Abstract
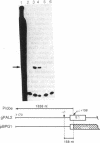
A 1.1-kilobase promoter fragment of the bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.5) gene PAL2 was translationally fused to the beta-glucuronidase reporter gene and transferred to tobacco by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated leaf disk transformation. The distribution of beta-glucuronidase activity in these transgenic plants is very similar to that of endogenous PAL2 transcripts in bean, with very high levels in petals; marked accumulation in anthers, stigmas, roots, and shoots; and low levels in sepals, ovaries, and leaves. Histochemical analysis of the spatial pattern of beta-glucuronidase activity showed that the PAL2 promoter is highly active in the shoot apical meristem, the zone of cell proliferation immediately adjacent to the root apical meristem, and in the early stages of vascular development at the inception of xylem differentiation. Wounding and light evoke specific changes in the spatial pattern of beta-glucuronidase activity in stems, including induction in the epidermis. These data indicate that the PAL2 promoter transduces a complex set of developmental and environmental cues into an integrated spatial and temporal program of gene expression to regulate the synthesis of a diverse array of phenylpropanoid natural products.
Full text
PDF

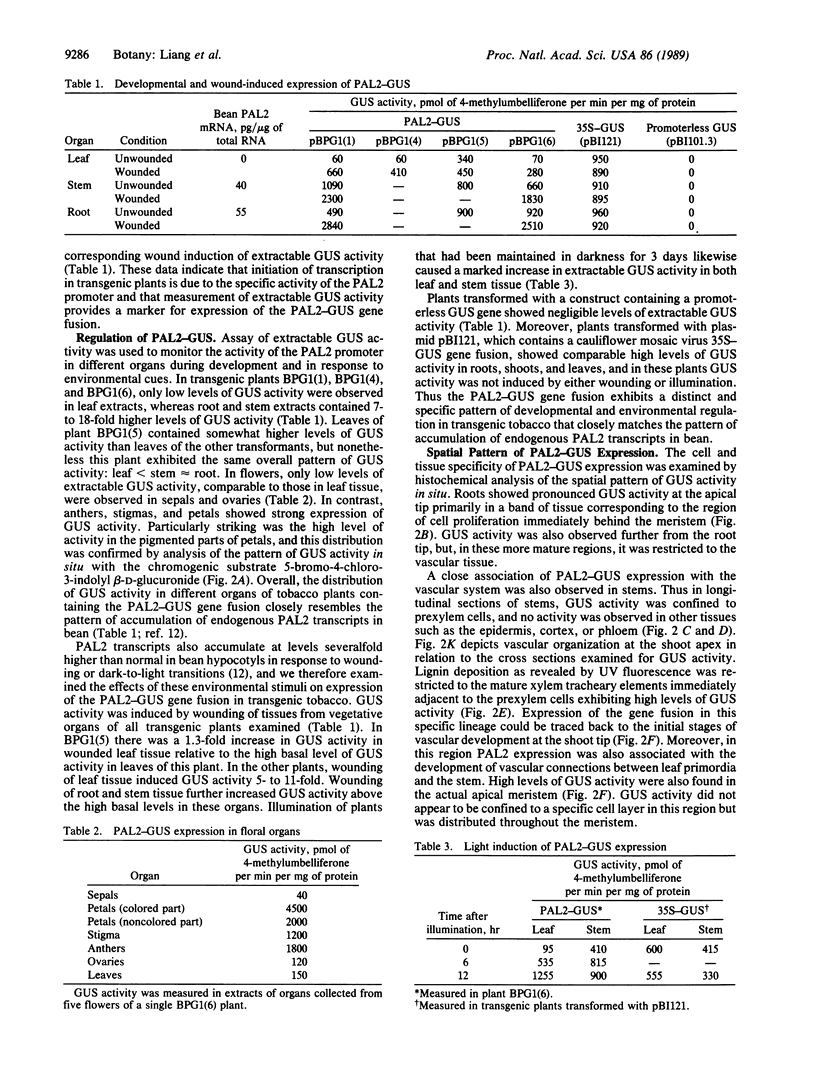


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. N., Dixon R. A., Bailey J. A., Rowell P. M., Lamb C. J. Differential induction of chalcone synthase mRNA activity at the onset of phytoalexin accumulation in compatible and incompatible plant-pathogen interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3384–3388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8711–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M., Shufflebottom D., Edwards K., Jefferson R., Schuch W. Tissue- and cell-specific activity of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase promoter in transgenic plants. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1899–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns A. N., Chen R. H., Wood H. N., Lynn D. G. Cell division promoting activity of naturally occurring dehydrodiconiferyl glucosides: do cell wall components control cell division? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolwell G. P., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Schuch W., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. L-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Phaseolus vulgaris. Characterisation and differential induction of multiple forms from elicitor-treated cell suspension cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Dey P. M., Lamb C. J. Phytoalexins: enzymology and molecular biology. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;55:1–136. doi: 10.1002/9780470123010.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Johnston A. W. Nodulation of legumes by Rhizobium: the recognized root? Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90436-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsch R. B., Fraley R. T., Rogers S. G., Sanders P. R., Lloyd A., Hoffmann N. Inheritance of functional foreign genes in plants. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):496–498. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4635.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Rubery P. H. Naturally occurring auxin transport regulators. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):346–349. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4863.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B., Schmid J., Lamb C. J. Vascular expression of a bean cell wall glycine-rich protein-beta-glucuronidase gene fusion in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1309–1314. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B., Templeton M. D., Lamb C. J. Specific localization of a plant cell wall glycine-rich protein in protoxylem cells of the vascular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton M. A., Lamb C. J. Transcriptional activation of plant defense genes by fungal elicitor, wounding, and infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):335–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. W., Dron M., Cramer C. L., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Differential regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase genes during plant development and by environmental cues. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14486–14492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn D. G., Chen R. H., Manning K. S., Wood H. N. The structural characterization of endogenous factors from Vinca rosea crown gall tumors that promote cell division of tobacco cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleman J., Boerjan W., Engler G., Seurinck J., Botterman J., Alliotte T., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Strong cellular preference in the expression of a housekeeping gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encoding S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):81–93. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubery P. H., Northcote D. H. Site of phenylalanine ammonia--lyase activity and synthesis of lignin during xylem differentiation. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1230–1234. doi: 10.1038/2191230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs T. Cellular interactions in tissue and organ development. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1986;40:181–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer E., Jahnen W., Hahlbrock K. In situ localization of light-induced chalcone synthase mRNA, chalcone synthase, and flavonoid end products in epidermal cells of parsley leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2989–2993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L. Alternative internal splicing in c-myb RNAs occurs commonly in normal and tumor cells. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4035–4039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02748.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields S. E., Wingate V. P., Lamb C. J. Dual control of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase production and removal by its product cinnamic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):389–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the susceptible plant cell: a novel adaptation of extracellular recognition and DNA conjugation. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]