Abstract
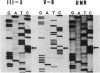
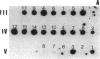
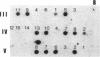
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) is a human X chromosome-linked dysmyelination disorder of the central nervous system for which the genetic defect has not yet been established. The jimpy mutation jp of the mouse is an X chromosome-linked disorder of myelin formation. The mutation is at an intron/exon splice site in the mouse gene for proteolipid protein (PLP). With the jimpy mouse mutation as a precedent, we focused our attention on the human PLP gene, which is found at Xq22. The polymerase chain reaction was used to amplify the exons of the PLP gene of an affected male from a large Indiana PMD kindred. DNA sequencing showed a C----T transition at nucleotide 40 of the second exon. An affected third cousin also showed this sequence variation, while two unaffected male relatives (sons of an obligate carrier female) had the normal cytidine nucleotide. Allele-specific oligonucleotides were used to generate data for linkage studies on the above mentioned PMD kindred. Our results show tight linkage (theta = 0) of PMD to PLP with a lod (logarithm of odds) score of 4.62. In six other unrelated PMD kindreds, only the normal-sequence oligonucleotide hybridized, which indicates genetic heterogeneity. The radical nature of the predicted amino acid change (proline to leucine), suggests that the PMD-causing defect may have been delineated in one kindred.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulloche J., Aicardi J. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: clinical and nosological study. J Child Neurol. 1986 Jul;1(3):233–239. doi: 10.1177/088307388600100310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl H. J., Schaich M., Budzinski R. M., Stoffel W. Individual exons encode the integral membrane domains of human myelin proteolipid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9807–9811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahim S., Riordan J. R. Lipophilin (PLP) gene in X-linked myelin disorders. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(1):303–310. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gencic S., Abuelo D., Ambler M., Hudson L. D. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: an X-linked neurologic disorder of myelin metabolism with a novel mutation in the gene encoding proteolipid protein. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):435–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin abnormalities in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. D., Puckett C., Berndt J., Chan J., Gencic S. Mutation of the proteolipid protein gene PLP in a human X chromosome-linked myelin disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8128–8131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen A. H., Ronca N. A., Greenfield E. A., Hans M. B. Defective biosynthesis of proteolipid protein in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Feb;21(2):159–170. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A., Samiullah M., Lees M. B. The structure of bovine brain myelin proteolipid and its organization in myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2912–2916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklin W. B., Campagnoni C. W., Deininger P. L., Gardinier M. V. Structure and expression of the mouse myelin proteolipid protein gene. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(3):383–394. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklin W. B., Gardinier M. V., King K. D., Kampf K. An AG----GG transition at a splice site in the myelin proteolipid protein gene in jimpy mice results in the removal of an exon. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madisen L., Hoar D. I., Holroyd C. D., Crisp M., Hodes M. E. DNA banking: the effects of storage of blood and isolated DNA on the integrity of DNA. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jun;27(2):379–390. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Alliel P. M., Dautigny A., Passage E., Pham-Dinh D., Mattei J. F., Jollès P. The gene encoding for the major brain proteolipid (PLP) maps on the q-22 band of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Apr;72(4):352–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00290964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. A single nucleotide difference in the gene for myelin proteolipid protein defines the jimpy mutation in mouse. J Neurochem. 1987 Dec;49(6):1873–1877. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Hillen H., Giersiefen H. Structure and molecular arrangement of proteolipid protein of central nervous system myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5012–5016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trofatter J. A., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M. LIPIN: an interactive data entry and management program for LIPED. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;39(1):147–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe I., Patel V., Goebel H. H., Siakotos A. N., Zeman W., DeMyer W., Dyer J. S. Early lesion of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: electron microscopic and biochemical study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Apr;32(2):313–333. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197304000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Riordan J. R. Assignment of the gene for myelin proteolipid protein to the X chromosome: implications for X-linked myelin disorders. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):940–942. doi: 10.1126/science.3840606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Riordan J. R., Willard H. F., Milner R., Kidd K. K. MSP RFLP for X-linked proteolipid protein gene (PLP) identified with either rat or human PLP cDNA clone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1882–1882. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEMAN W., DEMYER W., FALLS H. F. PELIZAEUS-MERZBACHER DISEASE. A STUDY IN NOSOLOGY. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1964 Apr;23:334–354. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196404000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]