Abstract
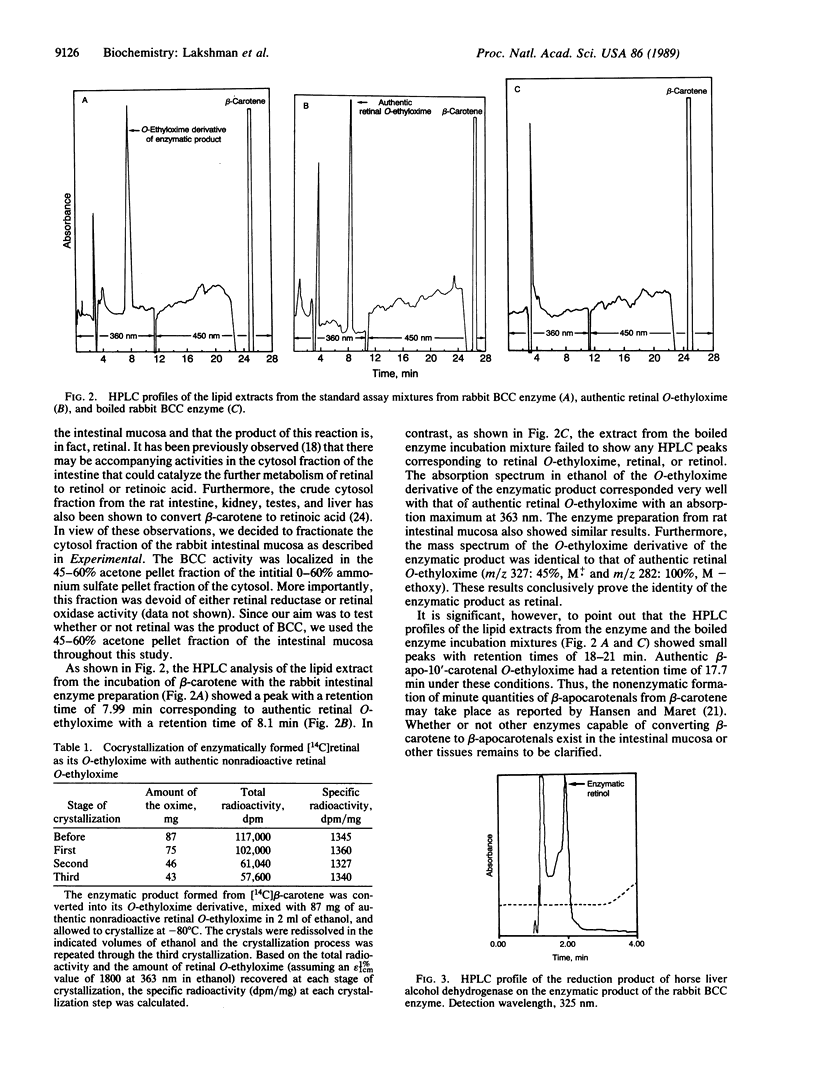
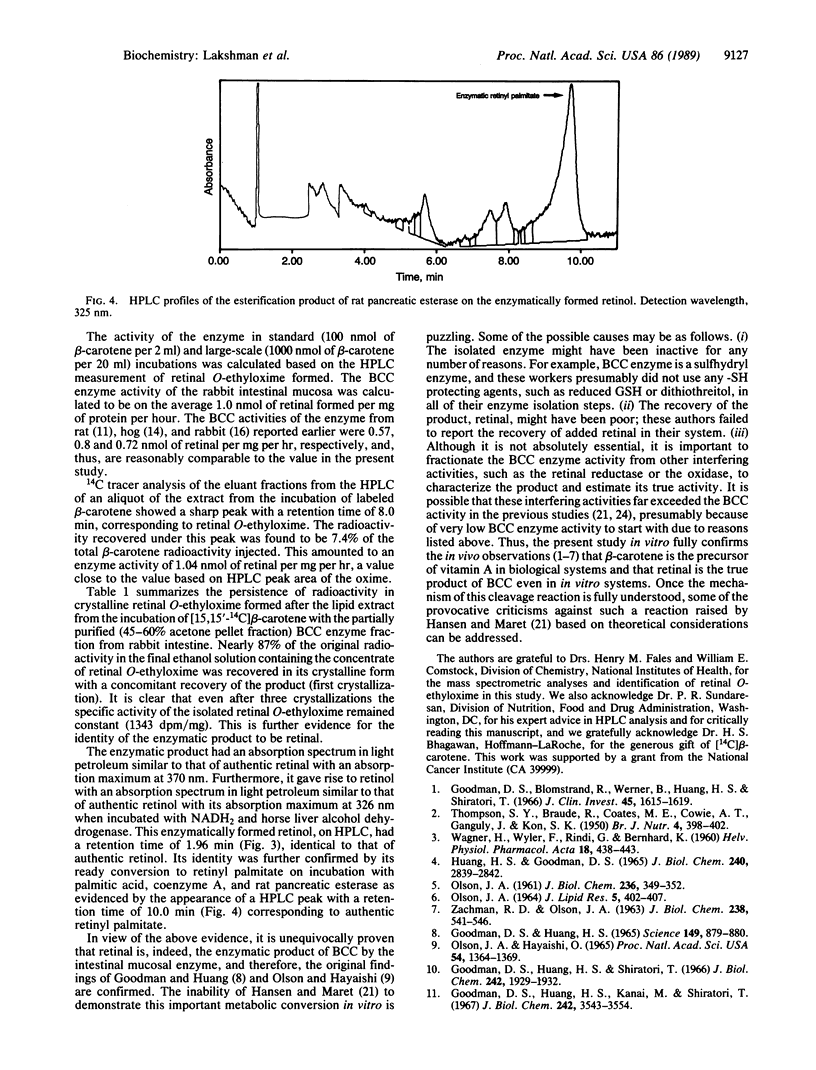
Enzymatic conversion of all-trans-beta-carotene to retinal by a partially purified enzyme from rabbit and rat intestinal mucosa was demonstrated. The enzymatic product was characterized based on the following evidence: (i) The product gave rise to its O-ethyloxime by treatment with O-ethylhydroxylamine with an absorption maximum at 363 nm in ethanol characteristic of authentic retinal O-ethyloxime. High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) of this derivative yielded a sharp peak with a retention time of 7.99 min corresponding to the authentic compound. The enzyme blank and boiled enzyme blank failed to show any significant HPLC peaks corresponding to retinal O-ethyloxime, retinal, or retinol. (ii) The mass spectrum of the O-ethyloxime of the enzymatic product was identical to that of authentic retinal O-ethyloxime (m/z 327: 45%, M+. and m/z 282: 100%, M--ethoxy). (iii) The specific activity of the enzymatically formed [14C]retinal O-ethyloxime remained constant even after repeated crystallization. (iv) The enzymatic product exhibited an absorption maximum at 370 nm in light petroleum characteristic of authentic retinal. Furthermore, it was reduced by horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase to retinol with an absorption maximum at 326 nm in light petroleum. This retinol was enzymatically esterified to retinyl palmitate by rat pancreatic esterase with a retention time of 10 min on HPLC corresponding to authentic retinyl palmitate. Thus, the enzymatic product of beta-carotene cleavage by the partially purified intestinal enzyme was unequivocally confirmed to be retinal.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fidge N. H., Smith F. R., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A and carotenoids. The enzymic conversion of beta-carotene into retinal in hog intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):689–694. doi: 10.1042/bj1140689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S., HUANG H. S. BIOSYNTHESIS OF VITAMIN A WITH RAT INTESTINAL ENZYMES. Science. 1965 Aug 20;149(3686):879–880. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3686.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawienowski A. M., Stacewicz-Sapuncakis M., Longley R. Biosynthesis of retinal in bovine corpus luteum. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jul;15(4):375–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Biosynthesis of vitamin A from beta-carotene. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Jul;22(7):963–965. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.7.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Blomstrand R., Werner B., Huang H. S., Shiratori T. The intestinal absorption and metabolism of vitamin A and beta-carotene in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1615–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI105468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Huang H. S., Shiratori T. Mechanism of the biosynthesis of vitamin A from beta-carotene. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):1929–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUANG H. S., GOODMAN D. S. VITAMIN A AND CAROTENOIDS. I. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF 14C-LABELLED VITAMIN A ALCOHOL AND BETA-CAROTENE IN THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2839–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S., Maret W. Retinal is not formed in vitro by enzymatic central cleavage of beta-carotene. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):200–206. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan M. R., Chansang H., Olson J. A. Purification and properties of carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase of rabbit intestine. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):477–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan M. R., Pope J. L., Olson J. A. The specificity of a partially purified carotenoid cleavage enzyme of rabbit intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 24;33(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90791-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli J. L., Race K. R. Biogenesis of retinoic acid from beta-carotene. Differences between the metabolism of beta-carotene and retinal. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17372–17377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON J. A. The conversion of radioactive beta-carotene into vitamin A by the rat intestine in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A., Hayaishi O. The enzymatic cleavage of beta-carotene into vitamin A by soluble enzymes of rat liver and intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Nov;54(5):1364–1370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A. The effect of bile and bile salts on the uptake and cleavage of beta-carotene into retinol ester (vitamin A ester) by intestinal slices. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):402–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Cama H. R. Enzymatic cleavage of carotenoids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklan D. Carotene Cleavage Activity in the corpus luteum of cattle. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1983;53(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklan D., Halevy O. Vitamin A metabolism in chick liver: some properties of the cytosolic lipid-protein aggregate. Br J Nutr. 1984 Jul;52(1):107–114. doi: 10.1079/bjn19840076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON S. Y., BRAUDE R., COATES M. E., COWIE A. T., GANGULY J., KON S. K. Further studies of the conversion of beta-carotene to vitamin A in the intestine. Br J Nutr. 1950;4(4):398–421. doi: 10.1079/bjn19500063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZACHMAN R. D., OLSON J. A. The uptake of C14-beta-carotene and its conversion to retinol ester (vitamin A ester) by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:541–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kuijk F. J., Handelman G. J., Dratz E. A. Rapid analysis of the major classes of retinoids by step gradient reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography using retinal (O-ethyl) oxime derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1985 Nov 27;348(1):241–251. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92458-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



