Abstract
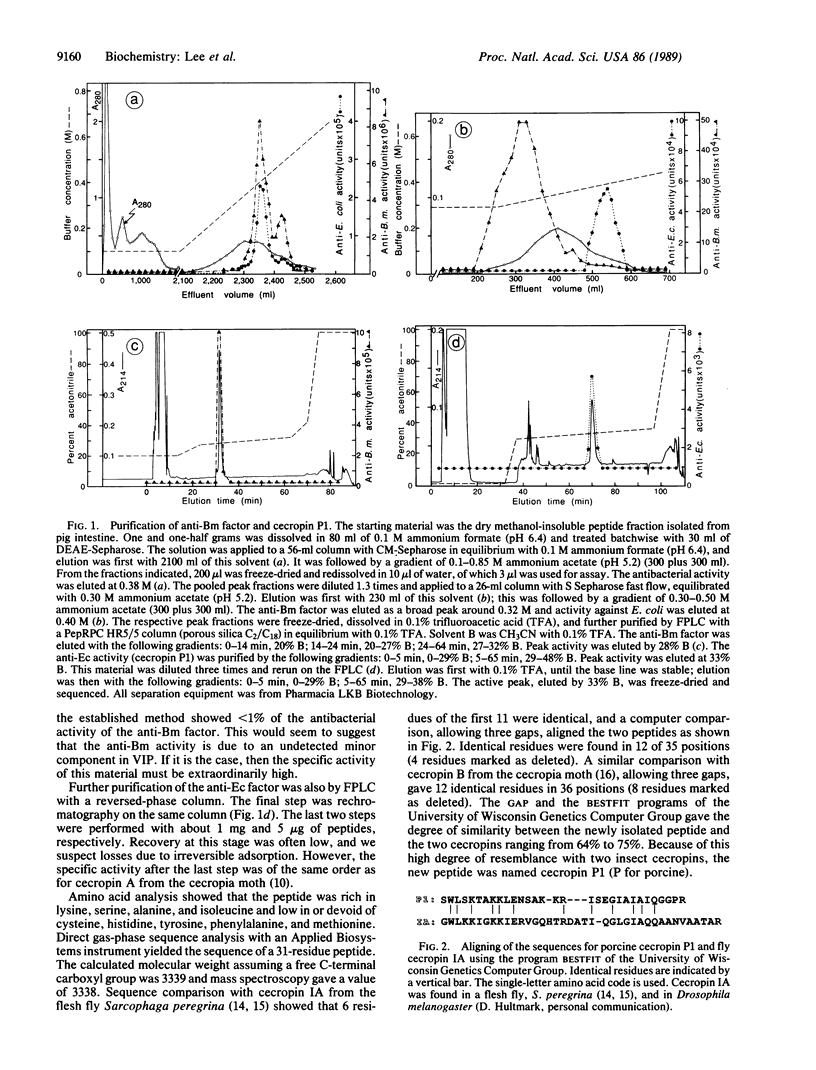
Pig small intestine was used as starting material for a batchwise isolation of a peptide fraction enriched in antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli (anti-Ec factor) and against Bacillus megaterium (anti-Bm factor). Separation and further purification were by different types of chromatography. Sequence analysis showed the anti-Bm factor to be apparently similar to vasoactive intestinal peptide. The anti-Ec factor was found to have a 31-residue sequence that was cecropin-like. It was named cecropin P1 and its structure was confirmed by solid-phase synthesis. Synthetic cecropin P1 with and without C-terminal amide was assayed on eight different bacteria. Mobility comparison between synthetic and natural cecropin P1 indicates that the natural peptide has a free C-terminal carboxyl group.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boman H. G., Hultmark D. Cell-free immunity in insects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson L., Russell V., Dunn P. E. A family of bacteria-regulated, cecropin D-like peptides from Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19424–19429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Andersson K., Steiner H., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):571–576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery J., Cederlund E., Jörnvall H. Sorbitol dehydrogenase. The primary structure of the sheep-liver enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. Q., Merrifield R. B., Boman I. A., Boman H. G. Effects on electrophoretic mobility and antibacterial spectrum of removal of two residues from synthetic sarcotoxin IA and addition of the same residues to cecropin B. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80837-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto N., Okada M., Takahashi H., Ming Q. X., Nakajima Y., Nakanishi Y., Komano H., Natori S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA and assignment of the C-terminal of sarcotoxin IA, a potent antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):717–722. doi: 10.1042/bj2390717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17112–17116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutt V., Said S. I. Structure of the porcine vasoactive intestinal octacosapeptide. The amino-acid sequence. Use of kallikrein in its determination. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Primary structure of sarcotoxin I, an antibacterial protein induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7174–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Skerlavaj B., Bolognesi M., Gennaro R. Structure and bactericidal activity of an antibiotic dodecapeptide purified from bovine neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9573–9575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Brown D. M., DeLange R. J., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of six antimicrobial peptides of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4579–4584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Hultmark D., Engström A., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):246–248. doi: 10.1038/292246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Lee J. Y., Gan R., Kockum K., Faye I., Boman H. G. The structure of the gene for cecropin B, an antibacterial immune protein from Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):371–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hofsten P., Faye I., Kockum K., Lee J. Y., Xanthopoulos K. G., Boman I. A., Boman H. G., Engström A., Andreu D., Merrifield R. B. Molecular cloning, cDNA sequencing, and chemical synthesis of cecropin B from Hyalophora cecropia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2240–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]