Abstract
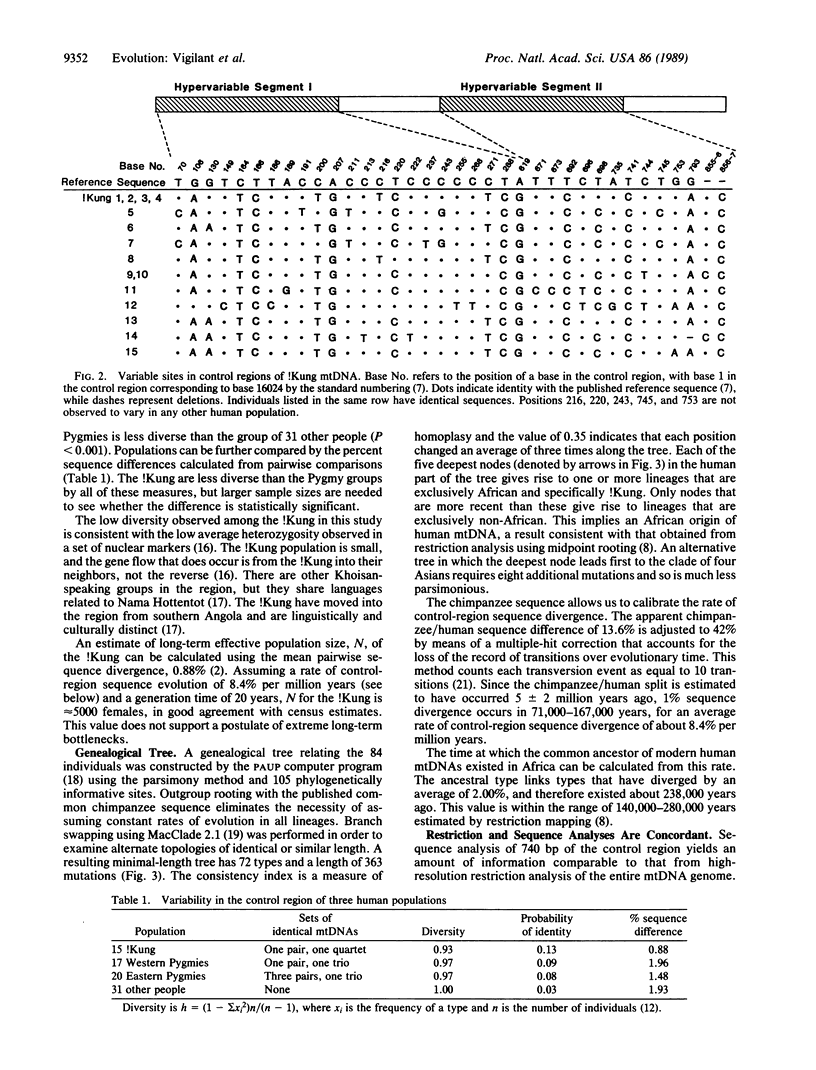
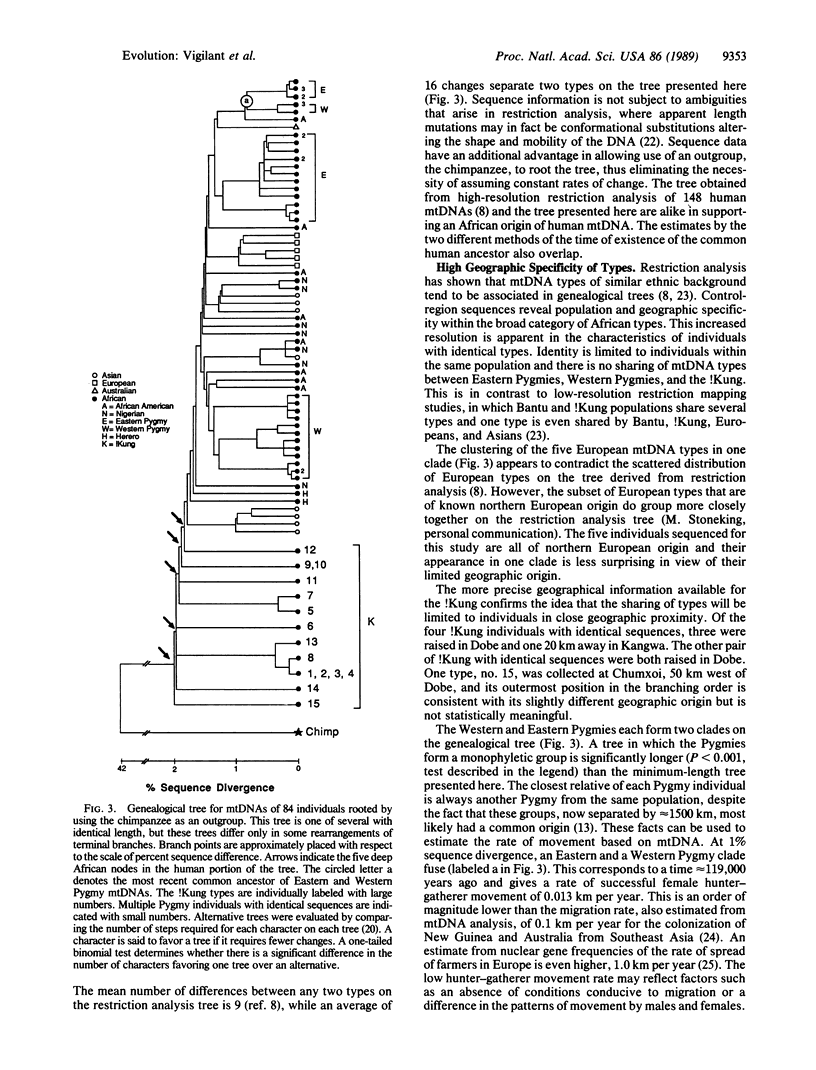
Hypervariable parts of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) were amplified enzymatically and sequenced directly by using genomic DNA from single plucked human hairs. This method has been applied to study mtDNA sequence variation among 15 members of the !Kung population. A genealogical tree relating these aboriginal, Khoisan-speaking southern Africans to 68 other humans and to one chimpanzee has the deepest branches occurring amongst the !Kung, a result consistent with an African origin of human mtDNA. Fifteen cases of unrelated individuals having identical sequences in the most variable parts of the mtDNA control region were found within populations of !Kung, Western Pygmies, and Eastern Pygmies, but no cases of identity were evident among these populations. This and other evidence of geographic structuring of the mitochondrial diversity in Africa, together with knowledge of the rate of accumulation of base changes in human mtDNA, implies that the average rate at which female lineages have moved their home bases during hunter-gatherer times could be as low as 13 meters per year. The technique of enzymatic amplification and direct sequencing applied to readily collected, highly stable biological materials such as hairs makes it possible to examine with high resolution many representatives of virtually any population.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquadro C. F., Greenberg B. D. Human mitochondrial DNA variation and evolution: analysis of nucleotide sequences from seven individuals. Genetics. 1983 Feb;103(2):287–312. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Bucci C., Hebert J. M., Kidd J. R., Kidd K. K., Friedlaender J. S., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Study of 47 DNA markers in five populations from four continents. Gene Geogr. 1987 Apr;1(1):47–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):31–36. doi: 10.1038/325031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics. 1983 Aug;104(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Piazza A., Menozzi P., Mountain J. Reconstruction of human evolution: bringing together genetic, archaeological, and linguistic data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6002–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foran D. R., Hixson J. E., Brown W. M. Comparisons of ape and human sequences that regulate mitochondrial DNA transcription and D-loop DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5841–5861. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Bowman B., Freiberger M., Ryder O. A., Wilson A. C. DNA sequences from the quagga, an extinct member of the horse family. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):282–284. doi: 10.1038/312282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Neumann R., Keyte J. Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10953–10971. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. J., Wallace D. C., Ferris S. D., Rattazzi M. C., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Radiation of human mitochondria DNA types analyzed by restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(3-4):255–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. Ancient origin of lactalbumin from lysozyme: analysis of DNA and amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):326–335. doi: 10.1007/BF02101195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay M., Jenkins T. Alpha-globin gene cluster haplotypes in the Kalahari San and southern African Bantu-speaking blacks. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):527–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santachiara-Benerecetti A. S., Beretta M., Negri M., Ranzani G., Antonini G., Barberio C., Modiano G., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Population genetics of red cell enzymes in Pygmies: a conclusive account. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Nov;32(6):934–954. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigilant L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Conformational mutation in human mtDNA detected by direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5945–5955. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. J., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. The polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]