Abstract
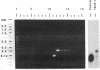
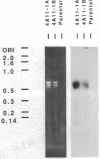
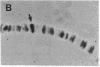
A cloned gene can be of interest because of its expression in a particular tissue or at a certain developmental stage, or because of homology to an interesting gene from another organism. In Drosophila its location in the genome is readily determined by in situ hybridization to the banded larval salivary gland polytene chromosomes, but it is more difficult to isolate mutations that may reveal its function. This paper describes a general method for detecting transposable element insertions into the gene in question. This "reverse genetics" then offers the possibility of observing a consequent mutant phenotype, providing a key to the normal function of the gene. The sensitivity of the polymerase chain reaction makes it possible to detect the occurrence of a single appropriate P-element transposon insertion among a population of mutagenized flies. This is accomplished by the use of oligonucleotide primers--one a sequence from within the cloned gene and the other homologous to the terminal sequence of the P-element DNA--to prime synthesis into the DNA flanking an insertion site. A segment of DNA, bounded by the two primers, will be a target for amplification only in a fly in which a P-element has inserted within about 2 kilobases of the gene primer. This technique has been used to detect P-element insertions near a gene expressed in the Drosophila compound eye. Potential problems with the technique and possible refinements in the screen are discussed. In principle, it could be utilized to detect insertion of a foreign element into any gene for which at least a partial sequence is known and could be extended to other organisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benzer S. BEHAVIORAL MUTANTS OF Drosophila ISOLATED BY COUNTERCURRENT DISTRIBUTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1112–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. A molecular gradient in early Drosophila embryos and its role in specifying the body pattern. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):537–545. doi: 10.1038/324537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Jones K., Hafen E., Rubin G. Rescue of the Drosophila phototransduction mutation trp by germline transformation. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1040–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.3933112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzolo M. J., Hyde D. R., VijayRaghavan K., Mecklenburg K., Benzer S., Meyerowitz E. Use of a new strategy to isolate and characterize 436 Drosophila cDNA clones corresponding to RNAs detected in adult heads but not in early embryos. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):527–539. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Voelker R. A. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila vermilion locus and its suppressible alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):404–408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vactor D., Jr, Krantz D. E., Reinke R., Zipursky S. L. Analysis of mutants in chaoptin, a photoreceptor cell-specific glycoprotein in Drosophila, reveals its role in cellular morphogenesis. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90517-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]