Abstract
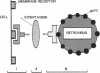
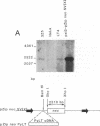
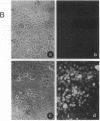
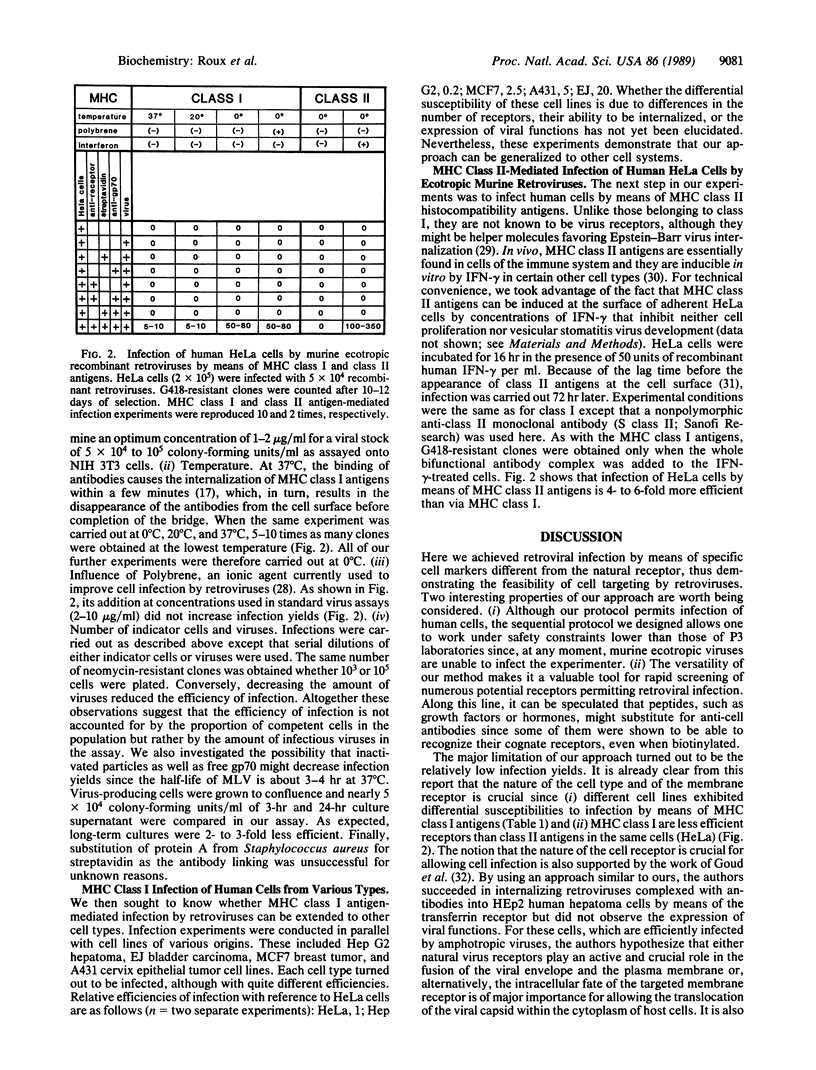
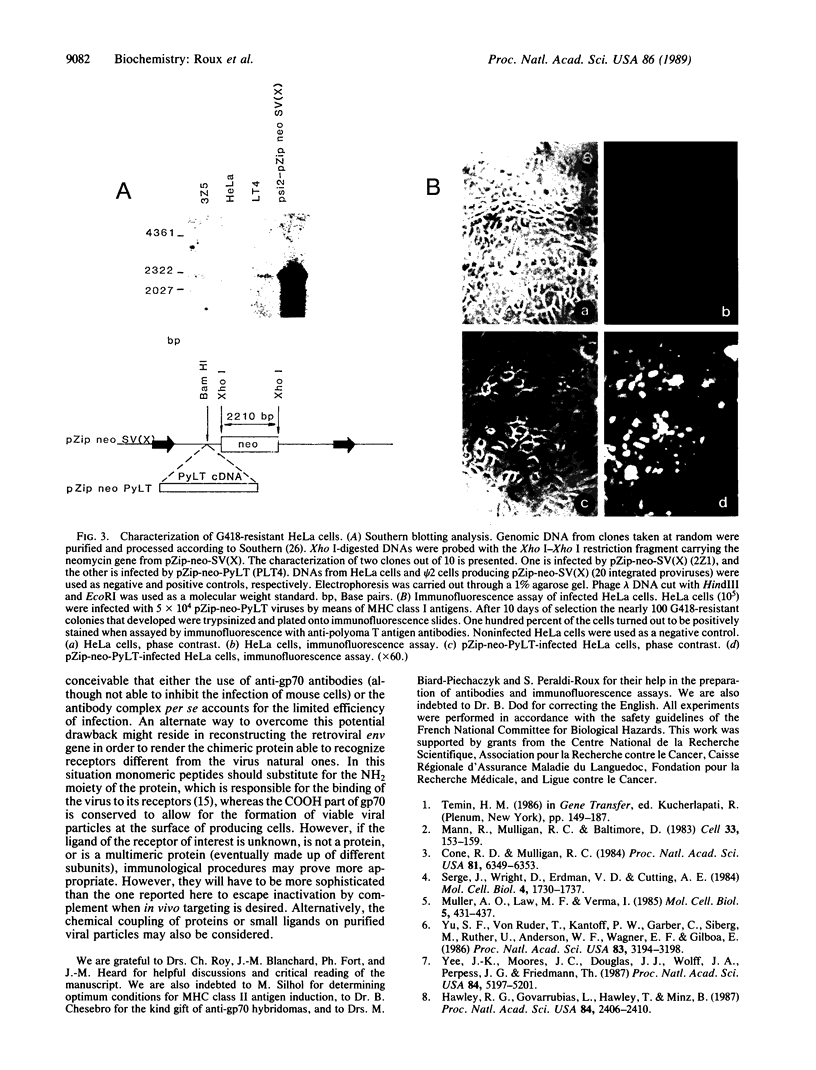
A technique for delivering genes carried by recombinant retroviruses into specific cell types could have numerous applications in oncology, developmental biology, and gene therapy. As a first step toward this remote goal we designed a procedure allowing in vitro cell targeting by retroviruses. Biotinylated antibodies against the viral envelope protein on one side, and against specific cell membrane markers on the other side, were bridged by streptavidin and used to link the virus to the host. The method was successfully used to infect human cells with ecotropic murine retroviruses by means of major histocompatibility complex class I and class II antigens and appears easily adaptable to other cell membrane markers. Moreover, the sequential protocol we designed, although allowing infection of human cells, requires less stringent safety constraints than would handling of amphotropic virus stocks.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen K. B., Nexø B. A. Entry of murine retrovirus into mouse fibroblasts. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Different murine cell lines manifest unique patterns of interference to superinfection by murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Legrain P., Buttin G. Antibody-mediated binding of a murine ecotropic Moloney retroviral vector to human cells allows internalization but not the establishment of the proviral state. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild B. C., Finer M. H., Housman D. E., Mulligan R. C. Development of retrovirus vectors useful for expressing genes in cultured murine embryonal cells and hematopoietic cells in vivo. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3795–3801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3795-3801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handelin B. L., Kabat D. Cell surface receptors for murine leukemia viruses: two assays and their implications. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Covarrubias L., Hawley T., Mintz B. Handicapped retroviral vectors efficiently transduce foreign genes into hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2406–2410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Morein B., Fries E., Simons K., Robinson P., Schirrmacher V., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Human (HLA-A and HLA-B) and murine (H-2K and H-2D) histocompatibility antigens are cell surface receptors for Semliki Forest virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3846–3850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. The antibody-induced clustering and endocytosis of HLA antigens on cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Cepko C. L., Mulligan R. C., Sharp P. A. Recombinant retroviruses encoding simian virus 40 large T antigen and polyomavirus large and middle T antigens. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1204–1217. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Conrad D. H. The murine lymphocyte receptor for IgE. II. Characterization of the multivalent nature of the B lymphocyte receptor for IgE. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1790–1795. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machy P., Truneh A., Gennaro D., Hoffstein S. Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules internalized via coated pits in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):724–726. doi: 10.1038/328724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond S., Peters G., Dickson C. Mouse mammary tumor virus can mediate cell fusion at reduced pH. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90405-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisert P. S., Spiro R. C., Townsend P. L., Stanford S. A., Sairenji T., Humphreys R. E. Functional association of class II antigens with cell surface binding of Epstein-Barr virus. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3776–3780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. M., Cochet M. M., Fellous M. Interferon and major histocompatibility complex genes: a model to analyse eukaryotic gene regulation? Interferon. 1986;7:47–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Wright D., Erdman V. D., Cutting A. E. Amphotropic retrovirus vector system for human cell gene transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima K., Vogt P. K. Enhancement and inhibition of avian sarcoma viruses by polycations and polyanions. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):414–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K., Moores J. C., Jolly D. J., Wolff J. A., Respess J. G., Friedmann T. Gene expression from transcriptionally disabled retroviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5197–5201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
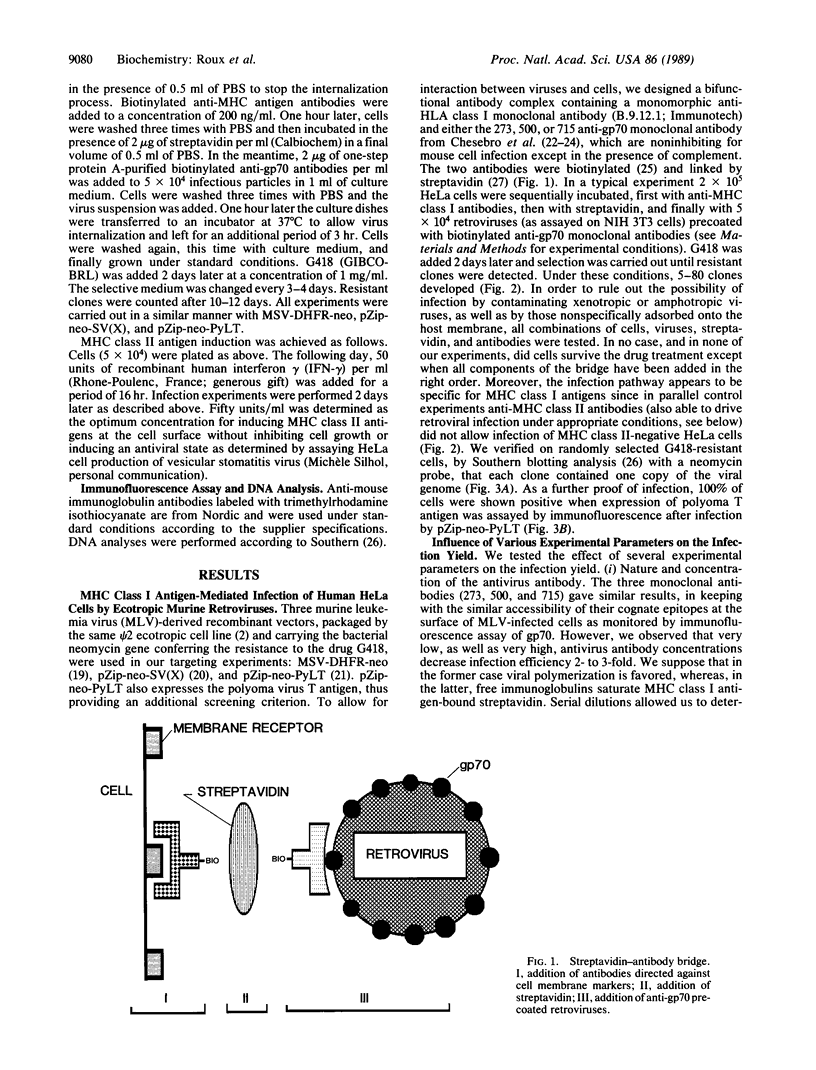
- Yu S. F., von Rüden T., Kantoff P. W., Garber C., Seiberg M., Rüther U., Anderson W. F., Wagner E. F., Gilboa E. Self-inactivating retroviral vectors designed for transfer of whole genes into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]