Abstract
The nuclear envelope (NE) separates the two major compartments of eukaryotic cells, the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Recent studies suggest that the uptake of nuclear proteins into the nucleus is initiated by binding of nuclear location signals (NLSs) contained within these proteins to receptors in the NE, followed by translocation through the nuclear pore complex. To examine the binding step without interference from intranuclear events, we have used a system consisting of (i) purified rat liver NEs fixed onto glass slides and (ii) the prototype simian virus 40 large T antigen (SV40 T) NLS conjugated to nonnuclear carrier proteins, and we have visualized the receptor-ligand interaction by indirect immunofluorescence. In this system, incubation of isolated NEs with the wild-type SV40 T NLS conjugate with carrier proteins resulted in binding that was signal sequence-dependent, could be competitively blocked with excess conjugated and unconjugated wild-type peptide, did not require ATP, and was not affected by the transport-inhibiting lectin wheat germ agglutinin. In contrast, only minimal binding was observed with a mutant SV40 T NLS conjugate. These results are consistent with those obtained in other, more complex in vitro systems and suggest that binding of the SV40 T NLS is receptor-mediated. Binding is largely abolished by extraction of the NE with the nonionic detergent Triton X-100, suggesting that the receptor is soluble in detergent. We find in the Triton X-100 supernatant four major NLS-binding proteins with apparent molecular masses of 76, 67, 59, and 58 kDa by photoaffinity labeling with a highly specific crosslinker, azido-NLS. The reduced complexity of the system described here should be useful for the functional study of other potential NLSs for the identification and isolation of their binding sites and for the screening of antibodies raised against these binding sites.
Full text
PDF

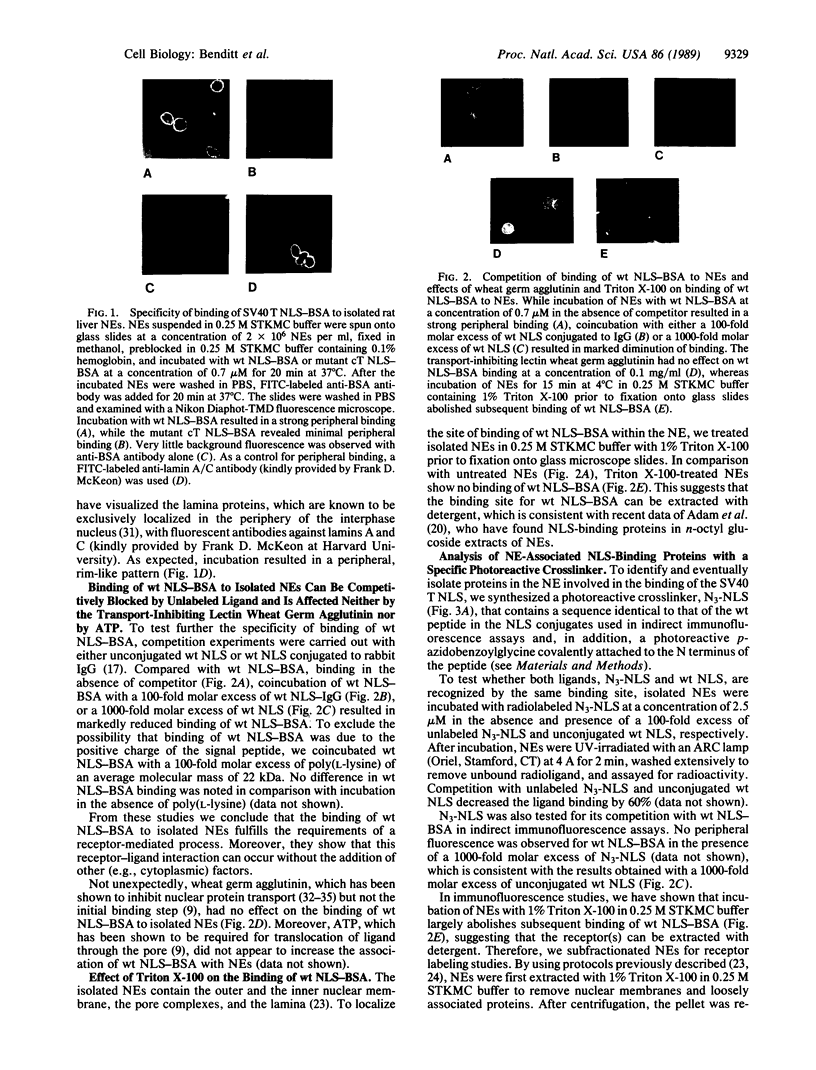


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Lobl T. J., Mitchell M. A., Gerace L. Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear location sequence. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):276–279. doi: 10.1038/337276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Schulz B., Scheer U., Peters R. Inhibition of nuclear accumulation of karyophilic proteins in living cells by microinjection of the lectin wheat germ agglutinin. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J., Dimmock N. J., Colman A. Identification of the sequence responsible for the nuclear accumulation of the influenza virus nucleoprotein in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Lanford R. E., Feldherr C. M. The effects of variations in the number and sequence of targeting signals on nuclear uptake. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1279–1287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer N., Blobel G. A modified procedure for the isolation of a pore complex-lamina fraction from rat liver nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):581–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDHERR C. M. THE EFFECT OF THE ELECTRON-OPAQUE PORE MATERIAL ON EXCHANGES THROUGH THE NUCLEAR ANNULI. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:43–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Kallenbach E., Schultz N. Movement of a karyophilic protein through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Newmeyer D. D., Price T. M., Forbes D. J. Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):189–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W. Nuclear lamins and cytoplasmic intermediate filament proteins: a growing multigene family. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Scheer U., Krohne G., Jarasch E. D. The nuclear envelope and the architecture of the nuclear periphery. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):39s–50s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.39s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blum A., Blobel G. Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):546–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G., Kornberg R. D. Synthetic peptides as nuclear localization signals. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):641–644. doi: 10.1038/322641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto-Sonobe N., Yoneda Y., Iwamoto R., Sugawa H., Uchida T. ATP-dependent association of nuclear proteins with isolated rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3426–3430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., White R. G., Dunham R. G., Kanda P. Effect of basic and nonbasic amino acid substitutions on transport induced by simian virus 40 T-antigen synthetic peptide nuclear transport signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2722–2729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G. The nuclear and the cytoplasmic pore complex: structure, dynamics, distribution, and evolution. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1977;(6):75–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Finlay D. R., Forbes D. J. In vitro transport of a fluorescent nuclear protein and exclusion of non-nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2091–2102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. Nuclear envelope permeability measured by fluorescence microphotolysis of single liver cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11427–11429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Bachmann M., Prochnow D., Richter H. P., Fasold H. Permeability measurements with closed vesicles from rat liver nuclear envelopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3540–3544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Fasold H. Preparation and characterization of nuclear-envelope vesicles from rat liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):203–212. doi: 10.1042/bj2410203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A., Gerace L. Integral membrane proteins specific to the inner nuclear membrane and associated with the nuclear lamina. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2029–2036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund U., Andersson K., Björkroth B., Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Visualization of the formation and transport of a specific hnRNP particle. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. J., Swift H. RNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm in Chironomus salivary glands. J Cell Biol. 1966 Oct;31(1):55–77. doi: 10.1083/jcb.31.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff B., Willingham M. C., Hanover J. A. Nuclear protein import: specificity for transport across the nuclear pore. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Oct;178(2):318–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki L., Kanda P., Lanford R. E. Identification of four nuclear transport signal-binding proteins that interact with diverse transport signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3028–3036. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Imamoto-Sonobe N., Matsuoka Y., Iwamoto R., Kiho Y., Uchida T. Antibodies to Asp-Asp-Glu-Asp can inhibit transport of nuclear proteins into the nucleus. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):275–278. doi: 10.1126/science.3051382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Imamoto-Sonobe N., Yamaizumi M., Uchida T. Reversible inhibition of protein import into the nucleus by wheat germ agglutinin injected into cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Dec;173(2):586–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]