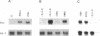Abstract
A cDNA clone for an auxin-regulated gene was isolated from a tobacco mesophyll protoplast cDNA library by differential screening. Nucleotide, sequence analysis showed that the deduced product of the gene, which we have designated par, is hydrophilic and is composed of 220 amino acids. No significant homology to other known proteins was detected. The mRNA of the par gene is approximately 900 bases long and its accumulation was detected in cultured mesophyll protoplasts as early as 30 min after the addition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid to the culture medium. The par mRNA was not detected in leaves or freshly prepared protoplasts or in protoplasts in the absence of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Expression of the par gene was detected at a low level in actively dividing BY-2 tobacco suspension culture cells. The conspicuous accumulation of par mRNA before the initiation of DNA synthesis in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts suggests that the par gene product could play a role in the initiation of meristematic activity in differentiated mesophyll cells.
Full text
PDF


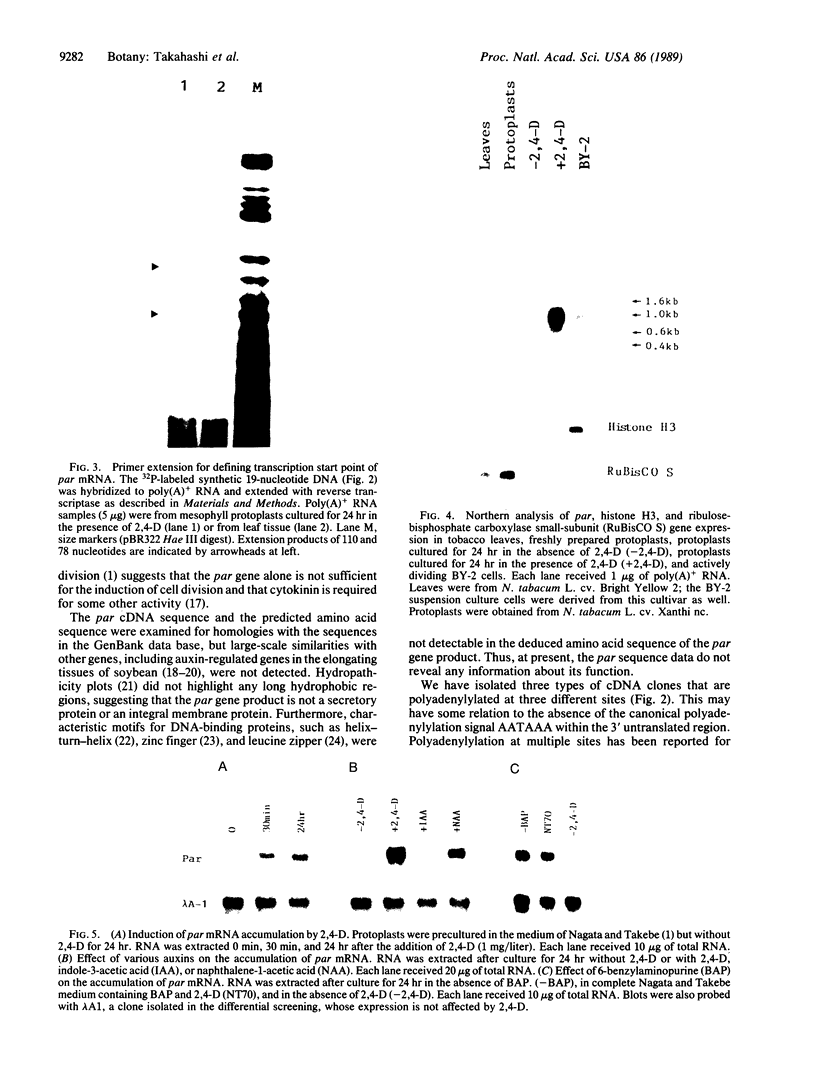

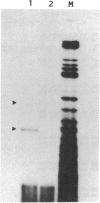
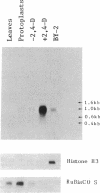
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainley W. M., Walker J. C., Nagao R. T., Key J. L. Sequence and characterization of two auxin-regulated genes from soybean. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10658–10666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauw G., De Loose M., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Alterations in the phenotype of plant cells studied by NH(2)-terminal amino acid-sequence analysis of proteins electroblotted from two-dimensional gel-separated total extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4806–4810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Cashmore A., Chua N. H. Nucleotide sequences of two pea cDNA clones encoding the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the major chlorophyll a/b-binding thylakoid polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1399–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecka E., Nagao R. T., Key J. L., Gurley W. B. Characterization of Gmhsp26-A, a stress gene encoding a divergent heat shock protein of soybean: heavy-metal-induced inhibition of intron processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1113–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Uhrhammer N., Guilfoyle T. J. Regulation of expression of an auxin-induced soybean sequence by cadmium. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6442–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure B. A., Hagen G., Brown C. S., Gee M. A., Guilfoyle T. J. Transcription, organization, and sequence of an auxin-regulated gene cluster in soybean. Plant Cell. 1989 Feb;1(2):229–239. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Y., Aspart L., Chartier Y. Auxin-induced regulation of protein synthesis in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts cultivated in vitro: I. Characteristics of auxin-sensitive proteins. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1027–1033. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Y., Chartier Y. Hormonal Control of Mitotic Development in Tobacco Protoplasts: TWO-DIMENSIONAL DISTRIBUTION OF NEWLY-SYNTHESIZED PROTEINS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1273–1278. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishide T., Emi M., Nakamura Y., Matsubara K. Corrected sequences of cDNAs for human salivary and pancreatic alpha-amylases [corrected]. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Fukuda R. Structure of the gene for the stringent starvation protein of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1153–1163. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernet T., Fleck J., Durr A., Fritsch C., Pinck M., Hirth L. Expression of the gene coding for the small subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during differentiation of tobacco plant protoplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;126(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]