Abstract
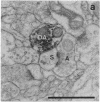
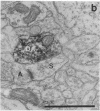
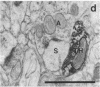
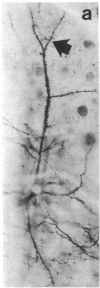
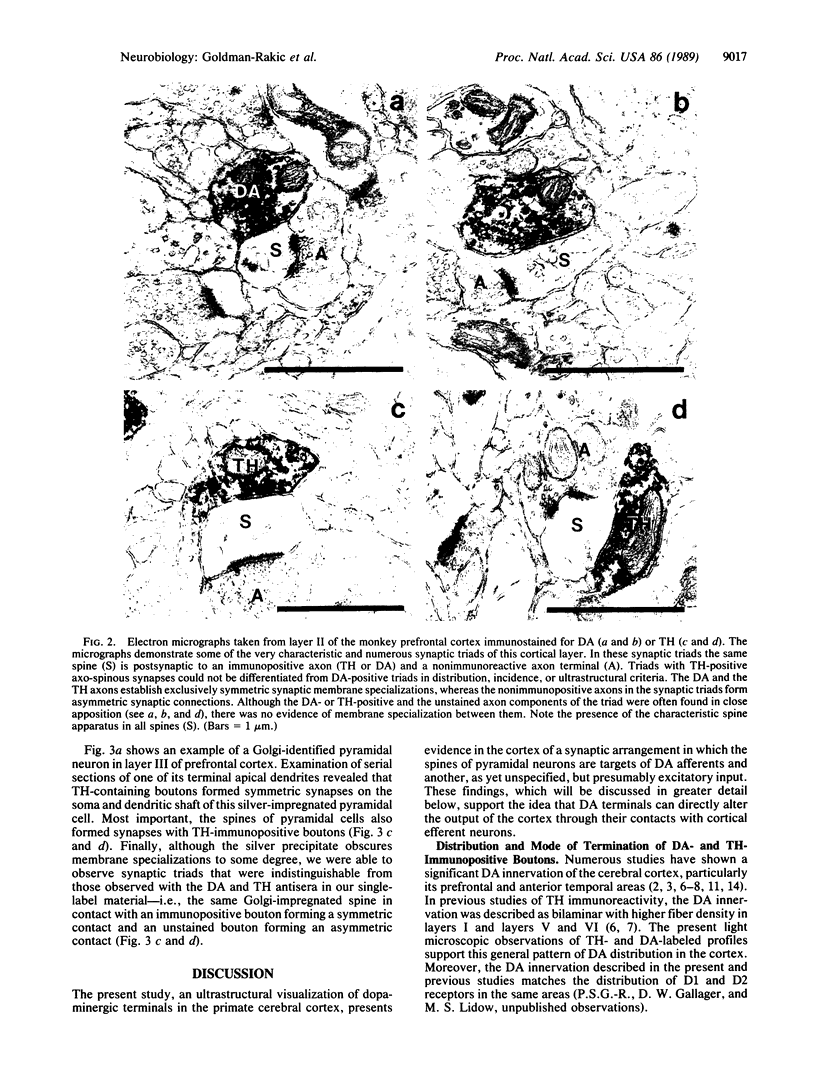
Dopamine (DA)-containing projections to the cerebral cortex are considered to play an important role in cognitive processes. Using a recently developed monoclonal antiserum directed against DA and an antibody directed against tyrosine hydroxylase in combination with Golgi impregnation and electron microscopy, we have observed that DA and tyrosine hydroxylase afferents establish symmetric membrane specializations with the soma, dendritic shafts, and spines of identified pyramidal cells in the prefrontal, cingulate, and motor cortex of primates. The axospinous contacts invariably formed part of a synaptic complex in which the dendritic spine of a pyramidal neuron was the target of both a DA-positive symmetric and an unlabeled asymmetric bouton. This arrangement allows direct DA modulation of the overall excitability of cortical projection neurons by altering local spine responses to excitatory inputs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger B., Trottier S., Verney C., Gaspar P., Alvarez C. Regional and laminar distribution of the dopamine and serotonin innervation in the macaque cerebral cortex: a radioautographic study. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 1;273(1):99–119. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozoski T. J., Brown R. M., Rosvold H. E., Goldman P. S. Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science. 1979 Aug 31;205(4409):929–932. doi: 10.1126/science.112679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney B. S., Aghajanian G. K. Dopamine and norepinephrine innervated cells in the rat prefrontal cortex: pharmacological differentiation using microiontophoretic techniques. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 1;19(11):1783–1789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagnaud J. L., Mons N., Tuffet S., Grandier-Vazeilles X., Geffard M. Monoclonal antibodies against glutaraldehyde-conjugated dopamine. J Neurochem. 1987 Aug;49(2):487–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Burt D. R., Snyder S. H. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science. 1976 Apr 30;192(4238):481–483. doi: 10.1126/science.3854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferron A., Thierry A. M., Le Douarin C., Glowinski J. Inhibitory influence of the mesocortical dopaminergic system on spontaneous activity or excitatory response induced from the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Powell J. F., Smith A. D. Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive boutons in synaptic contact with identified striatonigral neurons, with particular reference to dendritic spines. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):1189–1215. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frotscher M., Leranth C. Catecholaminergic innervation of pyramidal and GABAergic nonpyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampus. Double label immunostaining with antibodies against tyrosine hydroxylase and glutamate decarboxylase. Histochemistry. 1988;88(3-6):313–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00570289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frotscher M., Léránth C. The cholinergic innervation of the rat fascia dentata: identification of target structures on granule cells by combining choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry and Golgi impregnation. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jan 1;243(1):58–70. doi: 10.1002/cne.902430106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar P., Berger B., Febvret A., Vigny A., Henry J. P. Catecholamine innervation of the human cerebral cortex as revealed by comparative immunohistochemistry of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jan 8;279(2):249–271. doi: 10.1002/cne.902790208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Houser C. R., Jones E. G., Vaughn J. E. Synaptic organization of immunocytochemically identified GABA neurons in the monkey sensory-motor cortex. J Neurocytol. 1983 Aug;12(4):639–660. doi: 10.1007/BF01181528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Fuxe K., Goldstein M., Park D. Immunohistochemical studies on the localization and distribution of monoamine neuron systems in the rat brain II. Tyrosine hydroxylase in the telencephalon. Med Biol. 1977 Feb;55(1):21–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., DeFelipe J., Hendry S. H., Maggio J. E. A study of tachykinin-immunoreactive neurons in monkey cerebral cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1206–1224. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01206.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Powell T. P. An electron microscopic study of the laminar pattern and mode of termination of afferent fibre pathways in the somatic sensory cortex of the cat. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Jan 29;257(812):45–62. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Foote S. L., Goldstein M., Morrison J. H. The dopaminergic innervation of monkey prefrontal cortex: a tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 1988 May 24;449(1-2):225–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund J. S., Lund R. D. The termination of callosal fibers in the paravisual cortex of the rat. Brain Res. 1970 Jan 6;17(1):25–45. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos G. C., Parnavelas J. G., Buijs R. Monoaminergic fibers form conventional synapses in the cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 19;76(3):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A., Feldman M. L. The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat cerebral cortex. I. General description. J Neurocytol. 1976 Feb;5(1):63–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01176183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson S. L., St Mary J. S., Harding N. R. cis-Flupentixol antagonism of the rat prefrontal cortex neuronal response to apomorphine and ventral tegmental area input. Brain Res Bull. 1987 Jun;18(6):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(87)90207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Beckley S. C., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in the neostriatum. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 30;225(2):373–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90843-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Immunohistochemical localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in brain by light and electron microscopy. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 28;85(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaguchi T., Matsumura M. Laminar distributions of neurons sensitive to acetylcholine, noradrenaline and dopamine in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the monkey. Neurosci Res. 1985 Apr;2(4):255–273. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(85)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H., Scatton B., Moal M. L. Dopaminergic A10 neurones are involved in cognitive functions. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):150–151. doi: 10.1038/286150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Takagi H. A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1779–1783. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguéla P., Watkins K. C., Descarries L. Ultrastructural features of dopamine axon terminals in the anteromedial and the suprarhinal cortex of adult rat. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 23;442(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. M., Blanc G., Sobel A., Stinus L., Glowinski J. Dopaminergic terminals in the rat cortex. Science. 1973 Nov 2;182(4111):499–501. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4111.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eden C. G., Hoorneman E. M., Buijs R. M., Matthijssen M. A., Geffard M., Uylings H. B. Immunocytochemical localization of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex of the rat at the light and electron microscopical level. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):849–862. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92964-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]