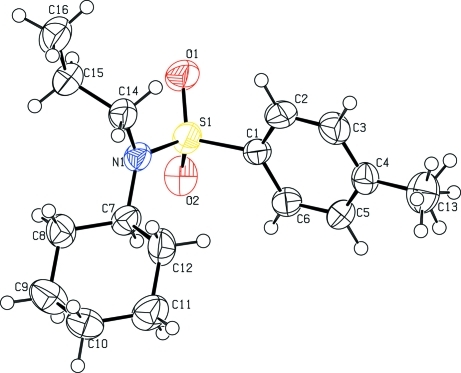
Abstract
The title compound, C16H25NO2S, is a sulfonamide derivative with the substitution of propyl and cyclohexyl groups at the N atom. The least-squares plane through all six C atoms of the cyclohexyl ring forms a dihedral angle of 58.88 (12)° with the toluene ring. No hydrogen-bonding interactions are present in the crystal structure.
Related literature
For the synthesis and related structures, see: Haider et al. (2009 ▶, 2010 ▶).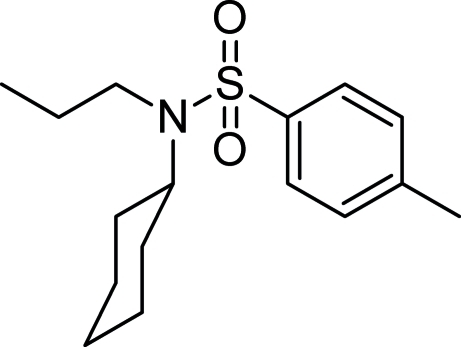
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H25NO2S
M r = 295.43
Monoclinic,
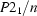
a = 7.8207 (5) Å
b = 25.2915 (16) Å
c = 8.3135 (6) Å
β = 102.411 (3)°
V = 1605.96 (19) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.20 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.16 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.980, T max = 0.988
12946 measured reflections
3004 independent reflections
1271 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.124
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.062
wR(F 2) = 0.128
S = 0.90
3003 reflections
183 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810006756/om2321sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810006756/om2321Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for providing a grant under the project of strengthening the Materials Chemistry Laboratory at GC University Lahore, Pakistan.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound (I) is an analogue to the structures (II) and (III) already published by our group (Haider et al., 2009, 2010). The cyclohexyl ring adopts the chair form, and it is orientented with the least-squares plane of all six carbon atoms at the dihedral angle of 58.88 (12)° with respect to the aromatic ring. This angle compares well with the analogous angle in (III) (59.92 (6)°) but differs slightly from that found in (II) (50.13 (9)°). Likewise, in the title compound (see Fig. 2) and in (II), no hydrogen bonding interaction was observed in the structure.
Experimental
A mixture of N-cyclohexyl-4-methyl benzene sulfonamide (1.089 g, 4.3 mmol), and sodium hydride (0.21 g, 8.6 mmol) in N, N-dimethylformamide (10 ml) was stirred at room temperature for half an hour followed by addition of propyl iodode ( 8.6 mmol). Stirring was continued further for a period of three hours and the contents were poured over crushed ice. The precipitated product was isolated, washed and crystallized from methanol solution by slow evaporation.
Refinement
The C—H H-atoms were positioned gemetrically and were refined using a riding model with C–H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq for aromatic (C), with C–H = 0.97 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq for methylene (C), and with C–H = 0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq for (C7). The low angle reflection (0 2 0) was omitted in the final refinement and the H-atoms for methyl (C13) were refined at two positions using the HFIX 127 command in SHELXL97 with C–H = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq for (C13).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The labelled diagram of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
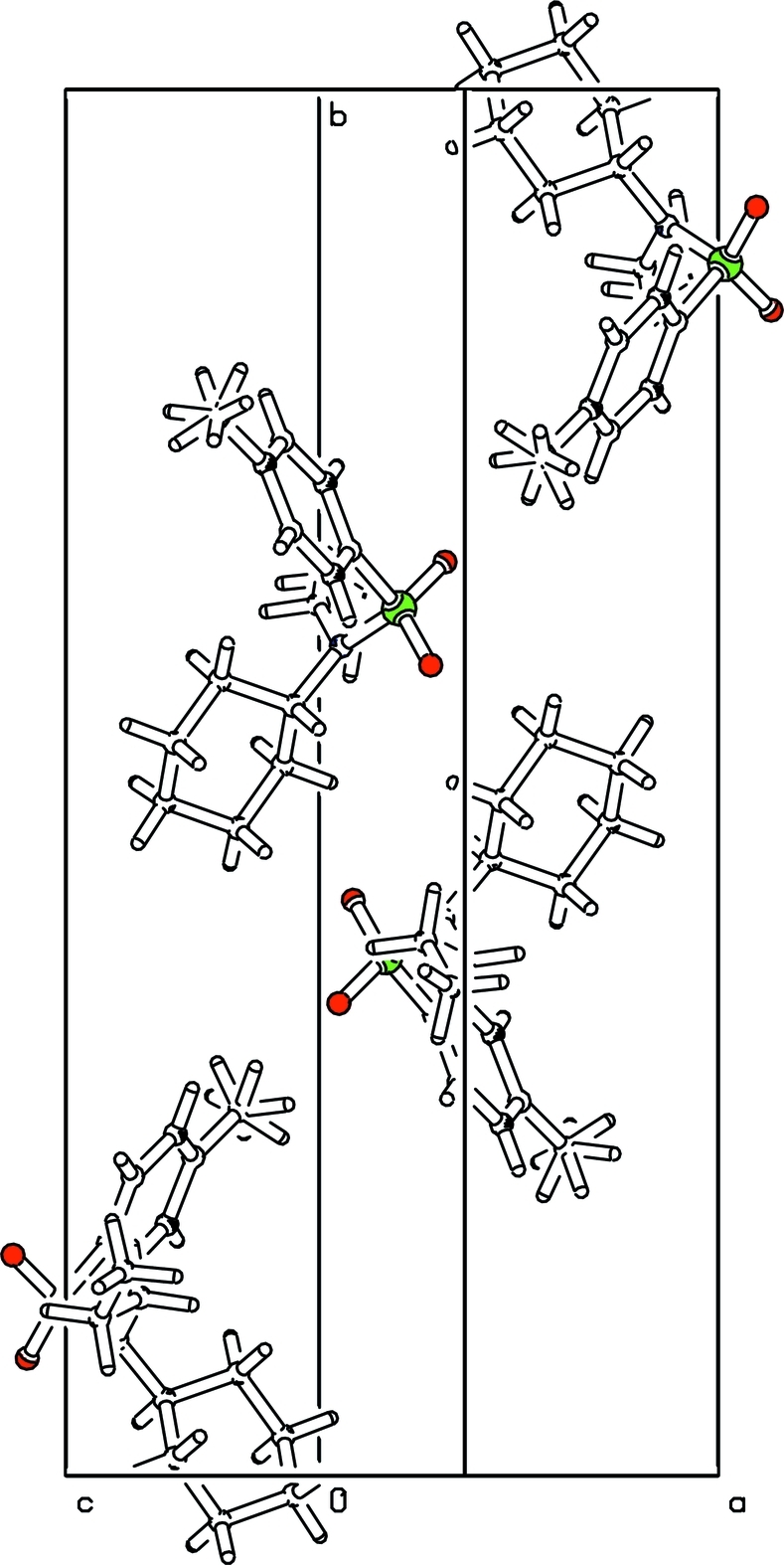
Unit cell packing for (I).
Crystal data
| C16H25NO2S | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 295.43 | Dx = 1.222 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 856 reflections |
| a = 7.8207 (5) Å | θ = 2.6–17.1° |
| b = 25.2915 (16) Å | µ = 0.20 mm−1 |
| c = 8.3135 (6) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 102.411 (3)° | Needle, colorless |
| V = 1605.96 (19) Å3 | 0.16 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3004 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1271 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.124 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.6°, θmin = 1.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.980, Tmax = 0.988 | k = −30→30 |
| 12946 measured reflections | l = −8→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.062 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.128 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.90 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0333P)2 + 0.8827P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3003 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 183 parameters | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1 | −0.12769 (14) | 0.12574 (4) | 0.82665 (13) | 0.0507 (3) | |
| O1 | −0.1615 (4) | 0.15917 (11) | 0.9551 (3) | 0.0687 (9) | |
| O2 | −0.2485 (3) | 0.08478 (11) | 0.7610 (3) | 0.0626 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.0618 (4) | 0.09828 (12) | 0.8964 (4) | 0.0444 (8) | |
| C1 | −0.1095 (5) | 0.16743 (15) | 0.6605 (5) | 0.0410 (10) | |
| C2 | −0.0304 (5) | 0.21596 (16) | 0.6879 (5) | 0.0570 (12) | |
| H2 | 0.0079 | 0.2283 | 0.7950 | 0.068* | |
| C3 | −0.0076 (5) | 0.24655 (16) | 0.5559 (6) | 0.0583 (12) | |
| H3 | 0.0477 | 0.2792 | 0.5761 | 0.070* | |
| C4 | −0.0647 (5) | 0.22991 (16) | 0.3951 (5) | 0.0475 (11) | |
| C5 | −0.1461 (5) | 0.18147 (16) | 0.3710 (5) | 0.0510 (11) | |
| H5 | −0.1880 | 0.1695 | 0.2639 | 0.061* | |
| C6 | −0.1676 (5) | 0.14986 (15) | 0.5021 (5) | 0.0464 (11) | |
| H6 | −0.2211 | 0.1170 | 0.4824 | 0.056* | |
| C7 | 0.1201 (5) | 0.05534 (15) | 0.7993 (5) | 0.0479 (11) | |
| H7 | 0.0146 | 0.0388 | 0.7337 | 0.058* | |
| C8 | 0.2179 (5) | 0.01308 (14) | 0.9125 (5) | 0.0559 (12) | |
| H8A | 0.1448 | 0.0002 | 0.9847 | 0.067* | |
| H8B | 0.3230 | 0.0282 | 0.9804 | 0.067* | |
| C9 | 0.2676 (6) | −0.03285 (16) | 0.8126 (6) | 0.0709 (14) | |
| H9A | 0.3344 | −0.0587 | 0.8867 | 0.085* | |
| H9B | 0.1620 | −0.0500 | 0.7525 | 0.085* | |
| C10 | 0.3749 (6) | −0.01397 (16) | 0.6925 (5) | 0.0611 (13) | |
| H10A | 0.3995 | −0.0436 | 0.6269 | 0.073* | |
| H10B | 0.4857 | 0.0000 | 0.7531 | 0.073* | |
| C11 | 0.2786 (6) | 0.02856 (18) | 0.5800 (5) | 0.0739 (14) | |
| H11A | 0.1737 | 0.0137 | 0.5110 | 0.089* | |
| H11B | 0.3526 | 0.0416 | 0.5089 | 0.089* | |
| C12 | 0.2289 (6) | 0.07402 (16) | 0.6810 (5) | 0.0654 (13) | |
| H12A | 0.3346 | 0.0908 | 0.7423 | 0.078* | |
| H12B | 0.1635 | 0.1002 | 0.6073 | 0.078* | |
| C13 | −0.0380 (6) | 0.26366 (17) | 0.2532 (5) | 0.0729 (14) | |
| H13A | 0.0274 | 0.2947 | 0.2949 | 0.109* | 0.50 |
| H13B | −0.1497 | 0.2739 | 0.1878 | 0.109* | 0.50 |
| H13C | 0.0254 | 0.2439 | 0.1865 | 0.109* | 0.50 |
| H13D | −0.0920 | 0.2470 | 0.1512 | 0.109* | 0.50 |
| H13E | 0.0851 | 0.2678 | 0.2583 | 0.109* | 0.50 |
| H13F | −0.0900 | 0.2978 | 0.2597 | 0.109* | 0.50 |
| C14 | 0.1931 (5) | 0.12873 (15) | 1.0130 (4) | 0.0508 (11) | |
| H14A | 0.1650 | 0.1660 | 0.9987 | 0.061* | |
| H14B | 0.3067 | 0.1233 | 0.9866 | 0.061* | |
| C15 | 0.2050 (5) | 0.11426 (15) | 1.1910 (5) | 0.0560 (12) | |
| H15A | 0.2365 | 0.0772 | 1.2070 | 0.067* | |
| H15B | 0.0913 | 0.1191 | 1.2179 | 0.067* | |
| C16 | 0.3390 (6) | 0.14751 (16) | 1.3061 (5) | 0.0729 (14) | |
| H16A | 0.4510 | 0.1438 | 1.2774 | 0.109* | |
| H16B | 0.3473 | 0.1359 | 1.4174 | 0.109* | |
| H16C | 0.3038 | 0.1839 | 1.2965 | 0.109* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0461 (7) | 0.0630 (7) | 0.0445 (7) | 0.0111 (7) | 0.0127 (5) | 0.0063 (6) |
| O1 | 0.076 (2) | 0.086 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0307 (17) | 0.0248 (16) | −0.0003 (16) |
| O2 | 0.0441 (18) | 0.072 (2) | 0.071 (2) | −0.0052 (16) | 0.0099 (15) | 0.0123 (16) |
| N1 | 0.042 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0063 (17) | 0.0035 (16) | 0.0006 (16) |
| C1 | 0.041 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.038 (3) | 0.005 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C2 | 0.067 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.002 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.013 (2) |
| C3 | 0.066 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.061 (3) | −0.007 (2) | 0.002 (3) | −0.002 (2) |
| C4 | 0.042 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C5 | 0.059 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C6 | 0.047 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.045 (3) | −0.005 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C7 | 0.044 (3) | 0.060 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C8 | 0.063 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.013 (2) |
| C9 | 0.073 (4) | 0.052 (3) | 0.097 (4) | 0.005 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C10 | 0.056 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.024 (3) | −0.009 (2) |
| C11 | 0.070 (4) | 0.100 (4) | 0.057 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C12 | 0.072 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.023 (2) |
| C13 | 0.074 (3) | 0.075 (3) | 0.070 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.016 (3) |
| C14 | 0.052 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C15 | 0.060 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C16 | 0.089 (4) | 0.075 (3) | 0.048 (3) | −0.011 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.004 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O2 | 1.429 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| S1—O1 | 1.430 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.516 (5) |
| S1—N1 | 1.627 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| S1—C1 | 1.767 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C14 | 1.469 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.522 (5) |
| N1—C7 | 1.482 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.371 (5) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.372 (5) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (5) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.381 (5) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (5) | C13—H13D | 0.9600 |
| C4—C13 | 1.507 (5) | C13—H13E | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.391 (5) | C13—H13F | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.507 (5) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C7—C12 | 1.508 (5) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.518 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.513 (5) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.526 (5) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.513 (5) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | ||
| O2—S1—O1 | 120.02 (18) | C10—C11—C12 | 110.3 (4) |
| O2—S1—N1 | 107.69 (17) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.6 |
| O1—S1—N1 | 106.65 (17) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.6 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 106.95 (18) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.6 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 106.83 (18) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.6 |
| N1—S1—C1 | 108.25 (16) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| C14—N1—C7 | 119.4 (3) | C7—C12—C11 | 111.7 (4) |
| C14—N1—S1 | 117.7 (2) | C7—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C7—N1—S1 | 118.8 (3) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.6 (4) | C7—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.9 (3) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C6—C1—S1 | 119.4 (3) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.9 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.9 (4) | C4—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.0 | C4—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.0 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.8 (4) | C4—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.1 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.1 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.1 (4) | C4—C13—H13D | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C13 | 121.9 (4) | H13A—C13—H13D | 141.1 |
| C3—C4—C13 | 121.0 (4) | H13B—C13—H13D | 56.3 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.8 (4) | H13C—C13—H13D | 56.3 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.1 | C4—C13—H13E | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.1 | H13A—C13—H13E | 56.3 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.7 (4) | H13B—C13—H13E | 141.1 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 | H13C—C13—H13E | 56.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | H13D—C13—H13E | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C12 | 114.1 (3) | C4—C13—H13F | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 110.6 (3) | H13A—C13—H13F | 56.3 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 110.2 (3) | H13B—C13—H13F | 56.3 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 107.2 | H13C—C13—H13F | 141.1 |
| C12—C7—H7 | 107.2 | H13D—C13—H13F | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 107.2 | H13E—C13—H13F | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 110.6 (3) | N1—C14—C15 | 114.1 (3) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | N1—C14—H14A | 108.7 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14A | 108.7 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | N1—C14—H14B | 108.7 |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14B | 108.7 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 108.1 | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.6 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 111.2 (3) | C14—C15—C16 | 112.0 (3) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 109.4 | C14—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.4 | C16—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 109.4 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.4 | C16—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 108.0 | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.9 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 111.0 (3) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.4 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.4 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.4 | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.4 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 108.0 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—N1—C14 | −161.9 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.2 (6) |
| O1—S1—N1—C14 | −31.8 (3) | S1—C1—C6—C5 | −177.0 (3) |
| C1—S1—N1—C14 | 82.8 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.2 (6) |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | 41.0 (3) | C14—N1—C7—C12 | −64.2 (5) |
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | 171.1 (3) | S1—N1—C7—C12 | 92.5 (4) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | −74.3 (3) | C14—N1—C7—C8 | 60.7 (4) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 167.1 (3) | S1—N1—C7—C8 | −142.6 (3) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | 37.4 (4) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | 176.3 (3) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | −77.1 (3) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −56.6 (5) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −16.1 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 56.6 (5) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | −145.8 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −56.2 (5) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | 99.7 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 55.7 (5) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.9 (6) | N1—C7—C12—C11 | −177.7 (3) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 175.9 (3) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 57.2 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (6) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −56.7 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (6) | C7—N1—C14—C15 | −104.2 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C13 | −179.7 (4) | S1—N1—C14—C15 | 98.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.2 (6) | N1—C14—C15—C16 | −178.8 (3) |
| C13—C4—C5—C6 | 178.7 (4) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: OM2321).
References
- Bruker (2007). SADABS, APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Haider, Z., Arshad, M. N., Simpson, J., Khan, I. U. & Shafiq, M. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Haider, Z., Khan, I. U., Zia-ur-Rehman, M. & Arshad, M. N. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810006756/om2321sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810006756/om2321Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report