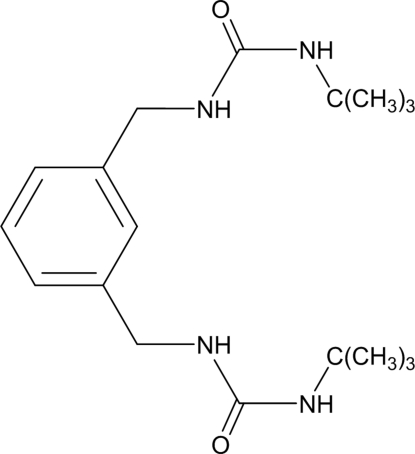
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H30N4O2
M r = 334.46
Orthorhombic,
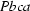
a = 18.070 (4) Å
b = 11.760 (3) Å
c = 18.221 (3) Å
V = 3872.0 (15) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.20 × 0.10 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer with an Oxford Cryosystems Cryostream cooler
43147 measured reflections
3781 independent reflections
2158 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.081
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.081
wR(F 2) = 0.235
S = 1.03
3781 reflections
235 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.86 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO/SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO/SCALEPACK; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005866/ci5033sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005866/ci5033Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O2i | 0.82 (2) | 2.12 (2) | 2.909 (4) | 162 (4) |
| N2—H2N⋯O2i | 0.81 (2) | 2.28 (2) | 3.034 (4) | 153 (4) |
| N3—H3N⋯O1ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.15 (2) | 2.941 (4) | 154 (4) |
| N4—H4N⋯O1ii | 0.81 (2) | 2.12 (2) | 2.889 (4) | 160 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 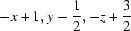 ; (ii)
; (ii) 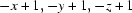 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Division of National Center for Research Resources, under grant No. G12RR013459. The purchase of the diffractometer was made possible by grant No. LEQSF (1999–2000)-ENH-TR-13, administered by the Louisiana Board of Regents. This research was also sponsored by the Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, US Department of Energy, under contract with Oak Ridge National Laboratory (MAH), and National Science Foundation under grant No. CHE-0821357.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Because of the ability of urea functional groups to form hydrogen bonds with an anion, urea-based compounds are known as effective hosts for a variety of anions (Brooks et al., 2008; Carr et al., 1998; Chauhan et al., 2008; Hiscock et al., 2009; Lorenzo et al., 2009; Tejeda et al., 2000) as well as neutral species (Kyne et al., 2001) and are often used for colorimetric detection for a specific anion in solution (Ghosh et al., 2007; Pérez-Casas et al., 2008). For example, simple acyclic ligands with mono-functional urea or thiourea groups are known to form 1:1 complexes with carboxylates, halides and phosphate in DMSO (Gomez et al., 2005). Encapsulation of sulfate anion was also structurally identified within the cavity formed by two tren-based urea ligands (Jose et al., 2007). In an effort to design multifunctional anion receptors (Hossain, 2008), we synthesized a urea-based compound containing two urea units, that can be useful in anion binding.
Single crystal X-ray analysis reveals that the bis-urea cleft crystallized in an orthorhombic space group without the involvement of solvent molecules. As illustrated in Fig. 1, the carbonyl groups of the two urea fragments are oriented in opposite directions. The methylene groups connected to the aromatic units are almost co-planar with the NH groups, as indicated by C13—N3—C14—N4 and C7—N1—C8—N2 torsion angles of -164.8 (3) and 177.6 (3)°, respectively. The NH groups are oriented almost perpendicular to the aromatic plane.
There are no intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the molecule, however, each C═O group forms two hydrogen bonds with two adjacent NH fragments resulting in the formation of centrosymmetric dimers with N···O distances of 2.889 (4) Å and 2.941 (4) Å (Fig. 2 and Table 1). Each dimer is then connected with four adjacent dimers forming a sheet parallel to the (100) (Fig. 3). Similar intermolecular bonding was previously reported for a mono-functional urea-based compound (Lo & Ng, 2008).
Experimental
To a solution of m-xylylenediamine (0.10 g, 1.0 mmol) in CH3CN (20 ml) was added two equivalents of tert-butyl isocyanate (0.20 g, 2.0 mmol) and the mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The white precipitate formed was separated by filtration, washed by diethyl ether, and dried under vacuum. Yield 40%. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 7.25-7.12 (ArH, m, 4H), 4.84(CH2NH, t, J = 5 Hz, 2H), 4.64 (CNH, s, 2H), 4.21 (ArCH2, d, J = 5 Hz, 4H), 1.30 (CCH3, s, 18H). A small portion of the sample was re-dissolved in CHCl3, and crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were grown by slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature.
Refinement
N-bound H atoms were located in a difference map and their coordinates were refined with a N–H distance restraint of 0.81 (1) Å. C-bound H atoms were placed in idealized positions [C–H = 0.95–0.99 Å] and thereafter treated as riding. Uiso(H) values were assigned as 1.2 times Ueq of the attached atom (1.5 for methyl). A torsional parameter was refined for each methyl group. The highest residual peak is located 1.50 Å from O2.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the centrosymmetric dimer. Colour code: O, red; N, blue; C, deep gray; and H, light gray.
Fig. 3.
Packing diagram of the title compound viewed along a axis.
Crystal data
| C18H30N4O2 | F(000) = 1456 |
| Mr = 334.46 | Dx = 1.147 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 4187 reflections |
| a = 18.070 (4) Å | θ = 2.5–26.0° |
| b = 11.760 (3) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 18.221 (3) Å | T = 90 K |
| V = 3872.0 (15) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.07 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer with an Oxford Cryosystems Cryostream cooler | 2158 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.081 |
| graphite | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −22→22 |
| 43147 measured reflections | k = −14→14 |
| 3781 independent reflections | l = −22→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.081 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.235 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1146P)2 + 3.4665P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3781 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmax = 0.86 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.34787 (13) | 0.2316 (2) | 0.50086 (12) | 0.0278 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.60321 (15) | 0.6965 (2) | 0.74637 (13) | 0.0341 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.41055 (18) | 0.2793 (3) | 0.60384 (16) | 0.0374 (9) | |
| H1N | 0.414 (2) | 0.267 (4) | 0.6479 (11) | 0.045* | |
| N2 | 0.32387 (16) | 0.1387 (3) | 0.60835 (15) | 0.0252 (7) | |
| H2N | 0.333 (2) | 0.138 (3) | 0.6520 (11) | 0.030* | |
| N3 | 0.66516 (18) | 0.6521 (3) | 0.64143 (16) | 0.0302 (8) | |
| H3N | 0.664 (2) | 0.664 (3) | 0.5948 (11) | 0.036* | |
| N4 | 0.58391 (18) | 0.8006 (3) | 0.64105 (15) | 0.0306 (8) | |
| H4N | 0.593 (2) | 0.798 (3) | 0.5976 (11) | 0.037* | |
| C1 | 0.5353 (2) | 0.3564 (3) | 0.59313 (18) | 0.0265 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.5746 (2) | 0.4512 (3) | 0.61638 (18) | 0.0284 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.5515 | 0.5237 | 0.6160 | 0.034* | |
| C3 | 0.6492 (2) | 0.4409 (3) | 0.64085 (18) | 0.0260 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.6807 (2) | 0.3341 (3) | 0.6401 (2) | 0.0359 (10) | |
| H4 | 0.7304 | 0.3254 | 0.6562 | 0.043* | |
| C5 | 0.6429 (3) | 0.2405 (4) | 0.6169 (2) | 0.0472 (12) | |
| H5 | 0.6661 | 0.1680 | 0.6165 | 0.057* | |
| C6 | 0.5719 (2) | 0.2520 (4) | 0.5945 (2) | 0.0399 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.5459 | 0.1860 | 0.5790 | 0.048* | |
| C7 | 0.4566 (2) | 0.3648 (3) | 0.5684 (2) | 0.0362 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.4372 | 0.4414 | 0.5801 | 0.043* | |
| H7B | 0.4542 | 0.3545 | 0.5146 | 0.043* | |
| C8 | 0.35958 (18) | 0.2172 (3) | 0.56722 (17) | 0.0221 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.2612 (2) | 0.0693 (3) | 0.58226 (18) | 0.0303 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.2850 (2) | −0.0051 (4) | 0.5169 (2) | 0.0393 (10) | |
| H10A | 0.2983 | 0.0437 | 0.4753 | 0.059* | |
| H10B | 0.2440 | −0.0551 | 0.5027 | 0.059* | |
| H10C | 0.3278 | −0.0513 | 0.5310 | 0.059* | |
| C11 | 0.1961 (2) | 0.1455 (4) | 0.5611 (2) | 0.0376 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.1792 | 0.1876 | 0.6044 | 0.056* | |
| H11B | 0.1556 | 0.0986 | 0.5423 | 0.056* | |
| H11C | 0.2119 | 0.1993 | 0.5231 | 0.056* | |
| C12 | 0.2391 (3) | −0.0088 (4) | 0.6458 (2) | 0.0457 (12) | |
| H12A | 0.2818 | −0.0548 | 0.6606 | 0.069* | |
| H12B | 0.1988 | −0.0590 | 0.6300 | 0.069* | |
| H12C | 0.2225 | 0.0374 | 0.6875 | 0.069* | |
| C13 | 0.6909 (2) | 0.5427 (3) | 0.6683 (2) | 0.0333 (10) | |
| H13A | 0.6883 | 0.5433 | 0.7225 | 0.040* | |
| H13B | 0.7435 | 0.5339 | 0.6545 | 0.040* | |
| C14 | 0.6158 (2) | 0.7160 (3) | 0.68049 (18) | 0.0272 (8) | |
| C15 | 0.5256 (2) | 0.8778 (3) | 0.66675 (18) | 0.0259 (8) | |
| C16 | 0.5559 (2) | 0.9634 (3) | 0.7207 (2) | 0.0362 (10) | |
| H16A | 0.5762 | 0.9234 | 0.7634 | 0.054* | |
| H16B | 0.5161 | 1.0143 | 0.7366 | 0.054* | |
| H16C | 0.5951 | 1.0079 | 0.6972 | 0.054* | |
| C17 | 0.4608 (2) | 0.8133 (4) | 0.6996 (2) | 0.0417 (11) | |
| H17A | 0.4416 | 0.7590 | 0.6635 | 0.063* | |
| H17B | 0.4216 | 0.8671 | 0.7131 | 0.063* | |
| H17C | 0.4773 | 0.7723 | 0.7435 | 0.063* | |
| C18 | 0.4988 (3) | 0.9395 (4) | 0.5971 (2) | 0.0434 (11) | |
| H18A | 0.5408 | 0.9771 | 0.5733 | 0.065* | |
| H18B | 0.4616 | 0.9966 | 0.6105 | 0.065* | |
| H18C | 0.4768 | 0.8843 | 0.5632 | 0.065* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0263 (14) | 0.0416 (16) | 0.0156 (13) | −0.0042 (12) | 0.0019 (10) | 0.0011 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0435 (17) | 0.0359 (16) | 0.0228 (14) | 0.0026 (13) | −0.0013 (11) | 0.0004 (11) |
| N1 | 0.038 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0201 (16) | −0.0192 (18) | −0.0036 (14) | 0.0074 (15) |
| N2 | 0.0255 (17) | 0.0353 (18) | 0.0147 (14) | −0.0036 (14) | −0.0021 (12) | 0.0024 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0365 (19) | 0.0284 (18) | 0.0256 (16) | 0.0014 (16) | 0.0007 (14) | 0.0007 (13) |
| N4 | 0.042 (2) | 0.0358 (19) | 0.0139 (14) | 0.0110 (16) | 0.0045 (14) | 0.0045 (13) |
| C1 | 0.028 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0214 (18) | −0.0013 (18) | 0.0065 (15) | −0.0001 (15) |
| C2 | 0.035 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0223 (18) | 0.0022 (18) | 0.0057 (16) | 0.0035 (15) |
| C3 | 0.028 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0221 (18) | −0.0024 (17) | 0.0082 (15) | 0.0018 (15) |
| C4 | 0.039 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.0043 (18) | 0.0051 (17) |
| C5 | 0.054 (3) | 0.028 (2) | 0.059 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C6 | 0.044 (3) | 0.034 (2) | 0.042 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0023 (19) |
| C7 | 0.034 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.036 (2) | −0.012 (2) | −0.0053 (18) | 0.0105 (18) |
| C8 | 0.0182 (18) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0179 (18) | 0.0015 (16) | 0.0030 (14) | −0.0008 (14) |
| C9 | 0.028 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0263 (19) | −0.0075 (18) | −0.0020 (16) | 0.0036 (16) |
| C10 | 0.043 (3) | 0.034 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.005 (2) | −0.0047 (19) | −0.0060 (19) |
| C11 | 0.026 (2) | 0.050 (3) | 0.037 (2) | −0.005 (2) | −0.0007 (17) | −0.0004 (19) |
| C12 | 0.046 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.037 (2) | −0.021 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.010 (2) |
| C13 | 0.032 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0033 (19) | −0.0038 (17) | 0.0035 (17) |
| C14 | 0.031 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0233 (19) | 0.0032 (18) | 0.0027 (16) | −0.0022 (16) |
| C15 | 0.029 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.0231 (18) | 0.0052 (17) | 0.0016 (15) | 0.0005 (15) |
| C16 | 0.046 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.032 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.0063 (18) | −0.0001 (16) |
| C17 | 0.040 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.038 (2) | −0.008 (2) | 0.0044 (19) | −0.0069 (19) |
| C18 | 0.055 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.033 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.0009 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C8 | 1.239 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.99 |
| O2—C14 | 1.243 (4) | C9—C11 | 1.527 (5) |
| N1—C8 | 1.352 (5) | C9—C12 | 1.530 (5) |
| N1—C7 | 1.455 (5) | C9—C10 | 1.539 (5) |
| N1—H1N | 0.819 (18) | C10—H10A | 0.98 |
| N2—C8 | 1.353 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.98 |
| N2—C9 | 1.475 (5) | C10—H10C | 0.98 |
| N2—H2N | 0.813 (18) | C11—H11A | 0.98 |
| N3—C14 | 1.367 (5) | C11—H11B | 0.98 |
| N3—C13 | 1.452 (5) | C11—H11C | 0.98 |
| N3—H3N | 0.860 (18) | C12—H12A | 0.98 |
| N4—C14 | 1.355 (5) | C12—H12B | 0.98 |
| N4—C15 | 1.468 (5) | C12—H12C | 0.98 |
| N4—H4N | 0.809 (18) | C13—H13A | 0.99 |
| C1—C2 | 1.388 (5) | C13—H13B | 0.99 |
| C1—C6 | 1.395 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.510 (5) |
| C1—C7 | 1.495 (5) | C15—C17 | 1.518 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.426 (5) | C15—C18 | 1.540 (5) |
| C2—H2 | 0.95 | C16—H16A | 0.98 |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (5) | C16—H16B | 0.98 |
| C3—C13 | 1.499 (5) | C16—H16C | 0.98 |
| C4—C5 | 1.362 (6) | C17—H17A | 0.98 |
| C4—H4 | 0.95 | C17—H17B | 0.98 |
| C5—C6 | 1.352 (6) | C17—H17C | 0.98 |
| C5—H5 | 0.95 | C18—H18A | 0.98 |
| C6—H6 | 0.95 | C18—H18B | 0.98 |
| C7—H7A | 0.99 | C18—H18C | 0.98 |
| C8—N1—C7 | 122.9 (3) | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—H1N | 117 (3) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C7—N1—H1N | 120 (3) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C8—N2—C9 | 124.4 (3) | C9—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C8—N2—H2N | 117 (3) | C9—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C9—N2—H2N | 118 (3) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C14—N3—C13 | 121.4 (3) | C9—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C14—N3—H3N | 114 (3) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C13—N3—H3N | 119 (3) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C14—N4—C15 | 126.2 (3) | C9—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C14—N4—H4N | 114 (3) | C9—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C15—N4—H4N | 119 (3) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.3 (4) | C9—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 121.7 (3) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.0 (4) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.8 (3) | N3—C13—C3 | 115.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | N3—C13—H13A | 108.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C3—C13—H13A | 108.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 117.7 (4) | N3—C13—H13B | 108.3 |
| C4—C3—C13 | 121.5 (4) | C3—C13—H13B | 108.3 |
| C2—C3—C13 | 120.8 (3) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.4 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.1 (4) | O2—C14—N4 | 124.7 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.0 | O2—C14—N3 | 121.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.0 | N4—C14—N3 | 113.9 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.3 (4) | N4—C15—C16 | 111.0 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.3 | N4—C15—C17 | 111.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C16—C15—C17 | 110.9 (3) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.9 (4) | N4—C15—C18 | 104.7 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 118.6 | C16—C15—C18 | 109.7 (3) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 118.6 | C17—C15—C18 | 108.6 (3) |
| N1—C7—C1 | 111.4 (3) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—H7A | 109.3 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C1—C7—H7A | 109.3 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—H7B | 109.3 | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C7—H7B | 109.3 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 108.0 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—N1 | 121.6 (3) | C15—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—N2 | 123.5 (3) | C15—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—N2 | 114.8 (3) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C11 | 110.3 (3) | C15—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C12 | 106.8 (3) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—C12 | 110.0 (3) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C10 | 110.4 (3) | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—C10 | 110.7 (3) | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C12—C9—C10 | 108.5 (3) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.3 (5) | C9—N2—C8—O1 | −7.1 (5) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 179.0 (3) | C9—N2—C8—N1 | 173.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.4 (5) | C8—N2—C9—C11 | −61.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C13 | −178.0 (3) | C8—N2—C9—C12 | 179.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (5) | C8—N2—C9—C10 | 61.2 (4) |
| C13—C3—C4—C5 | 178.4 (4) | C14—N3—C13—C3 | 94.4 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.6 (6) | C4—C3—C13—N3 | 157.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.7 (6) | C2—C3—C13—N3 | −24.4 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.3 (5) | C15—N4—C14—O2 | −4.9 (6) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −179.5 (4) | C15—N4—C14—N3 | 175.7 (3) |
| C8—N1—C7—C1 | −136.1 (4) | C13—N3—C14—O2 | 15.8 (6) |
| C2—C1—C7—N1 | −131.0 (4) | C13—N3—C14—N4 | −164.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C7—N1 | 48.2 (5) | C14—N4—C15—C16 | 72.8 (5) |
| C7—N1—C8—O1 | −1.7 (6) | C14—N4—C15—C17 | −51.5 (5) |
| C7—N1—C8—N2 | 177.6 (3) | C14—N4—C15—C18 | −168.9 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O2i | 0.82 (2) | 2.12 (2) | 2.909 (4) | 162 (4) |
| N2—H2N···O2i | 0.81 (2) | 2.28 (2) | 3.034 (4) | 153 (4) |
| N3—H3N···O1ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.15 (2) | 2.941 (4) | 154 (4) |
| N4—H4N···O1ii | 0.81 (2) | 2.12 (2) | 2.889 (4) | 160 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI5033).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Brooks, S. J., Caltagirone, C., Cossins, A. J., Gale, P. A. & Light, M. (2008). Supramol. Chem.20, 349–355.
- Carr, A. J., Melendez, R., Geib, S. J. & Hamilton, A. D. (1998). Tetrahedron Lett 39, 6646–6649.
- Chauhan, S. M. S., Bisht, T. & Garg, B. (2008). Tetrahedron Lett 49, 6646–6649.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Ghosh, A., Ganguly, B. & Das, A. (2007). Inorg. Chem 46, 9912–9918. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D. E., Fabbrizzi, L., Licchelli, M. & Monzani, E. (2005). Org. Biomol. Chem.3, 1495–1500. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hiscock, J. R., Caltagirone, C., Light, M. E., Hursthouse, M. B. & Gale, P. A. (2009). Org. Biomol. Chem 7, 1781–1783. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M. A. (2008). Curr. Org. Chem.12, 1231–1256.
- Jose, D. A., Kumar, D. K., Ganguly, B. & Das, A. (2007). Inorg. Chem.46, 5817–5819. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kyne, G. M., Light, M. E., Hursthouse, M. B., Mendoza, J. & Kilburn, J. D. (2001). J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 1258–1263.
- Lo, K. M. & Ng, S. W. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, A., Aller, E. & Molina, P. (2009). Tetrahedron65, 1397–1401.
- Nonius (2000). COLLECT. Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Pérez-Casas, C. & Yatsimirsky, A. K. (2008). J. Org. Chem.73, 2275–2284. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tejeda, A., Oliva, A. I., Simón, L., Grande, M., Caballero, M.-C. & Morán, J. R. (2000). Tetrahedron Lett.41, 4563–4566.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005866/ci5033sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005866/ci5033Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report