Abstract
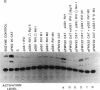
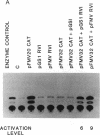
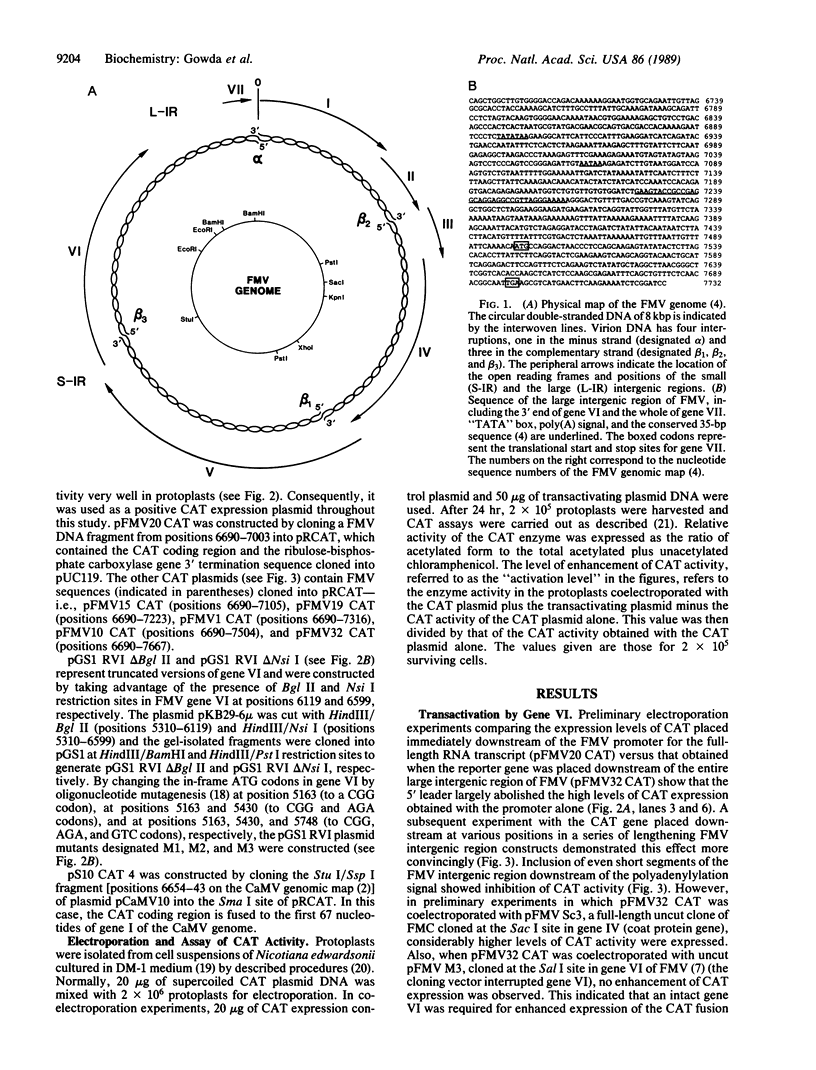
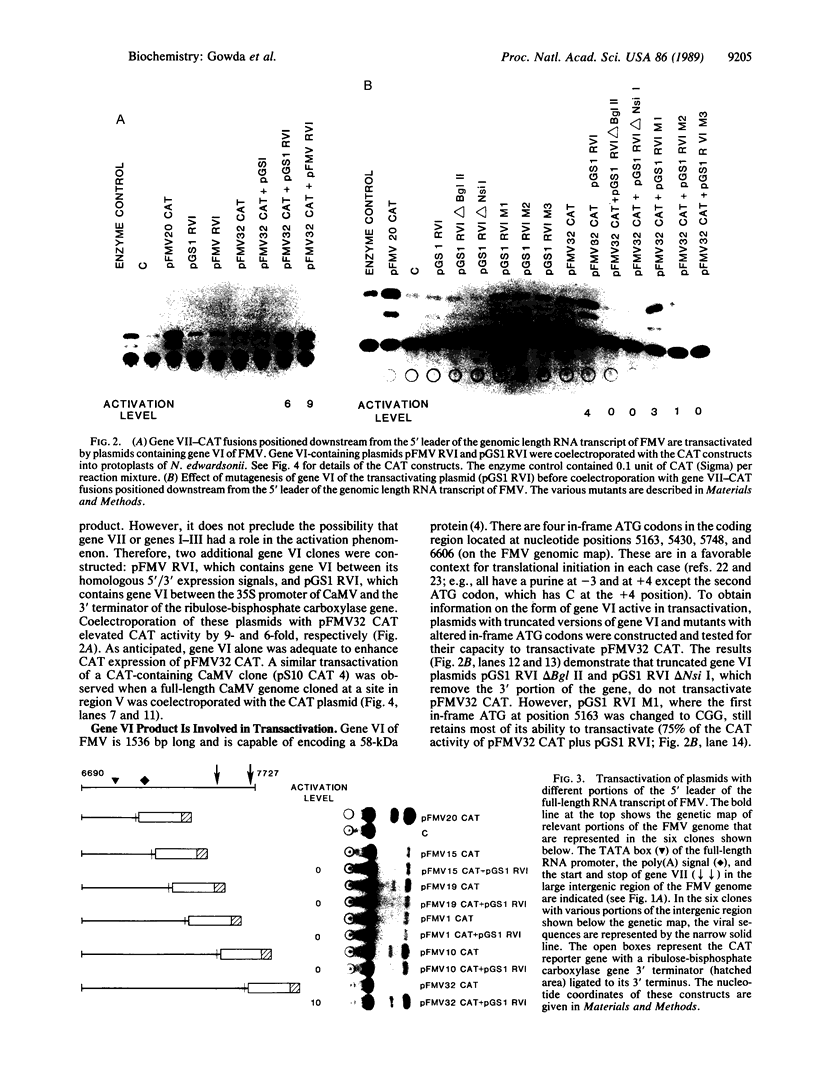
Experimental evidence for a molecular function for gene VI of the caulimoviruses is presented. Based on experiments with the figwort mosaic virus (FMV), it appears that gene VI has a role in the posttranscriptional expression of the closely packed genes (VII and I-V), which appear on the larger, full-length RNA transcript of this virus. Gene VI with its flanking 5'/3' expression signals included as a separate plasmid during electroporation of DNA into protoplasts of Nicotiana edwardsonii shows an unusual type of transactivation of a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene fused at its 5' end to a small open reading frame (gene VII) of the long 5' leader of the full-length RNA transcript of the FMV genome. The level of activity of the CAT gene is increased up to 20-fold over the activity of control plasmids when gene VI is included in the electroporation mixture. Mutagenesis of the coding portions of gene VI of pGS1 RVI, a transactivating plasmid used in the electroporation experiments, demonstrated that it was probably the polypeptide product of gene VI that was responsible for the transactivating effect. Experiments with various portions of the 5' leader of the large, full-length RNA of FMV showed that the coding region of gene VII is necessary for the transactivation event. Clones of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) or FMV with intact gene VI were found to reciprocally transactivate gene VII-CAT fusions (FMV) or gene I-CAT fusions (CaMV) located downstream of the 5' leader sequences of either viral genome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughman G. A., Jacobs J. D., Howell S. H. Cauliflower mosaic virus gene VI produces a symptomatic phenotype in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):733–737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughman G., Howell S. H. Cauliflower mosaic virus 35 S RNA leader region inhibits translation of downstream genes. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubert S. D., Schoelz J., Debao L., Shepherd R. J. Expression of disease symptoms in cauliflower mosaic virus genomic hybrids. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):537–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubert S., Shepherd R. J., Gardner R. C. Insertional mutagenesis of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Hohn T. Initiation of translation of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome from a polycistronic mRNA: evidence from deletion mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2731–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L., Jiricny J., Hohn T. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA using a repair-resistant nucleoside analogue: identification of an agnogene initiation codon. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck A., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Sadler J., Longstaff M. The sequence of carnation etched ring virus DNA: comparison with cauliflower mosaic virus and retroviruses. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3083–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richins R. D., Scholthof H. B., Shepherd R. J. Sequence of figwort mosaic virus DNA (caulimovirus group). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8451–8466. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardl C. L., Byrd A. D., Benzion G., Altschuler M. A., Hildebrand D. F., Hunt A. G. Design and construction of a versatile system for the expression of foreign genes in plants. Gene. 1987;61(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoelz J., Shepherd R. J., Daubert S. Region VI of cauliflower mosaic virus encodes a host range determinant. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2632–2637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd N. A., Jass J. R. Neuromuscular and vascular hamartoma of the small intestine: is it Crohn's disease? Gut. 1987 Dec;28(12):1663–1668. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.12.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]