Abstract
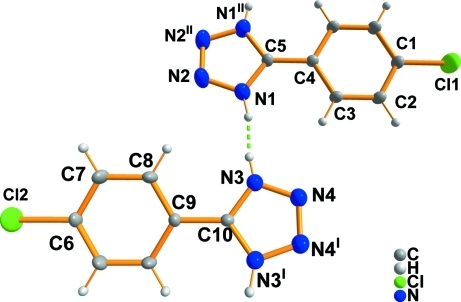
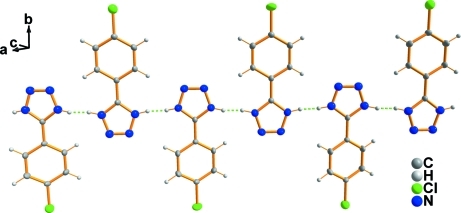
The two independent molecules of the title compound, C7H5ClN4, both lie on a twofold rotation axis that passes through the centroids of the five- and six-membered rings and the attached Cl C atom. One molecule is nearly planar [dihedral angle between rings = 0.22 (6)°], whereas the other is significantly twisted [dihedral angle = 17.38 (6)°]. In the crystal, adjacent molecules are linked by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds into a chain structure.
Related literature
For the synthesis, see: Xu et al. (2009 ▶). For a related structure, see: Luo et al. (2006 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C7H5ClN4
M r = 180.60
Monoclinic,
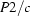
a = 9.4596 (19) Å
b = 11.437 (2) Å
c = 7.2988 (15) Å
β = 107.91 (3)°
V = 751.4 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.45 mm−1
T = 291 K
0.21 × 0.14 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995 ▶) T min = 0.912, T max = 0.952
7237 measured reflections
1720 independent reflections
1194 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.038
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.135
S = 1.05
1720 reflections
118 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.77 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2002 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810003788/ng2726sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810003788/ng2726Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H3⋯N3 | 0.85 (1) | 2.05 (1) | 2.889 (2) | 172 (1) |
| N3—H6⋯N1 | 0.83 (3) | 2.08 (4) | 2.889 (2) | 165.7 (2) |
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The tetrazole functional group attracted considerable attention over recent years, because of both the intriguing architectures in coordination chemistry and the potential applications in medicinal chemistry and materials science (Luo et al., 2006). Herein, we reported the synthesis and the crystal structure of the title compound.
In the asymmetric unit of the title compound, C7H5ClN4, contains two half molecules of 5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1H-tetrazole. In these two molecules, the centres of bezene and tetrazole rings locate on the symmetry plane, with the dihedral angle of 0.22 (6)° and 17.38 (6)°, respectively.
A one-dimensional chain structure is built up by N—H···N hydrogen bonds between the imino groups of the title compound.
Experimental
For the preparation of the title compound, 4-chlorobenzonitrile (13.7 g, 0.10 mol), ammonium chloride (13.4 g, 0.25 mmol) and NaN3 (7.8 g, 0.12 mol) were dissolved in DMF (120 ml). The mixture was heated to reflux stirred for 24 h under stirring. Then, it was cooled to room temperature and poured into cold water and acidified to pH = 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The suspension was filtrated, and the residue was washed with water and ethanol for several times, and then dried (11.1 g, 61.8 %). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by recrystallization in the EtOH solution.
Refinement
Due to the title compound molecules located on the symmetry planes, the H atoms bound to N atoms were disordered into two positions with the occupancies of 0.5, respectively. H atoms bound to N atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely. H atoms bound to C atoms were placed in calculated positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic) and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level for non-H atoms. Dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing view, showing one-dimensional chain structure. Dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonds.
Crystal data
| C7H5ClN4 | F(000) = 368 |
| Mr = 180.60 | Dx = 1.596 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yc | Cell parameters from 5352 reflections |
| a = 9.4596 (19) Å | θ = 3.1–27.5° |
| b = 11.437 (2) Å | µ = 0.45 mm−1 |
| c = 7.2988 (15) Å | T = 291 K |
| β = 107.91 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 751.4 (3) Å3 | 0.21 × 0.14 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 1720 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1194 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.038 |
| ω scan | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.912, Tmax = 0.952 | k = −14→14 |
| 7237 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.135 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0807P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1720 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 118 parameters | Δρmax = 0.77 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.0000 | 0.7724 (3) | 0.2500 | 0.0340 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.1238 (2) | 0.7123 (2) | 0.3612 (3) | 0.0375 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.2067 | 0.7530 | 0.4358 | 0.045* | |
| C3 | 0.1235 (2) | 0.59197 (19) | 0.3606 (3) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.2068 | 0.5518 | 0.4350 | 0.040* | |
| C4 | 0.0000 | 0.5293 (3) | 0.2500 | 0.0282 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.0000 | 0.4029 (3) | 0.2500 | 0.0288 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.5000 | −0.0727 (3) | 0.7500 | 0.0296 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.3680 (2) | −0.0135 (2) | 0.6704 (3) | 0.0389 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.2797 | −0.0544 | 0.6188 | 0.047* | |
| C8 | 0.3688 (2) | 0.1065 (2) | 0.6683 (3) | 0.0354 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.2809 | 0.1471 | 0.6119 | 0.042* | |
| C9 | 0.5000 | 0.1681 (2) | 0.7500 | 0.0258 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.5000 | 0.2975 (3) | 0.7500 | 0.0267 (6) | |
| Cl1 | 0.0000 | 0.92391 (7) | 0.2500 | 0.0492 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.5000 | −0.22534 (7) | 0.7500 | 0.0464 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.1109 (2) | 0.33285 (16) | 0.3488 (2) | 0.0349 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.1934 | 0.3493 | 0.4318 | 0.050 (15)* | 0.50 |
| N2 | 0.0660 (2) | 0.22079 (17) | 0.3089 (3) | 0.0418 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.3941 (2) | 0.36603 (16) | 0.6406 (3) | 0.0349 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.322 (5) | 0.352 (4) | 0.545 (6) | 0.016 (9)* | 0.50 |
| N4 | 0.4364 (2) | 0.47685 (17) | 0.6842 (3) | 0.0398 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0332 (14) | 0.0274 (17) | 0.0377 (15) | 0.000 | 0.0056 (12) | 0.000 |
| C2 | 0.0313 (10) | 0.0320 (12) | 0.0424 (11) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0011 (9) | −0.0024 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0270 (9) | 0.0298 (12) | 0.0349 (10) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0017 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0267 (13) | 0.0285 (17) | 0.0270 (13) | 0.000 | 0.0046 (11) | 0.000 |
| C5 | 0.0305 (13) | 0.0261 (15) | 0.0266 (12) | 0.000 | 0.0038 (11) | 0.000 |
| C6 | 0.0365 (14) | 0.0215 (15) | 0.0272 (13) | 0.000 | 0.0047 (12) | 0.000 |
| C7 | 0.0324 (11) | 0.0310 (12) | 0.0456 (12) | −0.0054 (8) | 0.0006 (10) | −0.0066 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0242 (9) | 0.0328 (12) | 0.0408 (11) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0021 (8) | −0.0002 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0292 (13) | 0.0219 (15) | 0.0238 (12) | 0.000 | 0.0044 (11) | 0.000 |
| C10 | 0.0248 (12) | 0.0282 (16) | 0.0244 (12) | 0.000 | 0.0037 (11) | 0.000 |
| Cl1 | 0.0465 (5) | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0709 (6) | 0.000 | 0.0090 (4) | 0.000 |
| Cl2 | 0.0591 (5) | 0.0225 (5) | 0.0503 (5) | 0.000 | 0.0061 (4) | 0.000 |
| N1 | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0275 (10) | 0.0356 (9) | 0.0027 (7) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0001 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0437 (10) | 0.0245 (10) | 0.0456 (10) | 0.0031 (8) | −0.0036 (8) | 0.0027 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0329 (9) | 0.0257 (10) | 0.0374 (9) | 0.0008 (7) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0000 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0259 (10) | 0.0450 (10) | 0.0016 (8) | −0.0027 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.385 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.373 (3) |
| C1—C2i | 1.385 (3) | C7—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C1—Cl1 | 1.732 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.392 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.376 (3) | C8—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H1 | 0.9300 | C9—C8ii | 1.392 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.397 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.480 (4) |
| C3—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—N3ii | 1.328 (3) |
| C4—C3i | 1.397 (3) | C10—N3 | 1.328 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.446 (4) | N1—N2 | 1.353 (3) |
| C5—N1i | 1.340 (3) | N1—H3 | 0.8492 |
| C5—N1 | 1.340 (3) | N2—N2i | 1.280 (4) |
| C6—C7ii | 1.382 (3) | N3—N4 | 1.338 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.382 (3) | N3—H6 | 0.83 (4) |
| C6—Cl2 | 1.746 (3) | N4—N4ii | 1.288 (3) |
| C2—C1—C2i | 120.5 (3) | C8—C7—H4 | 120.4 |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 119.77 (15) | C6—C7—H4 | 120.4 |
| C2i—C1—Cl1 | 119.77 (15) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.55 (19) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.6 (2) | C7—C8—H5 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—H1 | 120.2 | C9—C8—H5 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—H1 | 120.2 | C8—C9—C8ii | 119.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.05 (19) | C8—C9—C10 | 120.38 (13) |
| C2—C3—H2 | 119.5 | C8ii—C9—C10 | 120.38 (14) |
| C4—C3—H2 | 119.5 | N3ii—C10—N3 | 107.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C3i | 118.2 (3) | N3ii—C10—C9 | 126.18 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.88 (14) | N3—C10—C9 | 126.18 (13) |
| C3i—C4—C5 | 120.88 (14) | C5—N1—N2 | 107.97 (18) |
| N1i—C5—N1 | 106.6 (3) | C5—N1—H3 | 130.3 |
| N1i—C5—C4 | 126.70 (14) | N2—N1—H3 | 121.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 126.70 (14) | N2i—N2—N1 | 108.73 (11) |
| C7ii—C6—C7 | 121.3 (3) | C10—N3—N4 | 107.51 (18) |
| C7ii—C6—Cl2 | 119.34 (14) | C10—N3—H6 | 131 (3) |
| C7—C6—Cl2 | 119.34 (14) | N4—N3—H6 | 120 (3) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.1 (2) | N4ii—N4—N3 | 108.67 (11) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, y, −z+3/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H3···N3 | 0.85 (1) | 2.05 (1) | 2.889 (2) | 172 (1) |
| N3—H6···N1 | 0.83 (3) | 2.08 (4) | 2.889 (2) | 165.7 (2) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NG2726).
References
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Luo, J., Zhang, X.-R., Cui, L.-L., Dai, W.-Q. & Liu, B.-S. (2006). Acta Cryst. C62, m614–m616. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (1998). RAPID-AUTO Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku/MSC (2002). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC Inc., The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.-J., Pan, Y.-J. & Cui, L.-J. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810003788/ng2726sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810003788/ng2726Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report